SASE vs. ZTNA: What Is the Difference?
The difference between SASE and ZTNA is that SASE is a comprehensive cloud-native architecture that combines network and security services, while ZTNA is a specific component of SASE that provides secure access to applications based on identity verification.
SASE offers a broader scope, applying a consistent security policy across the entire network. ZTNA provides fine-grained access control, enforcing policies that limit user access to the necessary role-specific resources. Together, SASE and ZTNA represent a shift toward a more secure, flexible, and efficient network infrastructure.
What Is SASE?
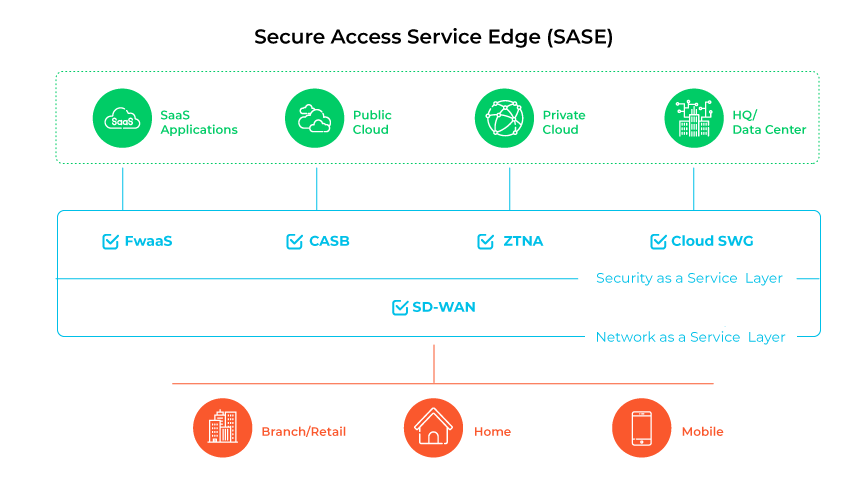
The secure access service edge (SASE) model is a unified cloud-native security approach that combines software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) with a range of security functionalities, including secure web gateway (SWG), cloud access security broker (CASB), firewall as a service (FWaaS), and Zero Trust network access (ZTNA) into a single integrated platform. SASE orchestrates various components to secure network connections, manage a comprehensive set of security features, enhance management workflows, and offer a flexible network structure that can adjust to evolving business needs.
SASE architecture addresses the shifting requirements for secure connectivity in modern enterprise settings. It expands the traditional network boundary to encompass all access points, aiming to enable secure and efficient cloud interactions for remote users, regardless of location.
SASE functions by directing network traffic through a cloud-native service platform that integrates multiple security and network functionalities. By placing these services at the network edge, closer to the points of user and device connectivity, it reduces latency, enhances network performance, and elevates the user experience. This strategy ensures uniform enforcement of security policies across the enterprise and centralizes control.
What Is ZTNA?
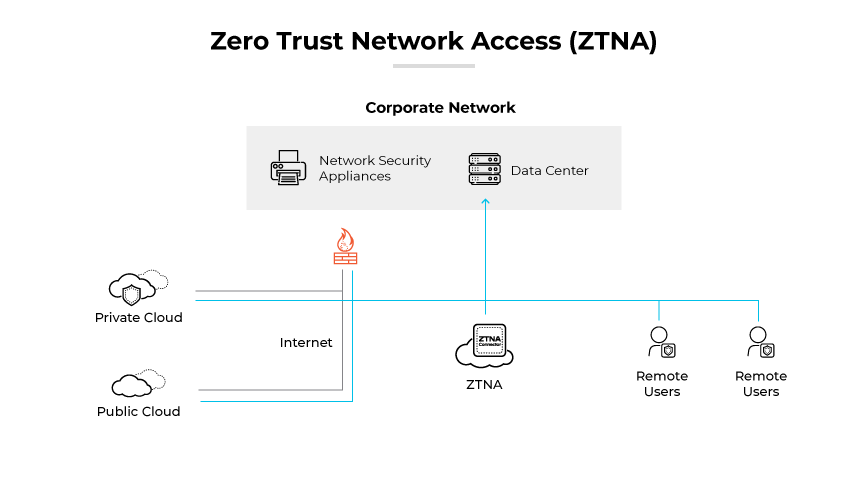
Zero Trust network access (ZTNA) is a set of technologies designed to securely manage remote access to applications and services by enforcing predefined access control policies. Unlike traditional VPNs, which provide broad access to a local area network, ZTNA solutions adopt a deny-by-default stance. Deny-by-default grants users access to explicitly authorized services only. As the number of remote users grows, it is crucial for organizations to understand the security advantages and potential gaps that come with ZTNA solutions.
