- 1. What makes data loss prevention essential today?
- 2. How does data loss prevention actually work?
- 3. What types of data loss prevention solutions are available?
- 4. Where does DLP stop, and what do you need alongside it?
- 5. How does data loss prevention map to security standards?
- 6. Where is data loss prevention headed next?
- 7. Data loss prevention FAQs
- What makes data loss prevention essential today?
- How does data loss prevention actually work?
- What types of data loss prevention solutions are available?
- Where does DLP stop, and what do you need alongside it?
- How does data loss prevention map to security standards?
- Where is data loss prevention headed next?
- Data loss prevention FAQs
What Is DLP (Data Loss Prevention)? An Overview
- What makes data loss prevention essential today?
- How does data loss prevention actually work?
- What types of data loss prevention solutions are available?
- Where does DLP stop, and what do you need alongside it?
- How does data loss prevention map to security standards?
- Where is data loss prevention headed next?
- Data loss prevention FAQs
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a security practice that identifies sensitive data and enforces policies to stop it from being accessed, shared, or transferred without authorization.
It applies monitoring and control across data in use, in motion, and at rest. DLP is used to reduce data breaches, prevent accidental leaks, and meet regulatory requirements.
What makes data loss prevention essential today?
Data breaches are more common and more expensive than ever.
And those figures only represent direct costs. They don't capture long-term damage to customer trust or reputation.
Here's why that matters.
Some result from external attackers. Others stem from careless mistakes or misconfigured systems. But regardless of cause, organizations are legally and contractually required to keep this data secure. Yet, IBM's report indicates that a third of organizations have even faced regulatory fines because of breaches.
And the challenge is growing.
Cloud services and SaaS platforms already complicate data protection. But AI introduces an even bigger shift. Employees are feeding sensitive information into generative AI tools without oversight.
IBM found shadow AI incidents added $670,000 to breach costs. Which means AI has become a new—and fast-growing—channel for data exposure. And that's only one dimension of how it's reshaping data security.
