Welcome back to our Best Practices for Managing Vulnerabilities in the Cloud series. In part one, we discussed how important it's to have complete visibility into vulnerabilities across your cloud estate, as well as the ability to effectively prioritize risk. But that’s only half the battle. The threat of cloud vulnerabilities is evolving and the stakes couldn't be higher.
In its annual release, the Verizon 2024 DBIR reported "substantial growth of attacks involving the exploitation of vulnerabilities as the critical path to initiate a breach. It almost tripled (180% increase) from last year."
But did you realize how much time passes from when a patch becomes available and a vulnerability is resolved? DBIR survival analysis of CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) showed that 85% weren't remediated at 30 days. The percentage drops to a no less impressive 50% at 55 days and 47% at 60 days. As startling as this is, 20% of KEVs remain at 120 days, according to the 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report.
Vulnerability management is a critical aspect of any cloud security strategy. You’re well aware of this if you’ve read part one of this vulnerability management series, which discusses gaining visibility across the application lifecycle and identifying the most impactful vulnerabilities. Before we dive into strategies to mitigate risk and enhance your vulnerability management program, let's quickly recap the best practices:
- Gain visibility across the application lifecycle
- Identify the most impactful vulnerabilities
- Take action and remediate vulnerabilities
- Monitor and report risk burndown
Part Two of this series will arm you with actionable insights and guidance to stay ahead of the curve when it comes to managing vulnerabilities. We’ll ensure your organization has the right tools to fix vulnerabilities, monitor progress and report on the success of your vulnerability management program.
Let’s get started…
Best Practice #3: Taking Action and Remediating Vulnerabilities
Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities are key steps to ensure that teams can focus on the risk that matters most. True security lies in actively addressing and remedying these vulnerabilities before they’re exploited by malicious actors. Effective remediation requires a systematic and proactive approach, encompassing the following key elements:
- Establish Clear Remediation Procedures: Develop precise and actionable protocols for addressing vulnerabilities, including delineating roles, responsibilities, escalation paths and timelines. A well-defined process ensures coordinated and consistent remediation efforts throughout the organization.
- Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management strategy to apply security patches and updates to vulnerable systems, applications and software. Automated patch management tools can streamline this process for workloads, such as virtual machines, ensuring that critical patches are applied quickly to mitigate known vulnerabilities. For other assets, such as container images and serverless functions, having a system in place that can detect the vulnerability in runtime and find the exact code that introduced it in your code repositories will enable the team to move at a much faster pace. This can improve service level agreements (SLA) and reduce mean time to remediation (MTTR) for business critical applications.
- Vulnerability Mitigation Techniques: In cases where immediate patching is not feasible, employ alternative mitigation techniques such as network segmentation, configuration hardening or the implementation of compensating controls to reduce the risk posed by vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Monitoring and Verification: Implement continuous monitoring mechanisms to detect new vulnerabilities and verify the effectiveness of remediation efforts. Regularly scan and assess systems for new vulnerabilities and conduct periodic penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to validate the security posture of your environment.
- Cross Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between security teams, IT operations and development teams to ensure that remediation efforts align with business priorities and objectives. Encourage open communication and knowledge sharing to facilitate the timely resolution of vulnerabilities.
