What Is SD-WAN as a Service (SD-WANaaS)?
SD-WANaaS is a service model where third-party providers manage and deliver SD-WAN functionalities to customers over the internet.
Distinct from managed SD-WAN, SD-WANaaS offers businesses centralized control and visibility over their network through a cloud-based management portal. Customers typically choose SD-WANaaS for efficient, secure, and optimized network performance across multiple locations without the need to handle the underlying infrastructure themselves.
How does SD-WANaaS work?
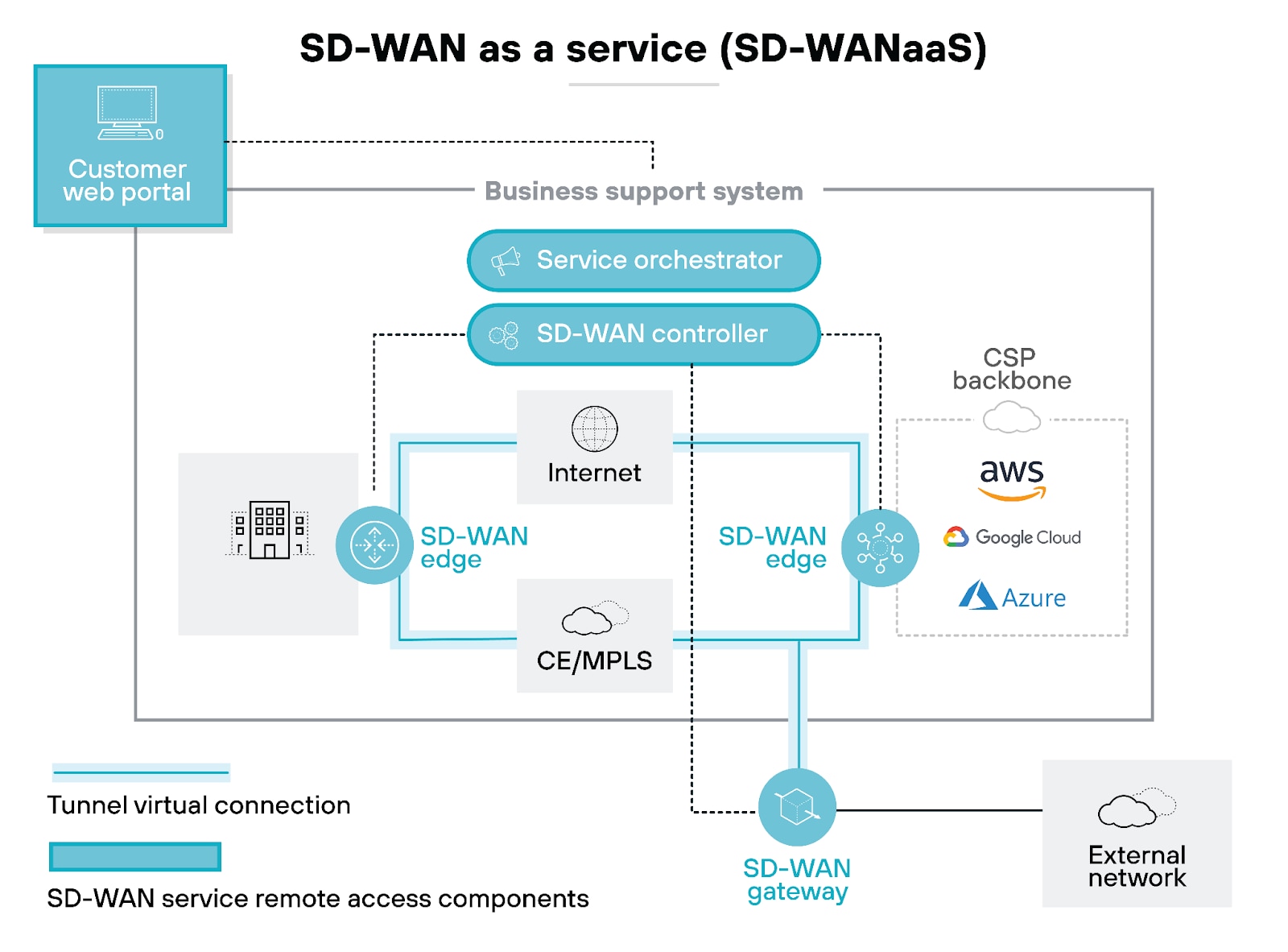
SD-WANaaS uses the same fundamental SD-WAN architecture you can expect from typical SD-WAN solutions. It relies on software-defined networking and security principles to manage and optimize WANs, in addition to handling network connections between data centers. And enhances performance and user experience.