ZTNA grants user access only after successful authentication to the ZTNA service. The service then facilitates access to the required application on behalf of the user via a secure, encrypted connection. This approach adds an extra layer of security to corporate applications and services by concealing IP addresses that would otherwise be exposed to the public.
Similar to the principles of software-defined perimeters (SDP), ZTNA applies the concept of a dark cloud, which hides applications and services from users unless they have explicit permission to access them. This strategy helps prevent lateral movement by attackers, who could otherwise use compromised endpoints or credentials to scan and pivot to other services.
What Are the Differences Between SASE and ZTNA?
| ZTNA vs. SASE: What Are the Differences? | ||
|---|---|---|
| SASE | ZTNA | |
| Architectural Integration | Integrates networking and security into a cloud-based service for remote and hybrid users. | Focuses on secure remote access with no intrinsic networking capabilities. |
| Scope of Application | Secures a broad range of enterprise environments. | Targets specific applications and services for remote users. |
| Network Design Philosophy | Emphasizes cloud-based capabilities deployed as needed. | Operates on a zero-trust principle, restricting access without network redesign. |
| Application Visibility and Access | Offers visibility across the entire network at the edge. | Visibility limited to user and application interaction. |
| Security Capabilities | Includes SWG, CASB, FWaaS, and ZTNA. | Focuses on identity verification and access tunnels. |
| Deployment and Management | Simplifies management by consolidating functions and services. | Typically requires integration into broader security strategies. |
| Access Control Strategies | Enforces security across all applications and data paths. | Access restricted to pre-defined services for authenticated users only. |
Architectural Integration
Architectural integration is a key difference between ZTNA and SASE. SASE integrates networking and security into a singular cloud-based service. This architecture supports remote and hybrid users through cloud gateways, avoiding traffic backhauls to data centers. Conversely, ZTNA focuses solely on secure remote access without intrinsic networking capabilities.
Scope of Application
SASE provides a comprehensive suite of security and networking features, designed to safeguard all types of enterprise environments. In contrast, ZTNA targets the secure access of remote users to specific applications and services.
Network Design Philosophy
SASE represents a shift in network design, emphasizing cloud-based capabilities deployed as needed. ZTNA operates on the Zero Trust principle that restricts access, with no inherent network redesign.
Application Visibility and Access
SASE operates at the network edge, offering visibility across the entire network. ZTNA, however, provides visibility limited to user and application interaction, based on stringent access control policies.
Security Capabilities
SASE encompasses a broad range of security functions such as SWG, CASB, and FWaaS, alongside ZTNA. ZTNA as a component focuses on identity verification and secure, narrow access tunnels for users.
Deployment and Management
SASE aims to simplify management by consolidating various functions and services. ZTNA, being one of these services, typically requires integration into broader security strategies like SASE.
Access Control Strategies
SASE enforces security across all applications and datapaths in a network. ZTNA's access control is more specific, restricting access to predefined services for authenticated users only.
What Are the Similarities Between SASE and ZTNA?
| ZTNA vs. SASE: What Are the Similarities? | |
|---|---|
|
|
Emphasis on Secure Remote Access
Both SASE and ZTNA facilitate secure remote access, addressing the needs of modern workforces. They provide solutions that enable secure connectivity for dispersed users, ensuring that access to applications and services is both safe and reliable.
Alignment with Cloud Transformation
SASE and ZTNA align with cloud transformation initiatives, offering services that are compatible with cloud and multicloud environments. They support the transition away from traditional network perimeters to more fluid, cloud-based infrastructures.
Focus on Identity and Access Management
Identity-based authentication and granular access control are central to both SASE and ZTNA. They prioritize verifying the identity of users and devices and enforce access policies that restrict entry to network services and applications based on user credentials.
Reduction of Operational Complexity
SASE and ZTNA both contribute to reducing network and security operations complexity. By delivering cloud-native capabilities, they simplify the resource management and eliminate the need for multiple disparate security products.
Enhanced Performance and User Experience
Improving network performance and the overall user experience is a shared objective of SASE and ZTNA. They employ techniques to minimize latency and optimize access, enhancing the efficiency of user interactions with applications.
