Secure Web Gateway vs. CASB: What Is the Difference?
The difference between SWG and CASB is that a secure web gateway primarily secures internet-bound traffic and enforces web policies, while a cloud access security broker extends security and compliance controls to cloud applications and services.
While SWGs typically handle traffic and data security for traditional web usage, CASBs provide a security layer that is specifically designed for the complexities of cloud computing, including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS platforms. CASBs often offer granular control over data and user activities in the cloud.
What Is an SWG?
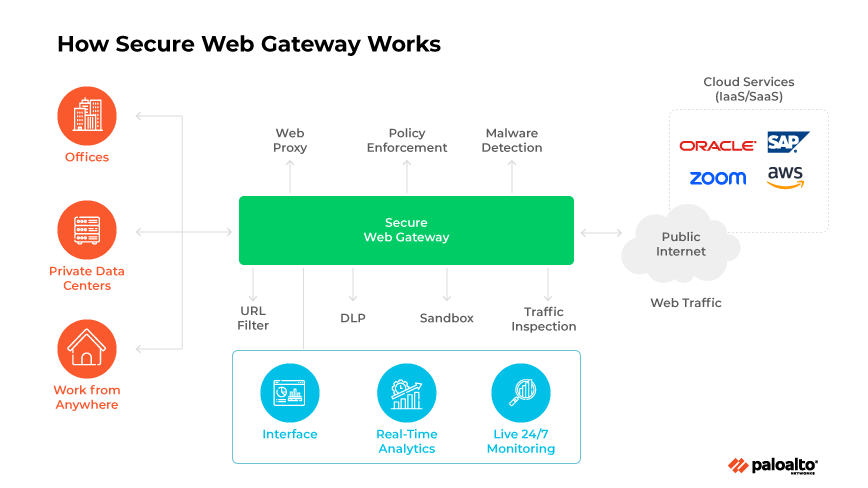
A secure web gateway (SWG) is a network security solution that filters internet traffic and enforces regulatory and corporate policy compliance. SWGs work both in the cloud and on premises.
Operating as a mediator between a corporate network and the internet, an SWG filters web traffic to maintain security protocols and usage policies. It oversees data exchange between the internet and the network.
SWG functionalities include URL filtering, application control capabilities, and antimalware and threat prevention. Deployment options range from cloud-based virtual machines and services to software applications and physical servers.
Secure web gateways examine traffic from user devices seeking internet access, routing each request, verifying user credentials, and evaluating compliance with usage policies. SWGs also inspect inbound data before it reaches the user, only granting access to requests it deems appropriate and secure.
SWGs provide a protective barrier against online threats and ensure adherence to usage policies, acting as internet gatekeepers to block hazardous web content and prevent potential data breaches.
What Is a Secure Web Gateway (SWG)?
What Is CASB?
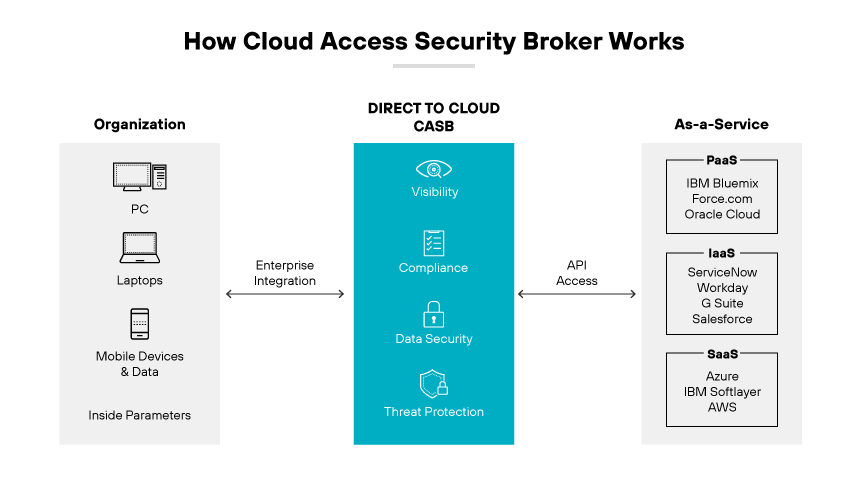
A cloud access security broker (CASB) is a security solution that acts as an intermediary between cloud service consumers and providers, ensuring compliance with enterprise security policies. It enforces these policies by combining and interjecting security protocols. CASB is a key component for organizations addressing cloud service risks, enforcing security policies, and complying with regulations, even for security services beyond their direct control.
CASBs operate based on four pillars:
1. Visibility
CASBs provide visibility and control over managed and unmanaged cloud services. This allows IT to govern access to activities and data within services. This way, organizations can discover all cloud services in use, report on cloud spend, and find redundancies in functionality and license costs.
2. Compliance
CASBs help ensure compliance in the cloud by enabling organizations to comply with regulations like HIPAA, PCI, and GDPR.
3. Data Security
CASBs use sophisticated cloud DLP detection mechanisms like document fingerprinting to prevent sensitive content from leaving or entering the cloud. This allows security teams to shuttle suspected violations to on-premises systems for further analysis, as well as identify and stop malicious activity before it escalates.
4. Threat Protection
CASBs defend against cloud threats and malware, ensuring employees don’t introduce or propagate threats through cloud services. They also detect and prevent unauthorized access to cloud services and data. CASBs provide advanced threat intelligence to avoid threats that may originate from cloud services.
