The White House released a memo on June 2, 2021, urging corporate executives and business leaders to increase cyber defenses and immediately prepare for ransomware attacks. The memo lays out the U.S. Government’s recommended best practices to help organizations assess their security posture, prepare for future ransomware attacks, and restore operations in the event of a breach. To accomplish this, the memorandum outlines five key focus areas for agencies to focus on:
- Backup your data, system images, and configurations; regularly test them; and keep the backups offline.
- Update and patch systems promptly.
- Test your incident response plan.
- Check your security team’s work.
- Segment your networks.
Legacy solutions have proven to be obsolete in combating ransomware attacks. An effective cyber defense requires advanced AI-powered security – automated across agencies’ networks and endpoints.
Palo Alto Networks has long been positioned to help our customers address ransomware threats, and we regularly promote such practices. Much of our portfolio of products and services can help organizations fight ransomware attacks across the enterprise, from prevention and discovery through remediation. And our Unit 42 threat researchers have been at the forefront of ransomware threat intelligence for years.
One key solution in our ransomware defense is Prisma Cloud. The solution helps organizations implement the recommended ransomware best practices for the cloud, including patch management and network segmentation, all with minimal time and effort.
A Pulse on Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are increasing and adversaries are becoming more brazen. In the 2021 Ransomware Threat Report, Unit 42 researchers shared that:
- The average ransom paid by organizations increased from $115,123 in 2019 to $312,493 in 2020, a 171% year-over-year increase.
- The highest ransom paid by an organization doubled from 2019 to 2020, up to $10 million from $5 million.
- From 2015 to 2019, the highest ransom demanded was $15 million. In 2020, the highest was $30 million.
The most successful ransomware attacks target businesses' critical systems, as the attacker can request higher ransom payments if a company is unable to operate. For example, JBS, the world’s largest meat processing company, was recently hit by a cyberattack that disrupted its North American and Australian operations. The company paid the attackers nearly $11 million to restore operations, which is believed to be the largest ransom ever paid.
Recent ransomware attacks have not only hindered companies' logistics, in some cases, they have impacted the global economy. With the spike in volume and growing economic impact of ransomware cases, The White House has called on business leaders to increase their cyber defenses and prepare for more ransomware attacks.
Reasoning Behind the Best Practices
The recent White House memo lists five best practices for safeguarding against ransomware attacks, including patching your systems and segmenting your networks, but why?
Networks are good at one thing – connecting systems. Users, devices and business-critical applications all communicate over reliable network pathways. However, hackers are very good at exploiting vulnerabilities using the same network paths available to users and applications. Often they will use three basic steps in a ransomware attack:
- Compromise: An attacker will probe the network for exposed vulnerabilities, and compromise any vulnerable machine(s) they find. No matter how strong you build perimeter defenses, an attacker will find their way onto the network.
- Move laterally: Once on the network, the adversary needs to find high-value systems or sensitive data. They do this by scanning the open, internal network to find attack paths to other vulnerable systems, then hop from machine to machine. This is known as lateral movement.
- Attack: Once the adversary lands on a critical digital asset, they take control and lock down the system and data.
So businesses must do two things to reduce risk in a scenario like this: Minimize the number of vulnerabilities on systems by patching them, and enforce segmentation to limit a system's exposure to the internal network.
Patch Management
Vulnerabilities are easy targets for exploits, so minimizing the number of vulnerabilities on the internal network creates fewer opportunities for attackers. The White House memo highlights the need to update and patch systems promptly. However, traditional cybersecurity tools are unable to provide meaningful context regarding vulnerabilities, making it difficult for security teams to assess their cyber risk and expedite patching. And for systems that cannot be patched, these tools lack workarounds or compensating controls to reduce risk.
Segmentation
Microsegmentation, also known as Zero Trust Segmentation, is a cloud network security control that segments systems to reduce the attack surface. In the event of a compromise, microsegmentation contains the breach and prevents lateral movement of malware by limiting the number of possible pathways on the internal network. While organizations may agree that microsegmentation is critical, many security teams find it too complex and time-consuming to implement.
How Prisma Cloud Supports Ransomware Best Practices for the Cloud
To support these ransomware best practices for the cloud, Prisma Cloud delivers vulnerability management for hosts, containers and serverless functions with Cloud Workload Protection and simplified microsegmentation with Identity-Based Microsegmentation.
Cloud Workload Protection: Update and Patch Systems
Cloud Workload Protection supercharges lifecycle vulnerability management with several different features.
- Rich analysis: The platform will create and maintain a "bill of materials" so that you don't need to wait for a scheduled scan to know whether a new CVE impacts your cloud.