Data loss prevention helps address these risks.
It gives organizations visibility into where sensitive data resides and how it moves. It applies policies that stop unauthorized access and prevent data from leaving approved environments.
Today, DLP is one of the few controls designed to deal directly with the problem that drives breach costs higher every year.
How does data loss prevention actually work?
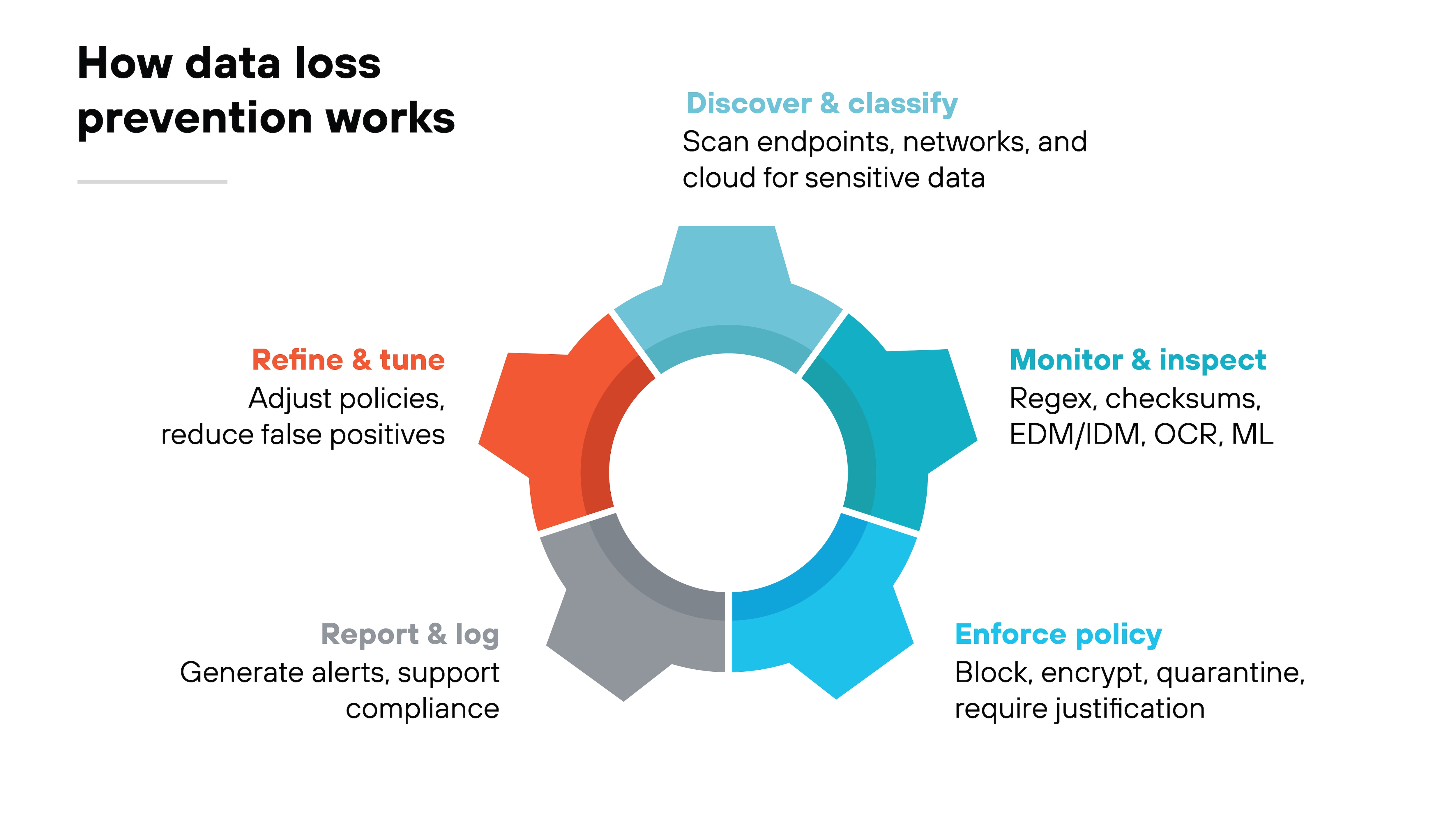
Data loss prevention works by applying controls at each stage of the data lifecycle.
-
The process starts with discovering and classifying information.
Tools scan endpoints, networks, and cloud systems to identify sensitive data such as financial records, intellectual property, or personal information. Classification ensures that policies can be applied according to data type and sensitivity.
-
Once data is identified, the system monitors how it's used and where it moves.
Inspection can be content-based, using techniques like regex or checksum validation. For higher accuracy, organizations use exact data match (EDM) or indexed document match (IDM) to fingerprint structured records or documents. Some tools add optical character recognition (OCR) an machine learning to detect sensitive content in images, PDFs, or unstructured files.
Why is that important?
Because raw content alone is rarely enough. Context—who is sending the data, from which device, and to where—helps determine whether an action violates policy.
Behavior patterns also matter. A single file transfer might be harmless. A surge of uploads to an unsanctioned service could signal risk.
-
When violations are detected, DLP enforces policy.
That might mean blocking a transfer, quarantining data, applying encryption, or requiring the user to justify the action. Every decision is logged, and incidents are reported to security teams.
Those reports are then used to refine policies and reduce false positives over time.
Essentially, DLP works by combining content, context, and behavior into a continuous cycle of discovery, monitoring, enforcement, and tuning.
What types of data loss prevention solutions are available?
Data loss prevention isn't a single tool. It's a set of controls applied at different points where data can leave organizational boundaries.
Each type focuses on a specific channel—devices, networks, email, or cloud platforms—but all use the same foundation: identifying sensitive data, monitoring how it moves, and enforcing policy when risks are detected.