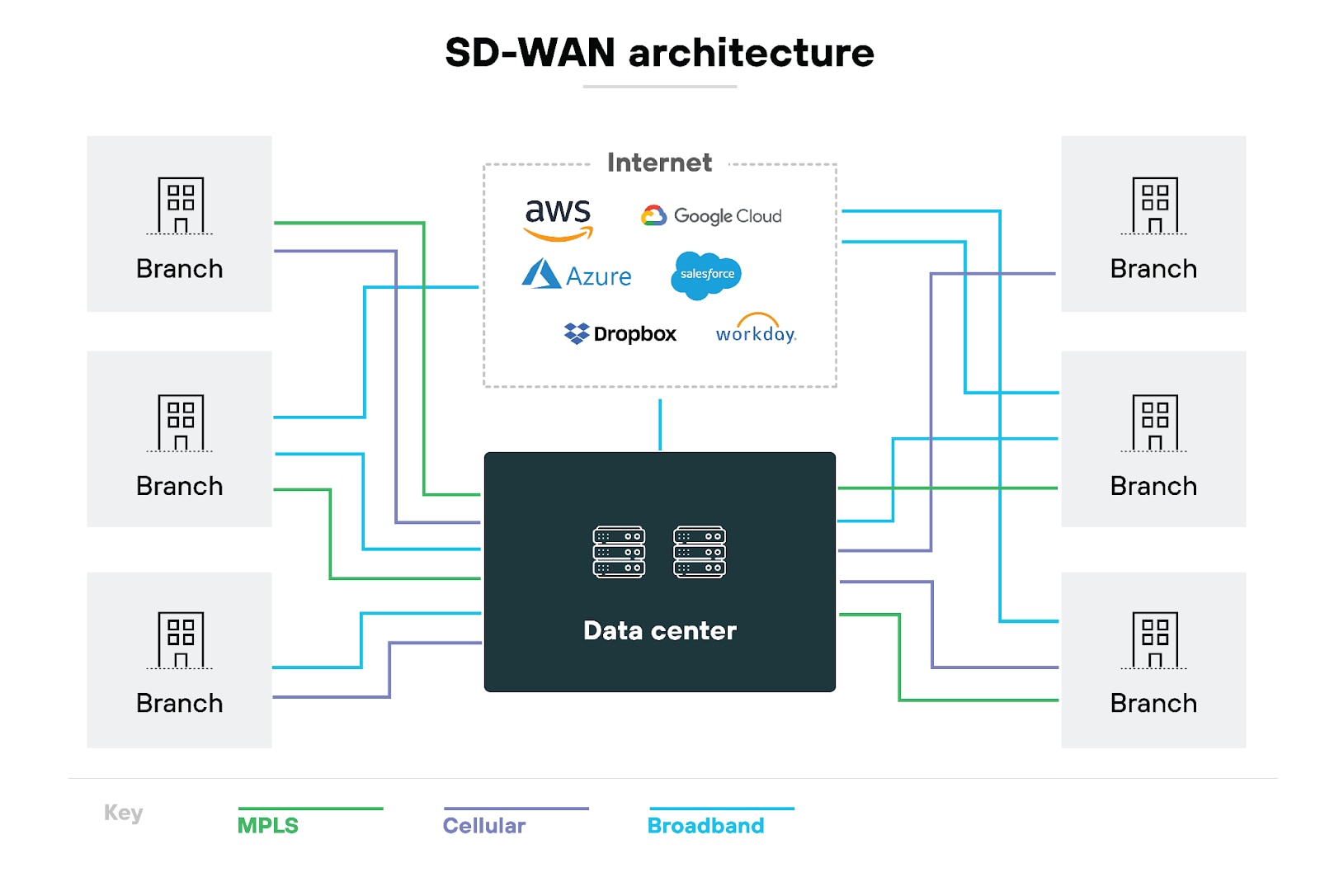
SD-WANaaS uses a cloud-based infrastructure to manage and optimize an organization's WAN, usually delivered and priced via a monthly subscription.