What Are the Differences Between SWG and CASB?
| CASB vs. Secure Web Gateway: What Are the Differences? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SWG | CASB |
| Deployment Focus | Manages web traffic and acts as a barrier between end-users and the internet. | Manages access to cloud services and protects data across all cloud applications. |
| Security Coverage | Secures internet-bound traffic, URL filtering, and antimalware measures. | Extends security policies to cloud apps, including SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. |
| Compliance and Data Protection | Monitors web traffic for regulatory compliance and data breach prevention. | Provides a broad range of compliance supports for cloud-hosted data and detailed DLP controls. |
| Threat Prevention and Security Management | Prevents threats at the web traffic level with antivirus and intrusion prevention systems. | Monitors and secures data movement across all cloud services with advanced threat protection. |
| Visibility and Control | Offers visibility and control over internet usage with web-based security policies. | Delivers deeper visibility into cloud service usage and granular control over cloud services. |
| Integration with SASE | Is a core component of SASE for secure web gateway functionality. | Integrated within SASE to extend security controls to cloud services. |
Deployment Focus
SWGs inspect and manage web traffic. They act as a barrier between end users and the internet, applying company policies to traffic for both outbound data to ensure no sensitive information leaks out and inbound data to protect against threats.
CASBs focus on managing access to cloud services. They protect an organization’s data across all cloud applications by providing visibility into shadow IT, assessing risks, and enforcing security policies, including services outside the traditional network perimeter.
Security Coverage
SWGs provide security primarily for internet-bound traffic. This includes filtering URLs to prevent access to malicious sites, applying antivirus and antimalware measures, and inspecting traffic for potential threats or data exfiltration.
CASB extends security policies to cloud applications and services, covering SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS environments. It addresses security concerns like identity verification, access control, and threat protection, which are not traditionally within the scope of an SWG.
Compliance and Data Protection
While SWGs contribute to regulatory compliance by monitoring and controlling web traffic and preventing data breaches, CASBs offer a broader range of compliance supports. CASBs help organizations meet compliance requirements for cloud-hosted data across various regulations and standards.
CASBs provide detailed controls for data security, such as DLP capabilities, which are essential for demonstrating compliance in cloud environments. CASBs also manage data access and sharing policies, further ensuring users handle data according to compliance mandates.
Threat Prevention and Management
SWG focuses on preventing threats at the web traffic level, with features like antivirus and intrusion prevention systems to block known threats and unauthorized content.
CASB, however, offers a more extensive threat management approach by monitoring and securing data movement across all cloud services. It uses advanced data and threat protection mechanisms to identify and mitigate cloud-specific threats such as compromised accounts and insider threats, which are beyond the purview of SWG solutions.
Visibility and Control
SWG tools provide visibility and control over internet usage and enforce web-based security policies.
CASBs deliver deeper visibility into cloud service usage, including unsanctioned applications (shadow IT). They offer granular control over data and user activities across all cloud services, enabling organizations to implement nuanced access policies that can vary by user, device, location, and other contexts.
Integration with SASE
Secure access service edge (SASE) integrates various networking and security functions, including SWG and CASB. While SWG is one of the core components of SASE, providing secure web gateway functionality, CASB is also a component of SASE architectures to extend security controls to cloud services. SWGs and CASBs serve different but complementary roles within a unified SASE framework.
What Are the Similarities Between SWG and CASB?
| Secure Web Gateway vs. Cloud Access Security Broker: What Are the Similarities? | |
|---|---|
|
|
Policy Enforcement
Both SWG and CASB enforce security policies to manage and secure data flow. SWGs apply policies to internet traffic, while CASBs enforce policies across cloud services. They authenticate users and allow or deny requests based on set policies. This ensures secure data exchange aligned with organizational standards.
Threat Mitigation
SWG and CASB share the common function of threat mitigation. SWGs protect against web-based threats through URL filtering and antivirus mechanisms, whereas CASBs extend this protection into the cloud environment. Both systems work to identify and block potential security risks, safeguarding organizational data.
Regulatory Compliance
SWG and CASB both contribute significantly to compliance. Both solutions offer tools to support regulatory compliance, such as data loss prevention (DLP) and access controls. They help organizations adhere to standards like GDPR, ensuring sensitive data protection and management according to legal requirements.
Data Security
At their core, SWG and CASB focus on data security. Through various methods like antivirus, antimalware, and DLP, they prevent unauthorized data exposure. Both technologies aim to detect and prevent the sensitive information exfiltration, maintaining the integrity of organizational data across the network and cloud services.
Adaptive Deployment
SWG and CASB solutions are adaptable in their deployment. SWGs can be implemented on physical servers, cloud services, or as software applications. Similarly, CASBs can be utilized as on-premises hardware, cloud-hosted software, or integrated through APIs. Both technologies offer flexible deployment options to fit the specific needs of an organization.
Can SWG and CASB Work Together?
While SWG and CASB have overlapping functions, they do not merge into a single solution. Rather, both tools reinforce each other, with CASB building upon the SWG’s capabilities to scrutinize traffic and execute security protocols. Instead of converging, CASBs can complement SWGs by adding an additional layer of security.
However, SWG and CASB are both instrumental for organizations transitioning to a secure access service edge (SASE) framework. Regardless of their potential convergence, SWG and CASB are both essential components within the SASE architecture.