Endpoint DLP
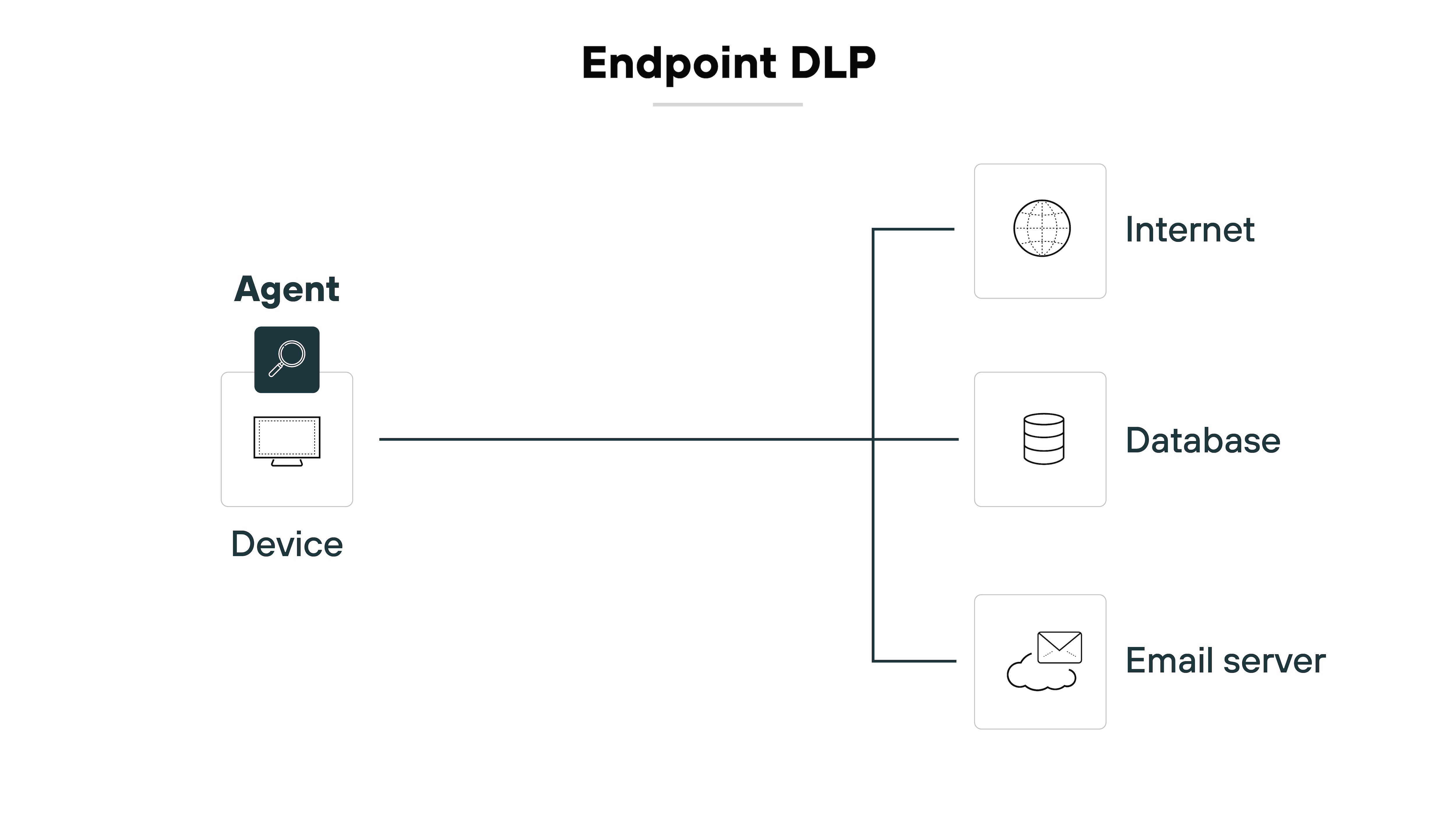
Endpoint DLP runs on user devices.
It monitors activity such as copying to USB drives, printing, screenshots, or use of the clipboard. It can also track uploads from local applications.
So organizations can stop sensitive data from leaving through unmanaged devices or offline methods.