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
First, SD-WANaaS uses a centralized control function that directs traffic across the WAN dynamically and efficiently. Customers can typically access centralized management via a cloud-based portal. Most providers offer an intuitive interface for users to monitor and manage their network.
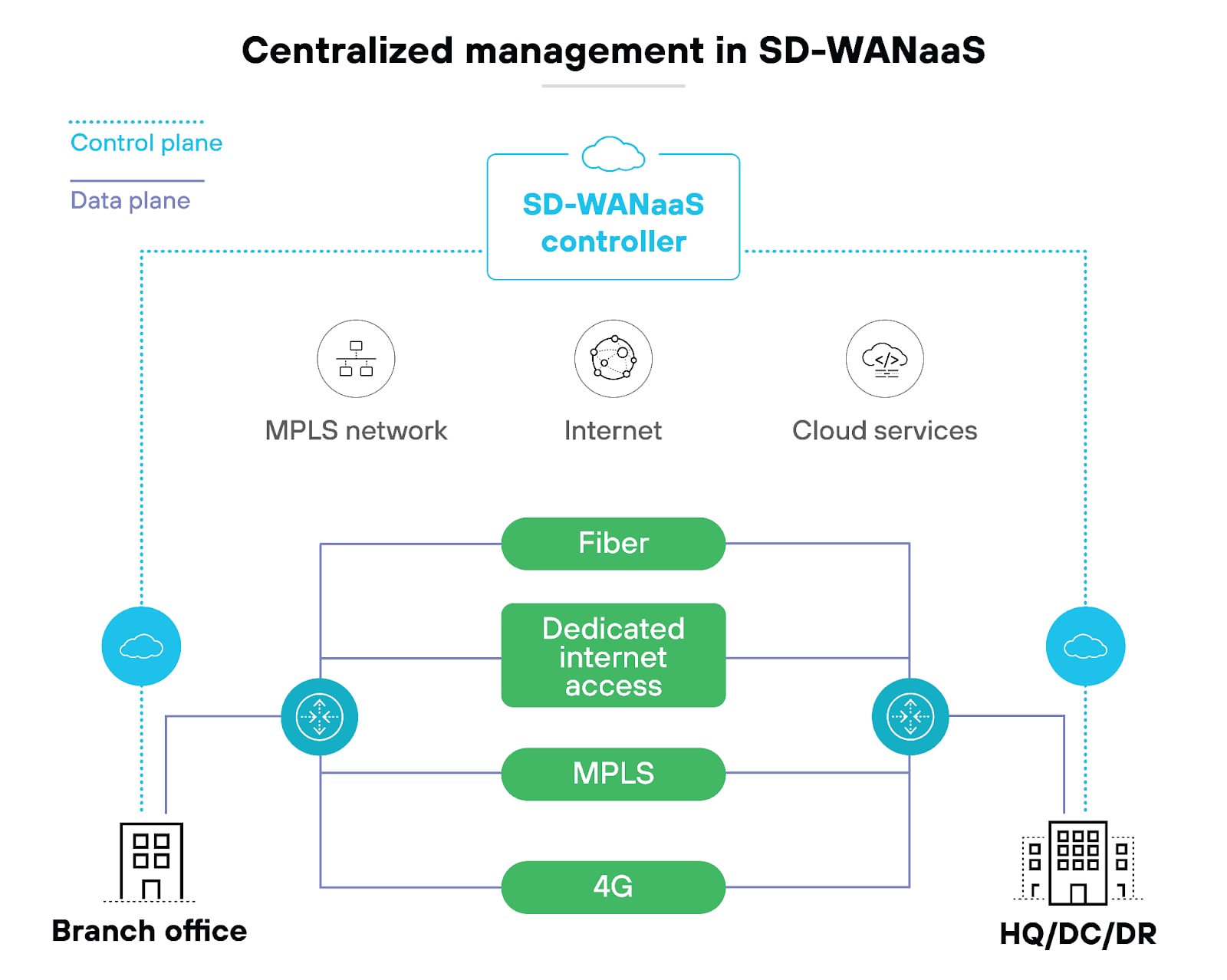
Just like with traditional SD-WAN, the system automatically routes traffic along the most optimal paths, whether over MPLS, broadband internet, or wireless connections like 4G and 5G.