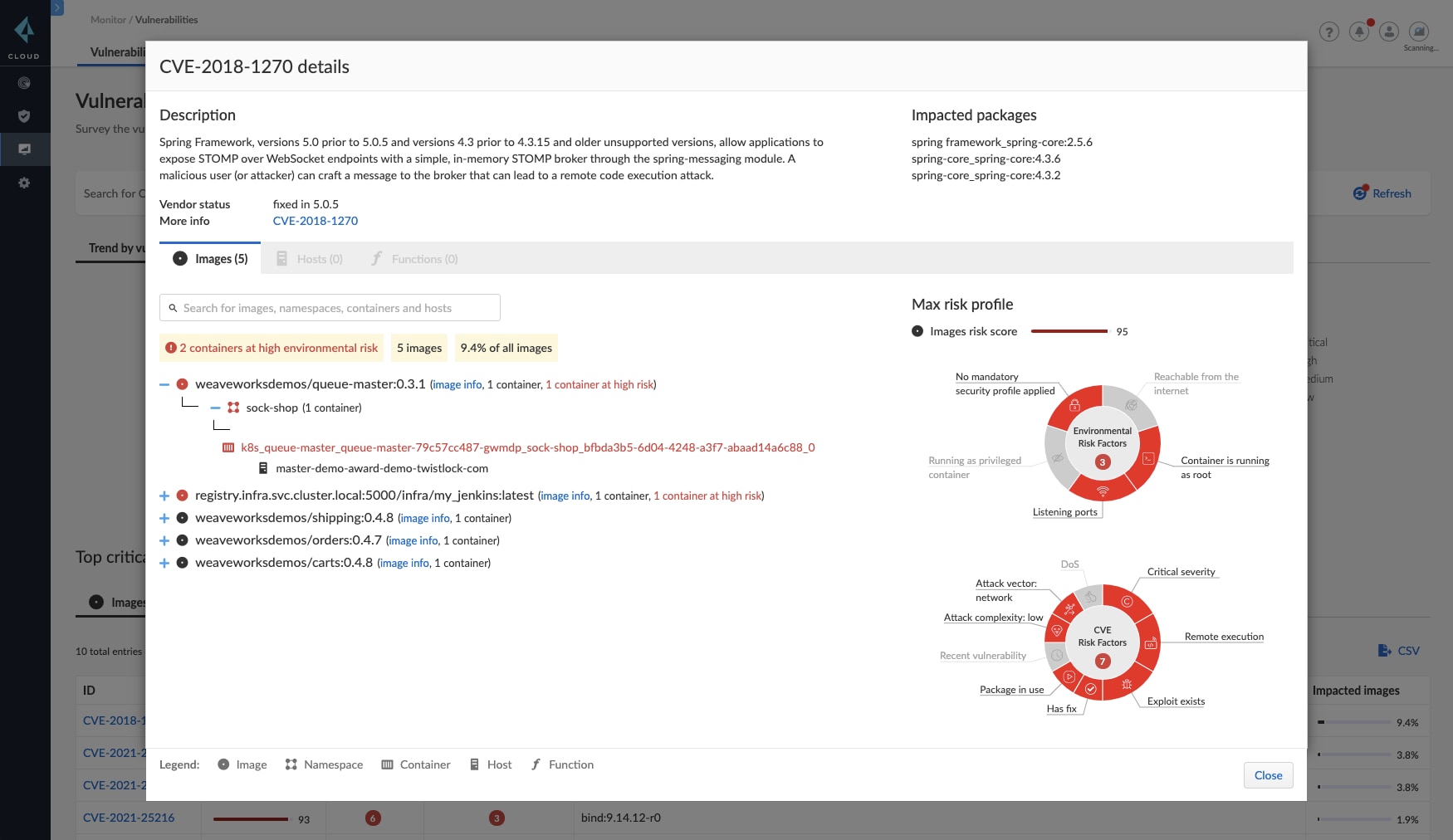
- Contextual, risk-based prioritization: Prisma Cloud can assess which of your workloads is most impacted by a vulnerability, then prioritize them into a top ten.
- Cross-workload and lifecycle protection: Because it monitors workloads, VMs, containers, and serverless functions across the application lifecycle, Prisma Cloud can alert the right team, identify the specific issue, and explain the fix.
- Deep Visibility: Prisma Cloud surfaces the most at-risk resources across public and private clouds via search fields, APIs, and interactive dashboards.
Where patching isn’t possible, or to protect against zero-day threats, then Prisma Cloud Web Application and API Security (WAAS) virtual patching provides compensating controls to protect vulnerable services.
Identity-Based Microsegmentation: Segment Applications
Prisma Cloud Identity-Based Microsegmentation makes microsegmentation easy. You can move from a flat network to a segmented, Zero Trust network across private and public clouds in four simple steps.