Network DLP
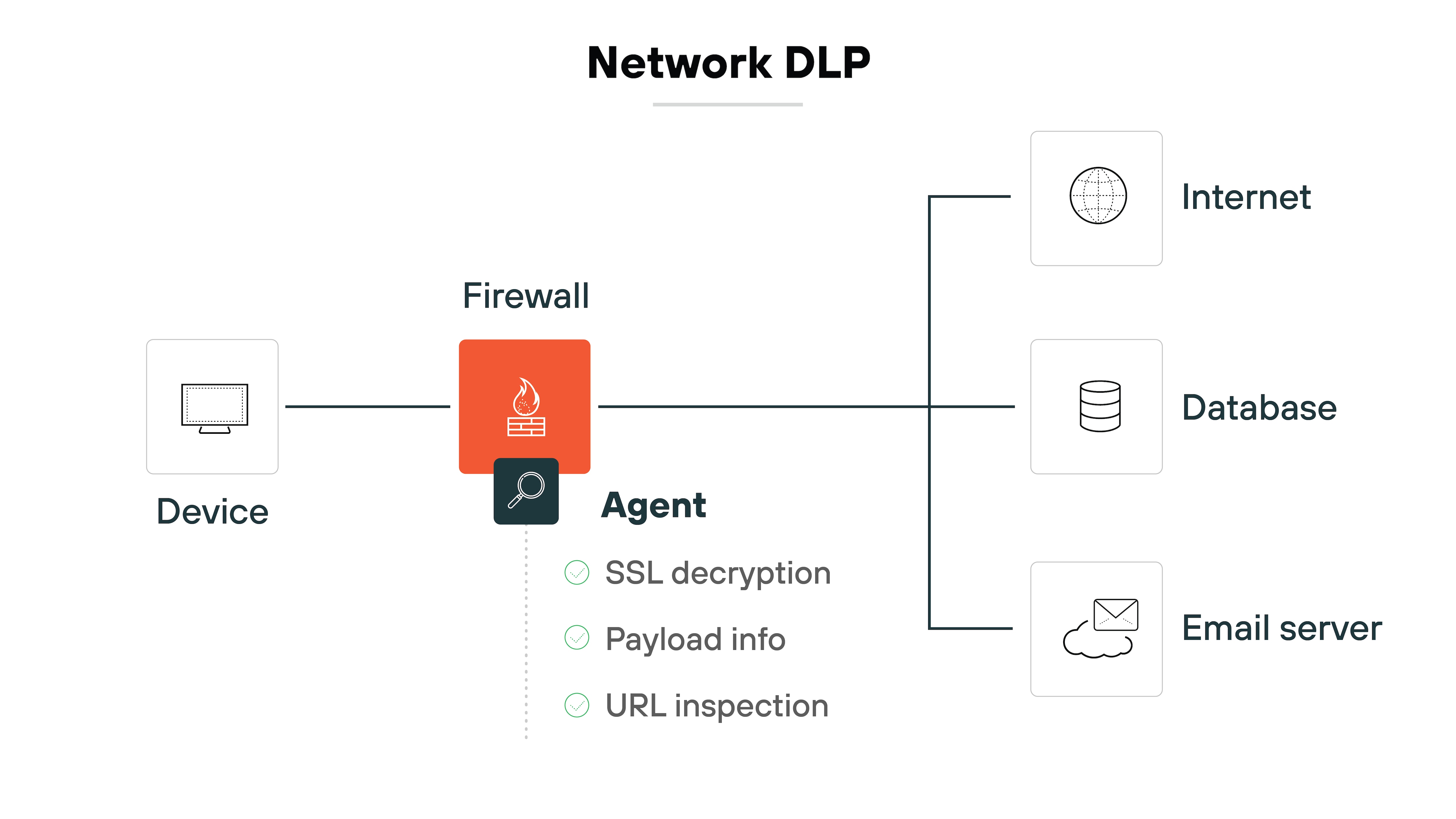
Network DLP inspects traffic moving across the corporate network. It looks at outbound channels like SMTP, HTTP(S), and FTP.
Some solutions work inline to block traffic in real time. Others use a span or tap to monitor without interfering. TLS decryption may be needed to analyze encrypted flows.
Email DLP

Email DLP enforces policy on outbound messages. It can detect sensitive content in subject lines, bodies, and attachments.