Like this:
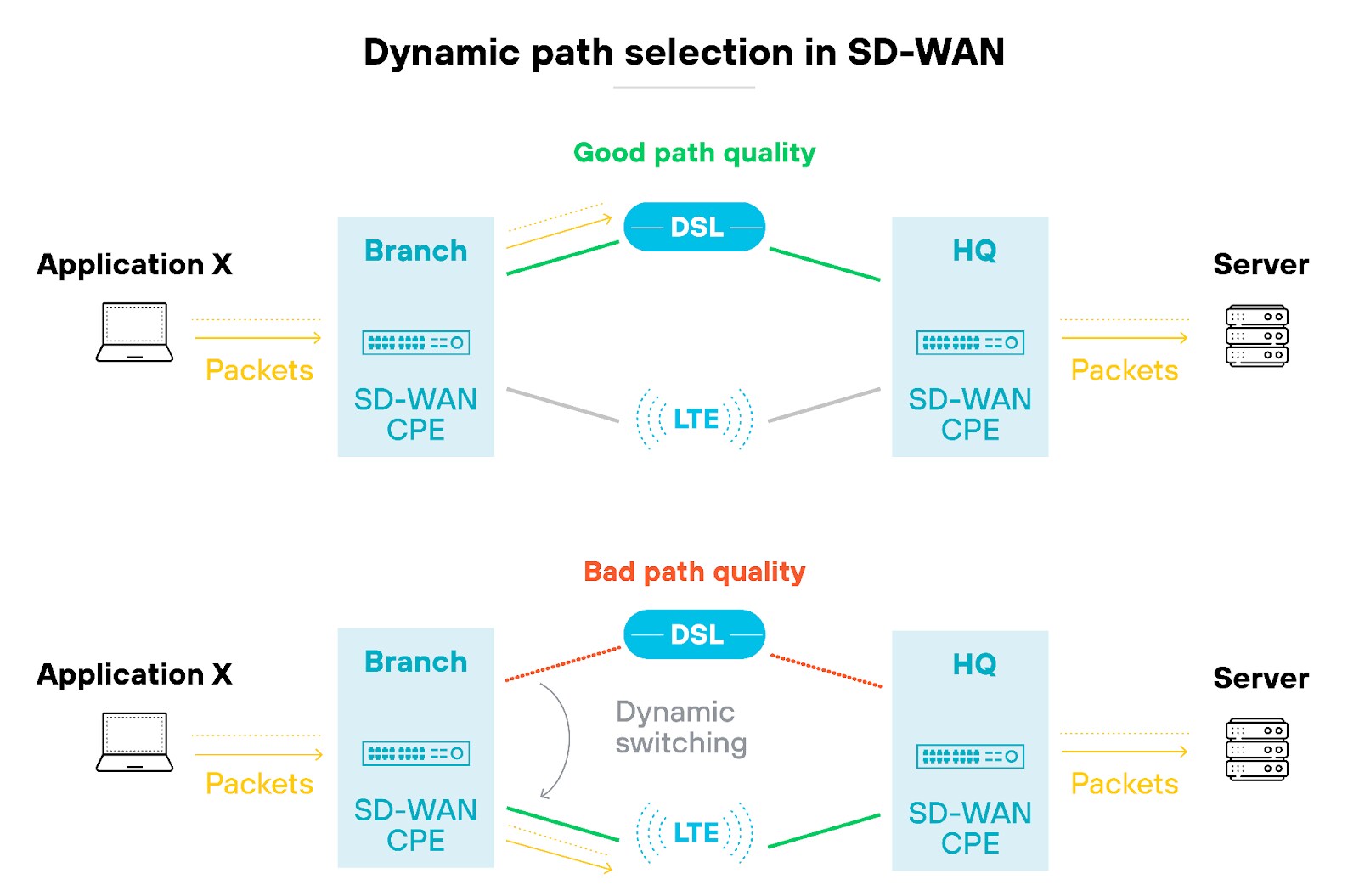
So businesses can adapt quickly to changing network conditions without manual intervention—and enjoy better performance for critical applications and a more resilient network overall.
Next, SD-WANaaS abstracts the complexity of the underlying network infrastructure. In other words, businesses don’t need to worry about the hardware or physical connections between sites.
The service provider handles all these aspects. So that the network stays robust and secure. The abstraction enables organizations to focus on their core activities instead of network management.
SD-WANaaS offers many of the same benefits of SD-WAN, except without the need for on-premises hardware or extensive in-house management, including:
- Operational simplicity
- Carrier-independent WAN connectivity and improved ROI
- Improved security
- Enhanced performance
- Improved connectivity and direct cloud access
- Seamless connectivity management
- Foundation to SASE strategy
- Integration with other network services
- 24/7 support
- Hardware lifecycle management
- Public cloud support
What is the difference between SD-WANaaS and managed SD-WAN?
It’s worth noting that as technology evolves, the distinctions between managed SD-WAN services and SD-WANaaS are becoming less clear. More technology providers are incorporating as-a-service consumption models, which blur the lines between these traditionally separate approaches.