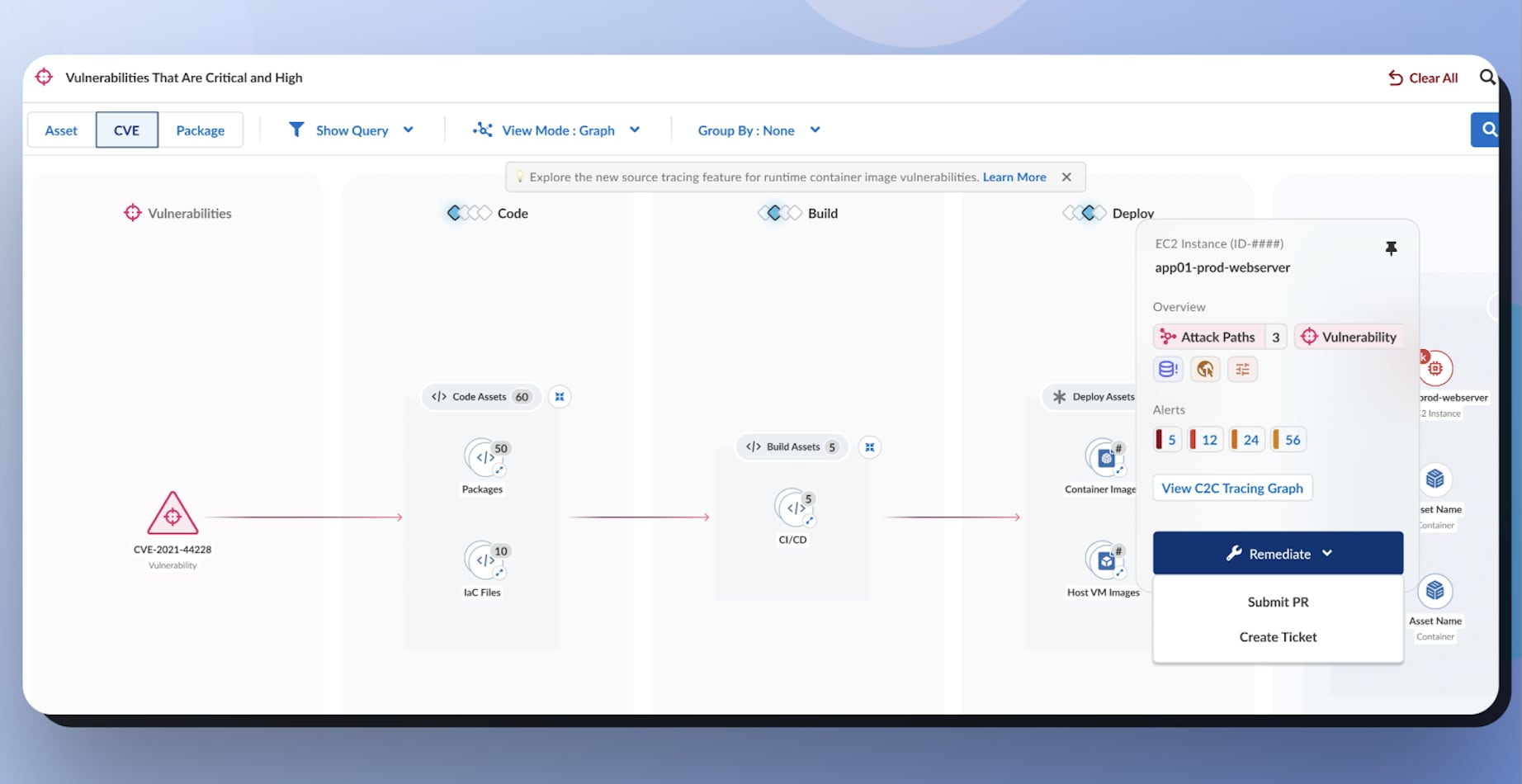
Prisma Cloud’s Approach to Remediating Vulnerabilities
Prisma Cloud assists users in remediating vulnerabilities by tracing them from runtime back to the code that initially introduced the vulnerability, streamlining developers' work and reducing MTTR. Additionally, Prisma Cloud enables users to create tickets, submit pull requests, and export vulnerability information, fulfilling other critical requirements that must be supported.
By taking decisive action to remediate vulnerabilities, organizations can boost their security posture and reduce the risk of cyber incidents.