Common actions include blocking the message, encrypting it, or holding it for review. This reduces the chance of misdirected emails or intentional data leaks.
Cloud and SaaS DLP
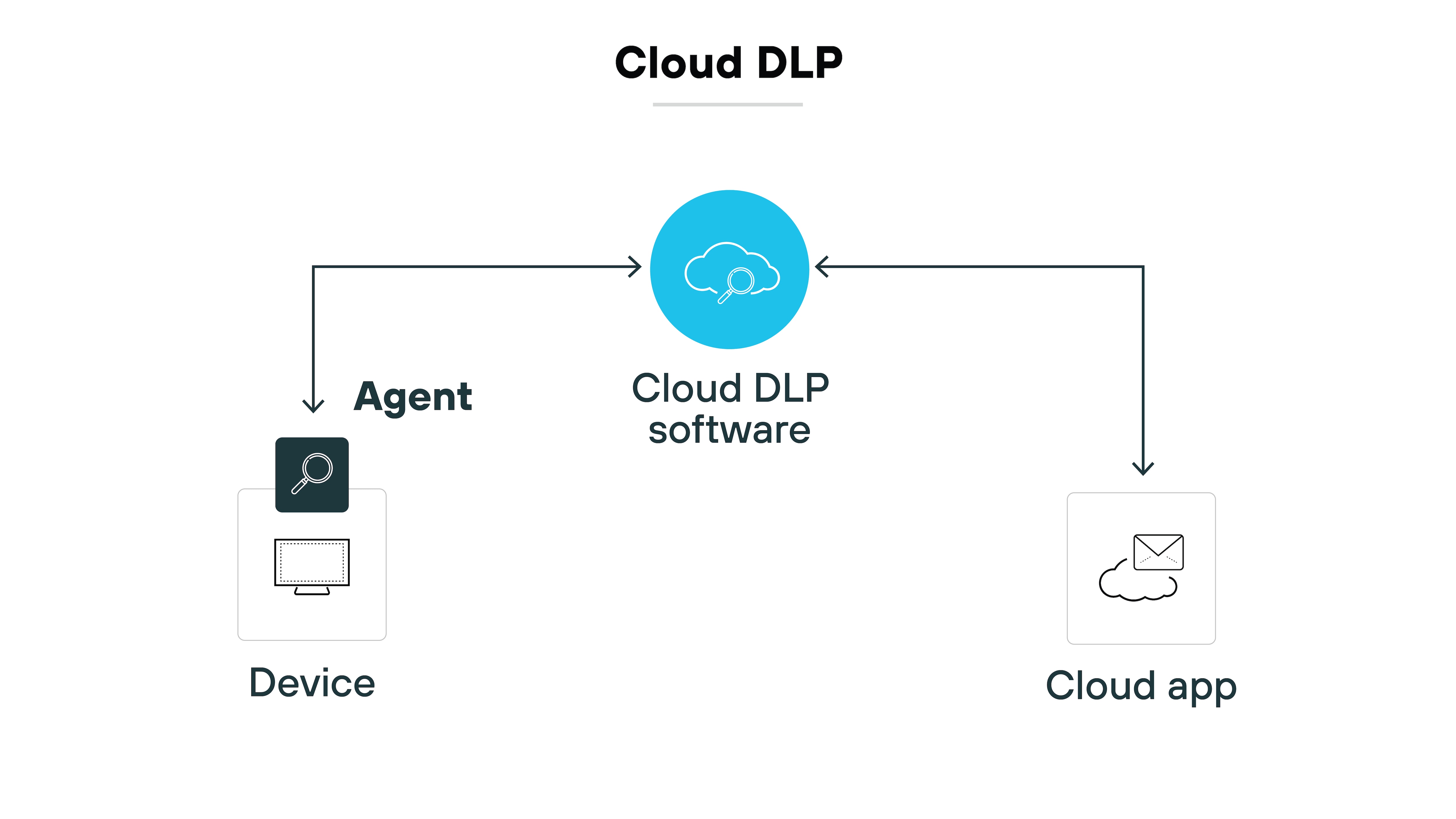
Cloud DLP protects data in software-as-a-service applications.