With this established, to understand SD-WANaaS (SD-WAN as a service), it’s helpful to start by differentiating it from managed SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network)—which it’s often confused with.
Both SD-WANaaS and managed SD-WAN are built on the same foundational SD-WAN technology. Which means they offer the same core functionalities, like dynamic traffic routing, centralized management, enhanced security, and application-aware policies.
So, each service aims to simplify and optimize network management, but they do so in distinct ways.
|
Parameters |
SD-WANaaS |
Managed SD-WAN |
|---|---|---|
|
Responsibility |
Customer handles day-to-day management and configuration |
Provider handles deployment, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance |
|
Hardware requirement |
Cloud-based solution, minimal hardware |
Involves on-premises hardware |
|
Control level |
More control and customization by the customer |
Hands-off approach, less control for the customer |
|
Flexibility & scalability |
High flexibility and scalability |
Moderate flexibility and scalability |
|
Pricing |
Typically available as a monthly subscription based on chosen functionality and features |
Offered through one-year or multi-year contracts, tailored to the number of customer sites, their locations, and the required link speeds |
|
Suitable for |
Businesses seeking more control and customization |
Businesses with limited IT resources |
Managed SD-WAN involves a service provider taking on full responsibility for the deployment, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance of the SD-WAN network service and infrastructure.