What Is the Difference Between SASE and Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security strategy that requires verification for every access request within a network, whereas SASE is an integrated network architecture that combines comprehensive security services, including Zero Trust principles, within a cloud-based infrastructure. Zero Trust operates on the assumption that trust should never be implicit within or outside the network, and access is granted only after thorough verification.
In contrast, SASE extends beyond access control, encompassing a range of security functions it delivers at the network edge to ensure secure access and optimal performance. SASE solutions support the dynamic, distributed nature of modern enterprises, applying Zero Trust as part of a broader, strategic approach to network security and management.
The Role of ZTNA in SASE

Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) plays a crucial role in SASE (secure access service edge) architecture by enforcing strict access control. In a SASE model, ZTNA provides fine-grained, identity-based access to organizational resources, ensuring only authenticated and authorized users can access specific applications and services. Adherence to the principle of "never trust, always verify" underpins the security model that SASE embodies, extending it across the network regardless of where resources or users are located.
ZTNA is embedded within the SASE framework to enhance security by segmenting access based on user profiles and their associated trust levels. It rejects the traditional, location-based perimeter defense in favor of a dynamic, risk-informed access strategy. This strategy assesses context, such as the user's role, location, and the device's security posture, before granting access. Assessing context reduces the attack surface against unauthorized entry and lateral movement within the network.
The integration of ZTNA into SASE architectures represents a transformative approach to network security. It shifts the focus from network-centric security models to user- and device-centric models, which is essential in a landscape where remote work and cloud-based assets are the norm. Within SASE, ZTNA enables direct, secure connections to applications, eliminating the need for remote users to connect via traditional VPNs, which can be a security liability due to their broad network access.
One of the main purposes of ZTNA in a SASE architecture is to provide agility and scalability. As businesses grow and adopt more cloud services, the ability to quickly adapt and enforce consistent security policies becomes paramount. ZTNA aids in this by allowing security teams to implement and manage policies centrally. This streamlines the secure access of a distributed workforce without the complexity of managing individual VPNs or legacy remote access solutions.
Benefits of Adopting SASE and ZTNA
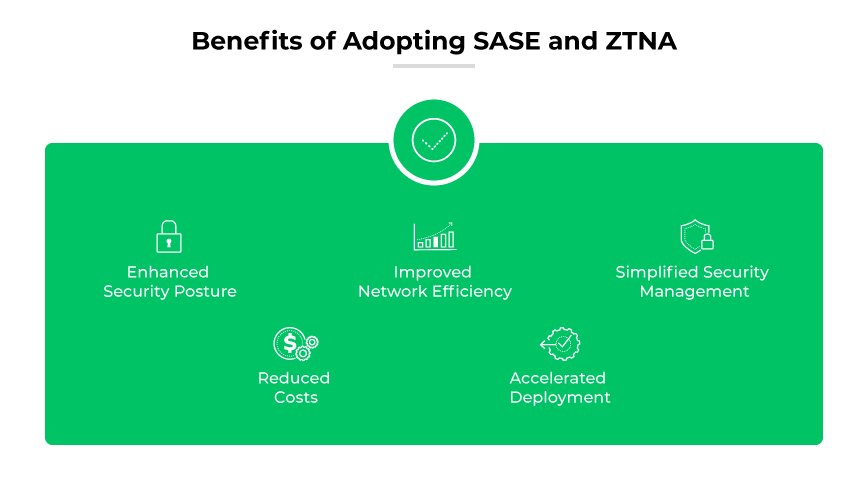
Implementing SASE and ZTNA together strengthens an organization's security posture. ZTNA ensures secure access through identity verification, while SASE extends security services to the network's edge. This combination mitigates risks of unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network.
Improved Network Efficiency
SASE and ZTNA reduce latency by facilitating direct connections to applications and avoiding the need to route traffic through a central hub. This approach leads to improved performance for remote users and distributed workforces.
Simplified Security Management
The integration of SASE with ZTNA streamlines network and security management. Organizations benefit from a unified platform to enforce policies, resulting in simplified operations and better control over the IT environment.
Reduced Costs
By converging networking and security into a single cloud-based platform, SASE with ZTNA can lower the total cost of ownership. It eliminates the need for multiple security solutions or appliances and reduces the complexity of network architecture.
Accelerated Deployment
Cloud-based deployment models of SASE and ZTNA enable rapid implementation across organizations, reducing the time and resources typically required for setting up traditional security infrastructure.