API-based approaches scan stored files and messages. Integration with CASB or SSE provides inline control for uploads and sharing. This is increasingly critical as more sensitive data moves to cloud platforms.
Where does DLP stop, and what do you need alongside it?
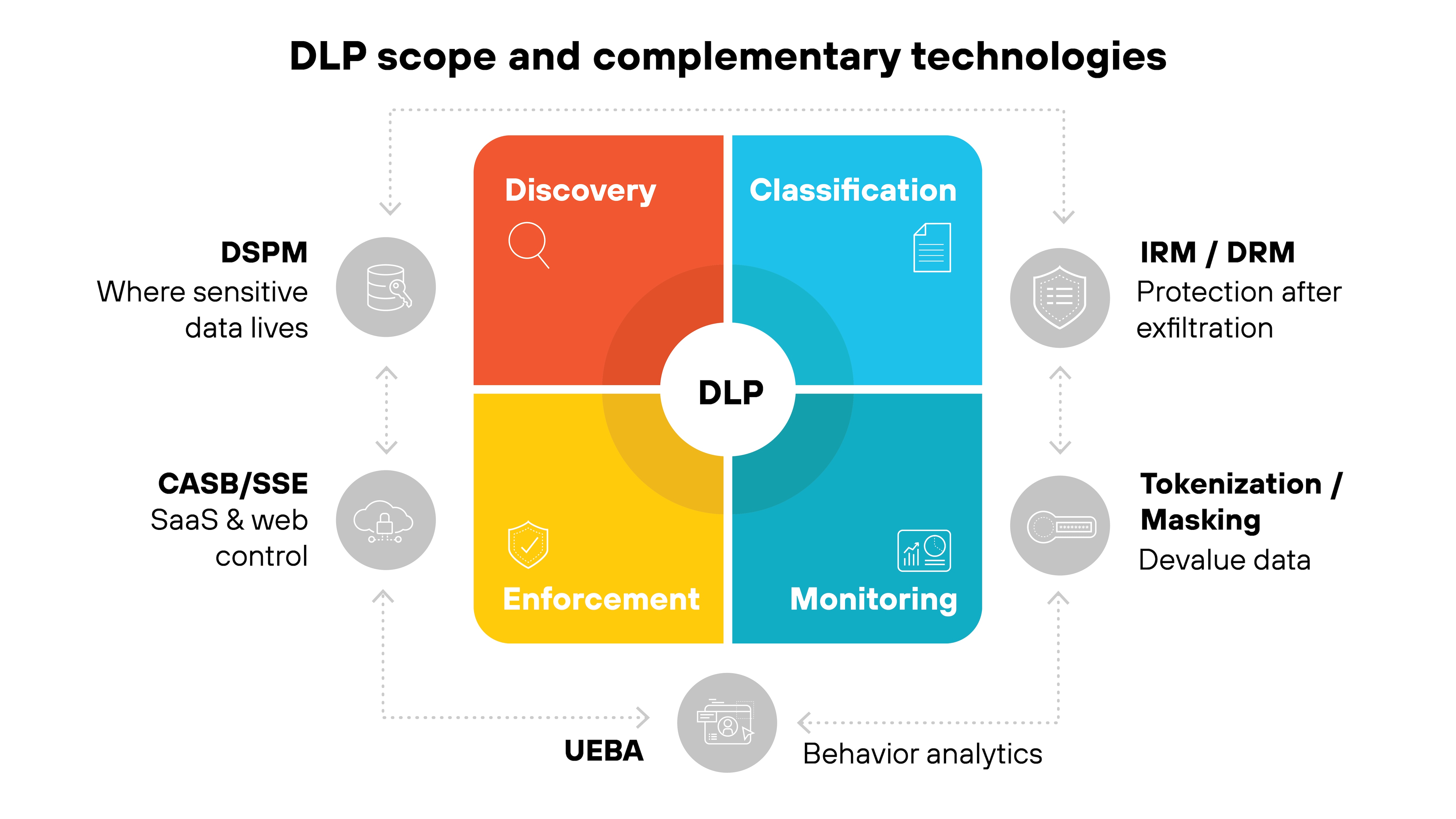
DLP plays a central role in monitoring and controlling sensitive data. But like any tool, it operates within a defined scope.