- Deploy: Put an agent onto hosts and containers in your environment in a safe, permissive mode which allows all communications so that operations and production systems are never disrupted
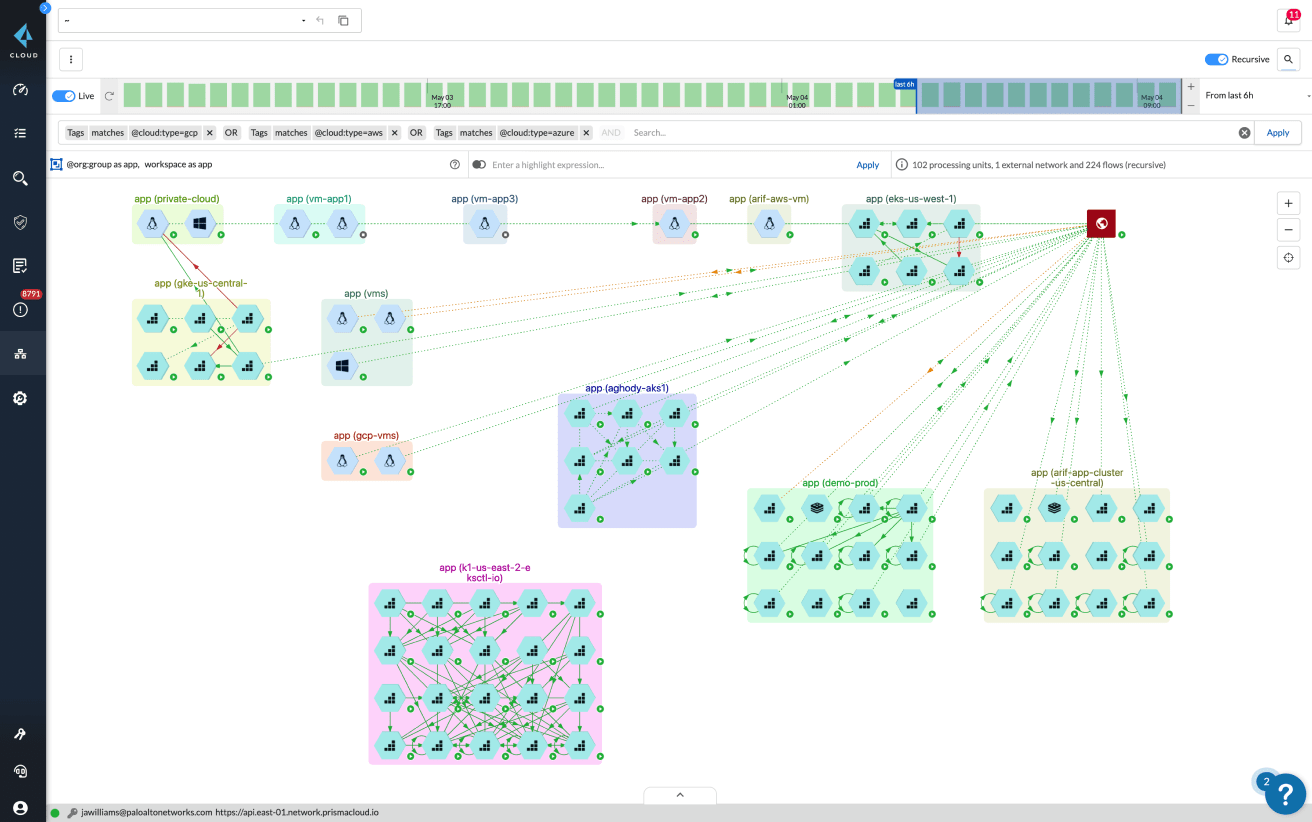
- Discover: See how your applications communicate on a real-time map to better understand their behavior.
- Build and validate: Generate segmentation policies for internal communications you want to allow on the network, and continue to monitor the environment to model the impact of a given policy.
- Enforce: Once you’ve validated policies, move the agent from a permissive state to a Zero Trust enforcement state, which implicitly denies all unauthorized communication requests.
Prisma Cloud enables you to insert network separation among regulated environments, business-critical application groups, and individual hosts/containers without changing the underlying network infrastructure.
Begin Using Prisma Cloud
As the White House memo states,
"...companies that view ransomware as a threat to their core business operations, rather than a simple risk of data theft, will react and recover more effectively. To understand your risk, business executives should immediately convene their leadership teams to discuss the ransomware threat and review corporate security posture and business continuity plans to ensure you have the ability to continue or quickly restore operations."
It is not enough to understand that ransomware is a threat – organizations must quickly and actively implement these ransomware best practices for the cloud.
The Cloud Workload Protection and Identity-Based Microsegmentation capabilities described above can help do just that, and are fully integrated into the Prisma Cloud platform.
Request a 30-day trial for Cloud Workload Protection and Cloud Network Security to get valuable hands-on experience with risk-based vulnerability management, runtime protection, and microsegmentation.