Aviation’s increasing reliance on operational technology (OT) has made cybersecurity a critical pillar of safety and continuity. Cyberthreats targeting airports and aircraft operations are growing more sophisticated, underscoring the need for proactive defense strategies. The 2023 TSA Cybersecurity Directive provides a structured framework to safeguard essential aviation operations, emphasizing that OT security is no longer just a compliance requirement but a strategic imperative for operational resilience.
The directive calls for regulated operators to implement a comprehensive set of security measures that ensure safety even when one part of the network is compromised. These measures include:
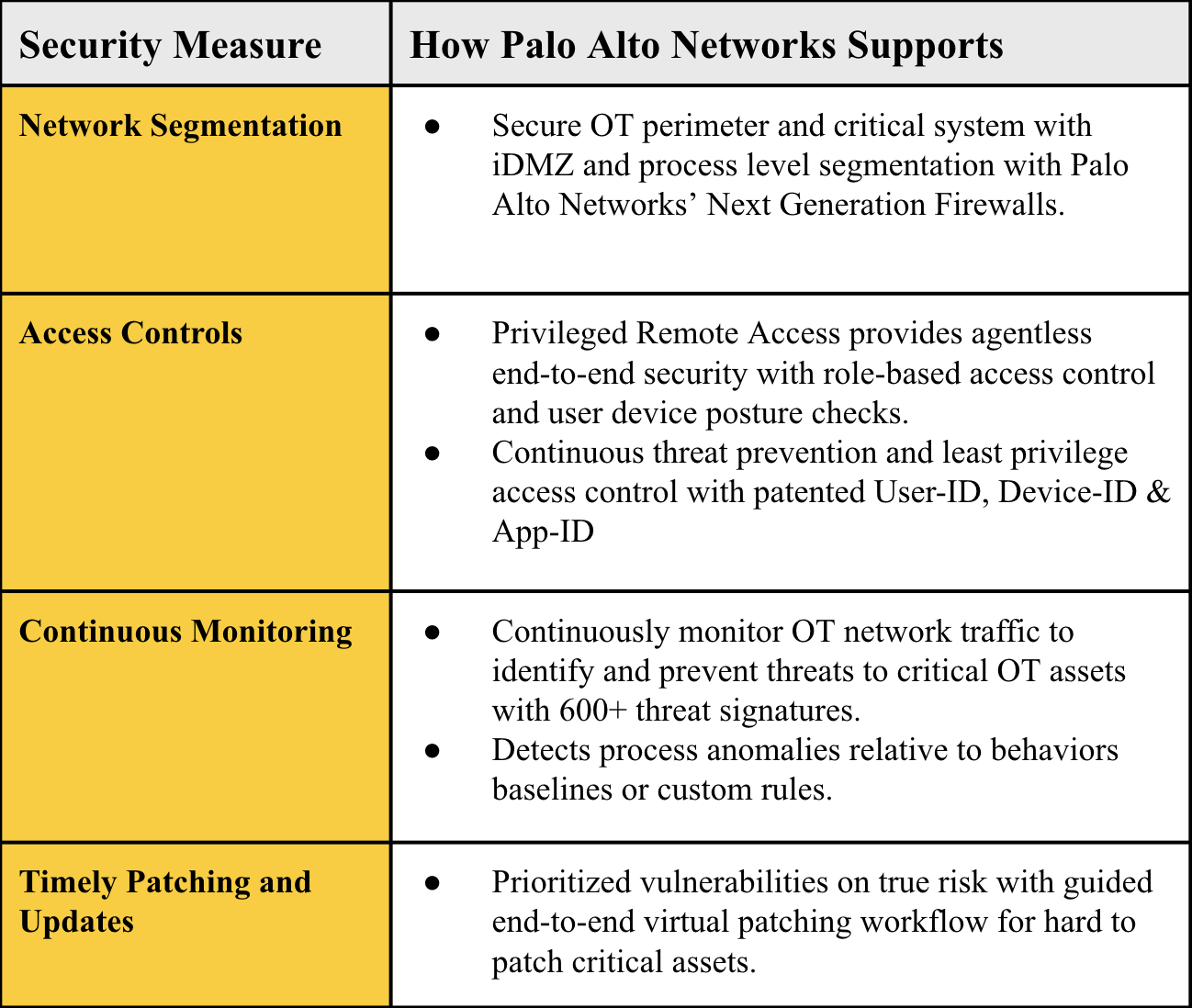
- Network Segmentation: Develop policies and controls that ensure operational technology (OT) systems continue to function even if an IT system is compromised.