It can't always see inside encrypted or obfuscated traffic. And it's not designed to control what happens to information once it legitimately leaves managed environments.
That's why organizations pair DLP with complementary technologies.
- DSPM shows where sensitive data lives across cloud and hybrid environments.
- CASB or SSE extend control to SaaS and web applications.
- IRM and DRM apply protections that stay with the file after it moves.
Other tools address different dimensions.
- Tokenization and masking reduce the value of data if it's exposed.
- UEBA adds behavior analytics to flag unusual activity that may not be visible through content inspection alone.
DLP enforces policies where data is discovered, classified, and monitored. But it needs other technologies to expand that protection by covering blind spots, extending control into new environments, and continuing safeguards beyond the network edge.
How does data loss prevention map to security standards?
DLP isn't defined by any one standard. Instead, it maps across multiple frameworks and regulations that govern how organizations must control, monitor, and protect data.
The goal is the same: prevent unauthorized disclosure while keeping data available for business use.
What follows is a starter set of the most widely recognized frameworks and regulations where DLP capabilities align directly with published requirements.
| Frameworks, regulations, and DLP tie-ins |
|---|
| Framework / Regulation | Type | Relevant requirement and DLP tie-in |
|---|---|---|
| NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 | Framework / standard | Controls such as AC-4 (information flow enforcement) and SC-7(10) map directly to DLP policies that monitor, restrict, and log data transfers. |
| NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF 2.0) | Framework | Protect > Data Security and Detect > Anomalies & Events align with DLP's role in identifying and controlling sensitive data movement. |
| ISO/IEC 27001 | International standard | Annex A.8 and A.13 call for protecting data in storage and transit. DLP supports compliance by enforcing access and information-flow controls. |
| ISO/IEC 27040 | International standard | Specifies storage security measures, including confidentiality and information-flow restrictions, which DLP helps implement. |
| PCI DSS | Regulation / industry standard | Requirement 3 (protect stored cardholder data) and Requirement 4 (encrypt transmission) align with DLP monitoring and blocking unauthorized handling of PCI data. |
| HIPAA Security Rule | Regulation (US healthcare) | Requires safeguards for PHI, including access control and transmission security, which DLP enforces across endpoints, email, and networks. |
| GDPR | Regulation | Article 32 requires security of processing. DLP maps to this by monitoring personal data flows and preventing unauthorized disclosures. |
This list isn't exhaustive. Other frameworks, sector-specific rules, and national privacy laws also tie back to DLP. But these are the anchors most organizations look to when building or auditing a data protection program.
Where is data loss prevention headed next?
- By 2027, 70% of CISOs in larger enterprises will adopt a consolidated approach to address both insider risk and data exfiltration use cases.
- By 2027, organizations incorporating intent detection and real-time remediation capabilities into DLP programs will realize a one-third reduction in insider risks.
Data loss prevention is evolving. It's no longer just about scanning files and blocking transfers. The focus is shifting toward context, behavior, and integration with broader data security platforms.
Traditional content-based DLP creates noise and requires heavy tuning. But modern approaches add user and activity context, intent detection, and behavior analytics to make policies more precise.
Also, most organizations today want DLP capabilities delivered inside larger platforms such as secure service edge (SSE), insider risk, and DSPM. The consolidation reduces overhead and keeps policies consistent across environments.