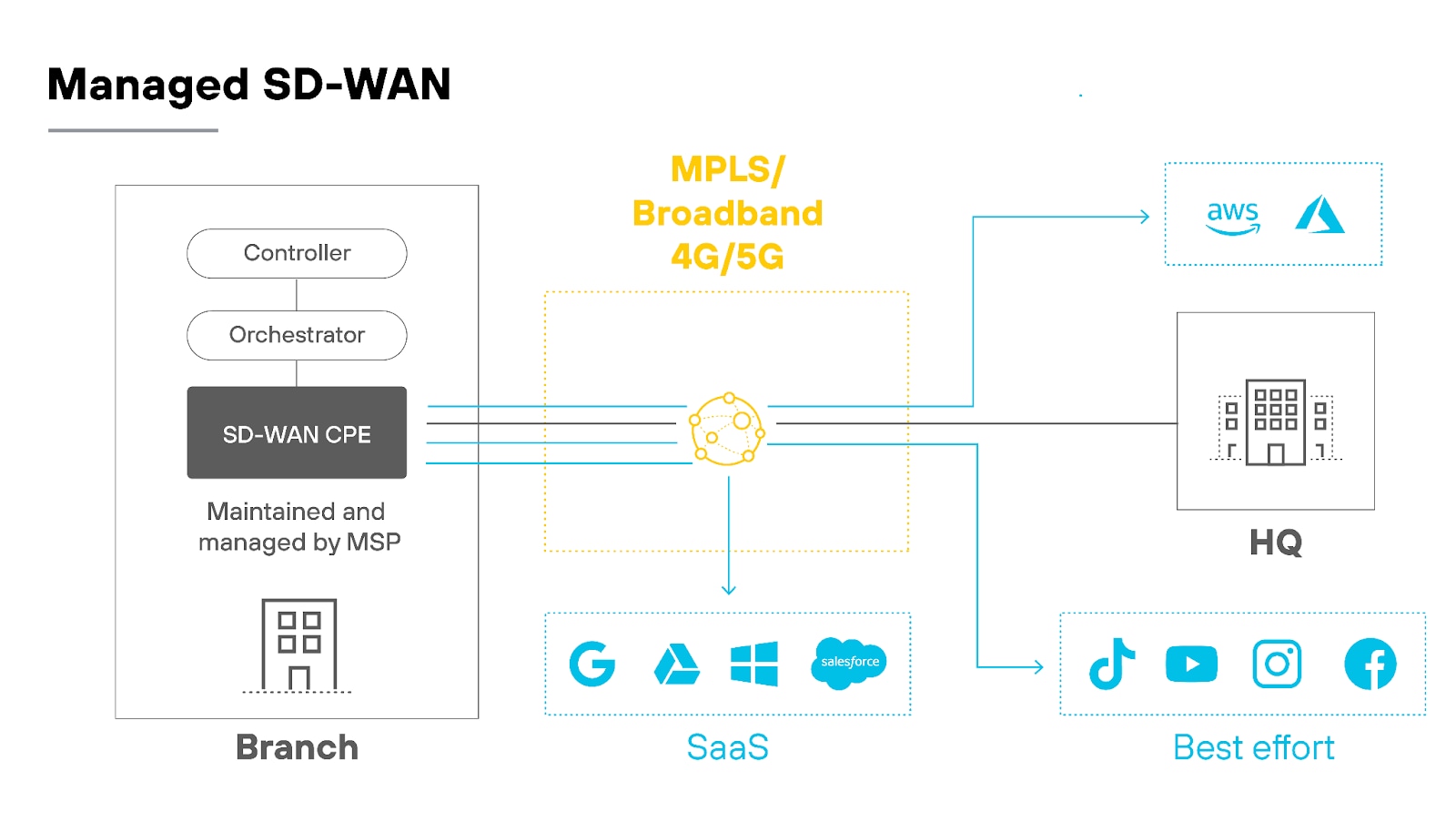
SD-WANaaS, conversely, is a cloud-based solution that doesn't require extensive on-premises hardware.
Instead, the service is delivered over the internet. Customers manage their network through a cloud-based portal. While the provider maintains the core infrastructure and keeps it up-to-date, day-to-day management and network configuration typically fall to the customer.
This model generally provides more flexibility and scalability. Businesses can adjust network settings and resources as needed in real time.