- Access Controls: Implement measures to prevent unauthorized access to critical cyber systems.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use detection policies and real-time analytics to identify and respond to cybersecurity threats.
- Timely Patching and Updates: Reduce exploitation risks by applying security patches and updates in a risk-based, timely manner.
Network Segmentation for Isolation and Operational Continuity
Effective network segmentation is a cornerstone of OT security. It begins with real-time asset discovery that maps devices, their network behaviors, firmware versions, vulnerabilities and risk factors. This intelligence drives segmentation policies that isolate critical OT assets from IT breaches while ensuring continuous operations.
As digital transformation expands the OT attack surface through IT-OT convergence, SCADA modernization and remote operations, traditional segmentation methods are becoming inadequate. The 2018 Bristol Airport ransomware incident illustrates this risk. A more strategic segmentation approach could have contained the threat and protected essential systems. Executive leaders increasingly recognize zero-trust architectures and network segmentation as a core cybersecurity control that reduces exposure while maintaining operational integrity.
Robust Access Controls for Least-Privilege Enforcement
Access control must go beyond simply restricting unauthorized entry. A risk-based policy framework should govern every aspect of an organization’s security, from user credentials to device and application permissions.
A cybersecurity assessment of airport building automation systems in 2018 revealed vulnerabilities in HVAC and lighting controls. With stronger access controls, only authorized personnel and devices would have been able to interact with these systems, significantly reducing exploitation risks. In aviation, where operational uptime is non-negotiable, enforcing least-privileged access is both a security necessity and a strategic business decision.
Continuous Monitoring for Real-Time Threat Detection
Traditional monitoring methods often fail to keep up with rapidly evolving OT environments. Advanced monitoring solutions that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning can establish behavioral baselines, enabling real-time anomaly detection and faster incident response.
Modern OT security integrates threat prevention, URL filtering, DNS security and signature-based detections, providing unified visibility across both legacy and emerging IoT/ OT devices. This approach helps bridge gaps between fragmented asset inventories and disparate security tools. During the 2017 Triton malware attack, AI-driven monitoring could have potentially detected unauthorized modifications before they escalated into a full-scale crisis. As threats become more sophisticated, continuous monitoring is now a top priority for aviation executives seeking to safeguard mission-critical assets.
Timely Patching and Updates for Proactive Vulnerability Management
Traditional patching cycles often do not align with the needs of critical OT environments. Virtual patching serves as an essential safeguard, reducing the attack surface while permanent updates are scheduled.
A risk-based patching strategy prioritizes remediation efforts based on business criticality, exploitability, internet exposure and active threat patterns. The global impact of the WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 demonstrated the danger of delayed patching. Although fixes were available, slow deployment led to widespread disruption. Aviation operators can enhance security while maintaining operational continuity by integrating continuous threat intelligence with automated workflows such as Guided Virtual Patching.
A Blueprint for Resilient Aviation OT Security
The TSA Cybersecurity Directive offers more than a path to compliance—it provides a framework for operational resilience. Aviation organizations can transform regulatory challenges into strategic advantages by embracing robust network segmentation, comprehensive access controls, continuous monitoring and timely patching. In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, where cyberthreats are increasingly sophisticated, leaders must prioritize proactive defense strategies that keep pace with emerging risks.
Strengthen Your Aviation OT Security Today
Take the first step toward comprehensive OT security tailored to your operational needs. Experience a free trial of Industrial OT Security today and equip your organization with the tools to safeguard critical aviation operations.