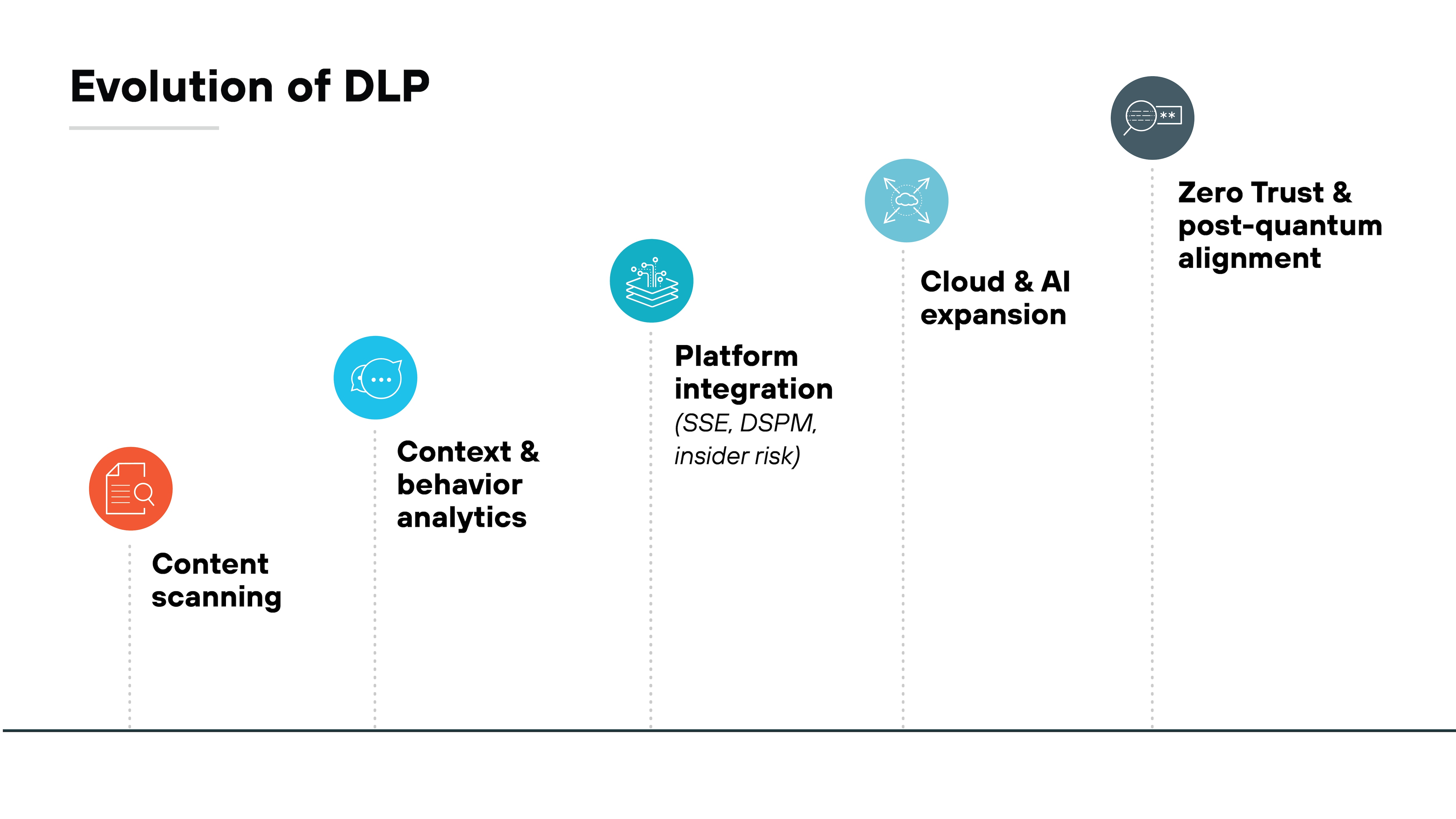
Cloud and AI are reshaping expectations too.
Sensitive data now flows through SaaS apps, multicloud services, and generative AI tools. Which means DLP has to expand into API-based cloud scanning, inline SaaS enforcement, and monitoring of AI prompts and outputs.
Vendors are also embedding AI into DLP itself to improve classification accuracy, triage, and investigations.
Looking further ahead, DLP is expected to align with Zero Trust architectures and support cryptoagility as post-quantum encryption becomes mainstream. The result is less about standalone enforcement and more about adaptive controls that protect data wherever it lives or moves.
DLP is becoming smarter, more integrated, and better aligned with the way organizations actually use and secure data today.