The main difference between the two is the level of control and management.
Managed SD-WAN offers a more hands-off approach because the provider handles most of the operational aspects.
In contrast:
SD-WANaaS requires more active involvement from the customer in managing and configuring the network.
Tip
Managed SD-WAN is generally suitable for businesses with limited IT resources, while SD-WANaaS might appeal to those looking for more control and customization options.
Further reading:
Why do businesses need SD-WANaaS?

Businesses need SD-WANaaS because it provides an alternative SD-WAN solution for managing and scaling networks via the cloud without on-premises hardware or expensive dedicated staff.
Organizations with multiple branch offices, undergoing rapid growth, or in the process of adopting cloud-first strategies often choose SD-WANaaS.
It’s particularly beneficial for businesses with limited IT resources because it makes network management a lot easier. It also improves security without tons of on-premises equipment or the need for in-house expertise.
What are the pros and cons of SD-WANaaS?

SD-WANaaS offers several advantages that make it an appealing option for many businesses. However, like any technology solution, it also has its drawbacks.
Let’s explore both sides to give you a clear picture.
Pros:
One of the main benefits of SD-WANaaS is its advanced security features. These can include encrypted tunnels and comprehensive security protocols that protect data as it traverses the network.
Another advantage is the scalability of SD-WANaaS. Businesses can easily add new sites or increase bandwidth without significant infrastructure changes. The flexibility is especially beneficial for organizations experiencing growth or seasonal variations in network demand.
Plus, as mentioned, SD-WANaaS is typically offered on a subscription basis. This model means businesses receive the latest technology updates and support without the need for substantial upfront investment. It’s a cost-effective way to keep network infrastructure up to date.
Cons:
However, there are also some potential downsides to consider. One is the reliance on third-party providers. While outsourcing network management can free up internal resources, it also means that businesses depend on the provider for service continuity and issue resolution. The dependency can sometimes lead to slower response times or less flexibility in making immediate adjustments.
Another drawback is the recurring cost associated with the subscription model. For some businesses—especially smaller ones— ongoing fees can add up over time and may be higher compared to a DIY approach.
Lastly, while SD-WANaaS simplifies many aspects of network management, it may not provide the same level of customization as an in-house solution. Businesses with very specific or unique networking needs might find the service less adaptable to their requirements.
SD-WAN as a service pricing: How much does SD-WANaaS cost?
SD-WANaaS pricing is influenced by various factors and can follow different models. Understanding these elements makes it easier to choose a pricing plan that aligns with your needs and budget, ensuring the best value for the investment.
As noted, SD-WANaaS providers usually offer a subscription-based pricing model, where businesses pay a recurring monthly or annual fee. This fee often covers software updates, support, and access to the management portal.
SD-WANaaS pricing factors
Several factors can affect the pricing of SD-WANaaS:
- Number of sites: The more locations a business needs to connect, the higher the cost due to increased resource requirements and complexity.
- Bandwidth requirements: Higher bandwidth demands can increase prices. Organizations with significant data traffic or performance-critical applications may incur higher costs.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): SLAs that guarantee higher levels of service and uptime typically come at a premium.
- Security features: Enhanced security measures such as advanced encryption and threat detection can add to the overall cost.
- Additional features: Features like analytics, application and WAN optimization, and integration with other services can influence pricing. Customizable options may also come with additional fees.

SD-WANaaS cost considerations
When assessing SD-WANaaS pricing, consider the following:
- Total cost of ownership (TCO): Evaluate both the upfront costs and long-term expenses, including maintenance, support, and potential upgrades.
- Scalability: Ensure the pricing model supports future growth, allowing for the addition of sites and increased bandwidth without excessive cost increases.
- Return on investment (ROI): Consider potential savings from improved network performance, reduced downtime, and enhanced security, which can offset the initial investment over time.
- Vendor reputation: Choose a reputable provider with a proven track record. Reliable service and robust support can justify higher costs.