This proactive approach, combined with comprehensive visibility and prioritization efforts, lays the foundation for an effective vulnerability management program. However, be aware—you aren’t quite finished yet. There’s still the matter of staying on top of it all. That brings us to best practice number four…
Best Practice #4: Monitor and Report Risk Burndown
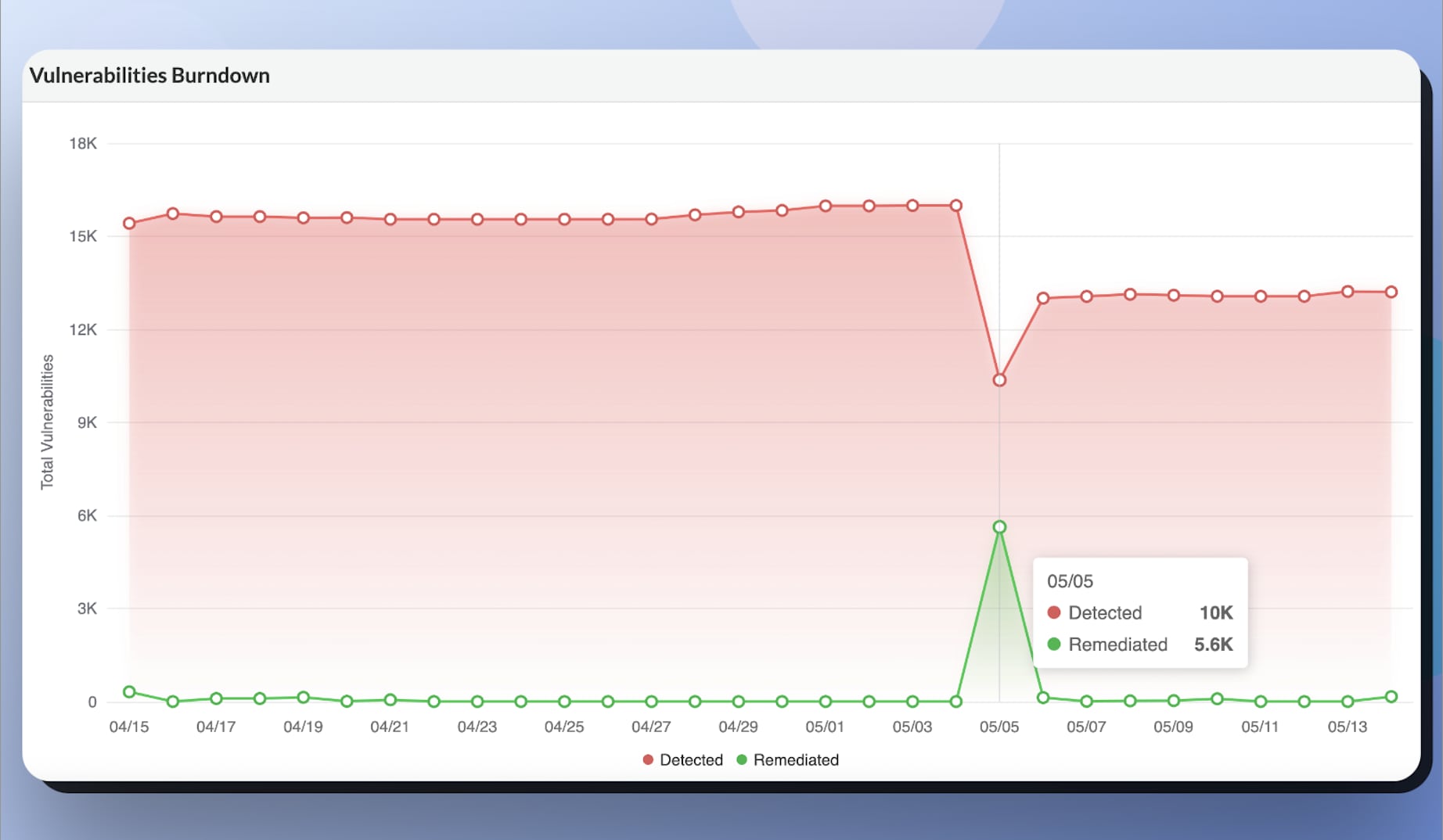
Monitoring and reporting on vulnerability metrics are vital components of any organization's cybersecurity strategy. By regularly tracking these metrics, organizations can effectively assess their risk exposure by identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their severity, potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. With this understanding, it’s possible to allocate resources strategically to address the most critical risks first, reducing the overall risk to the organization. The ability to report on progress addressing vulnerabilities is also critical in fulfilling compliance requirements from regulatory bodies. These often mandate the monitoring and reporting of vulnerability metrics to ensure that organizations meet regulatory standards and avoid potential penalties.
Tracking vulnerability metrics over time enables organizations to identify trends and patterns in their security posture so they can continuously improve their security policies and procedures. By allocating resources efficiently and demonstrating transparency through regular reporting, teams are able to effectively communicate their security efforts to stakeholders and maintain trust in their security practices.
Prisma Cloud’s Approach to Monitoring and Reporting on Risk Burndown
Prisma Cloud makes it easy for users to monitor and report vulnerability metrics with the vulnerability management dashboards. Teams can also generate reports based on the information in the dashboards to track their risk at a high level.
Learn More
While achieving comprehensive visibility and prioritization are the first steps in building an effective foundation for vulnerability management, remediating vulnerabilities, monitoring and reporting risk burndown are the final pieces in reducing the risk caused by vulnerabilities.
For more specific insights into how Prisma Cloud can help your organization manage vulnerabilities from code to cloud, see how we can help you find and fix the XZ Utils vulnerability.