- 1. What drives SD-WAN adoption?
- 2. Application performance and reliability
- 3. Reduced connectivity and operational costs
- 4. Agile branch and site deployment
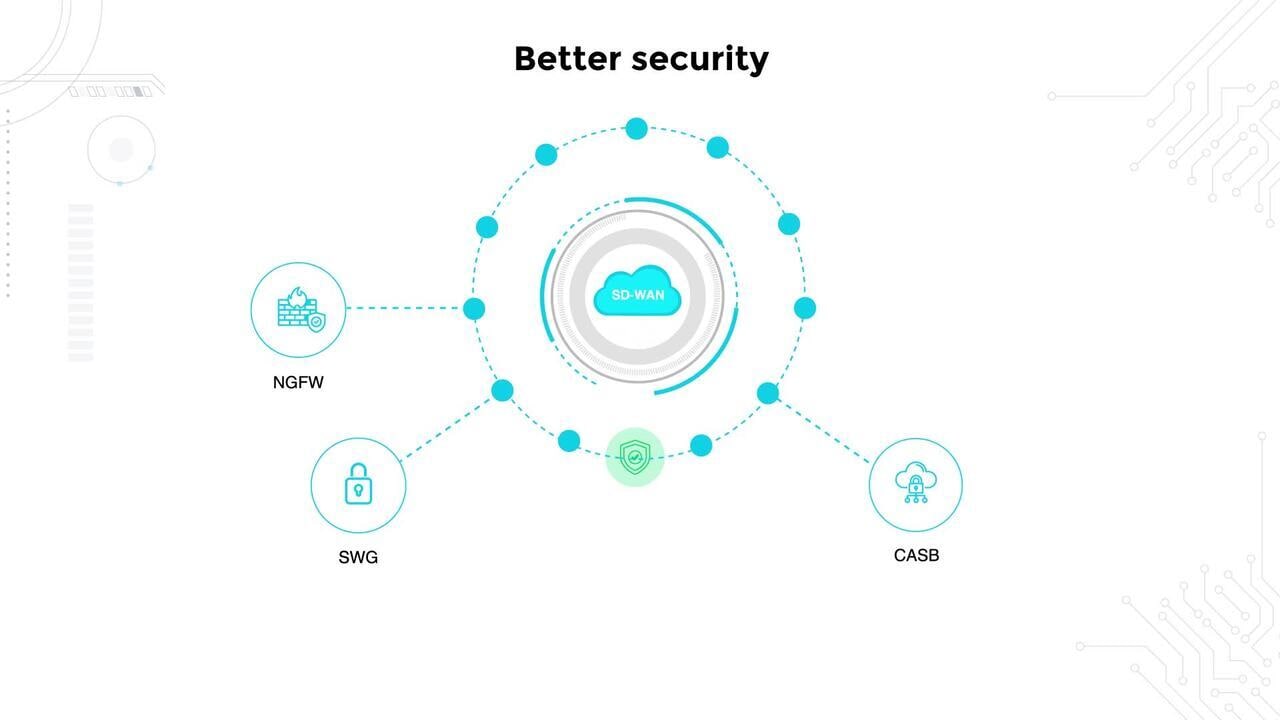
- 5. Consistent security posture
- 6. Centralized visibility and control
- 7. Optimized access to cloud and SaaS applications
- 8. SD-WAN benefits FAQs
Breaking Down the Real-World Benefits of SD-WAN
The benefits of SD-WAN include:
- Application performance and reliability
- Reduced connectivity and operational costs
- Agile branch and site deployment
- Consistent security posture
- Centralized visibility and control
- Optimized access to cloud and SaaS applications
Each of these reflects measurable outcomes, not just features. Taken together, they explain why SD-WAN remains central to enterprise networking strategy.
What drives SD-WAN adoption?
In 2025, SD-WAN is no longer a new technology. It's become the way many organizations keep pace with a network environment that has shifted dramatically. Legacy WAN models, built for centralized applications and predictable traffic, just don't match how businesses operate today.
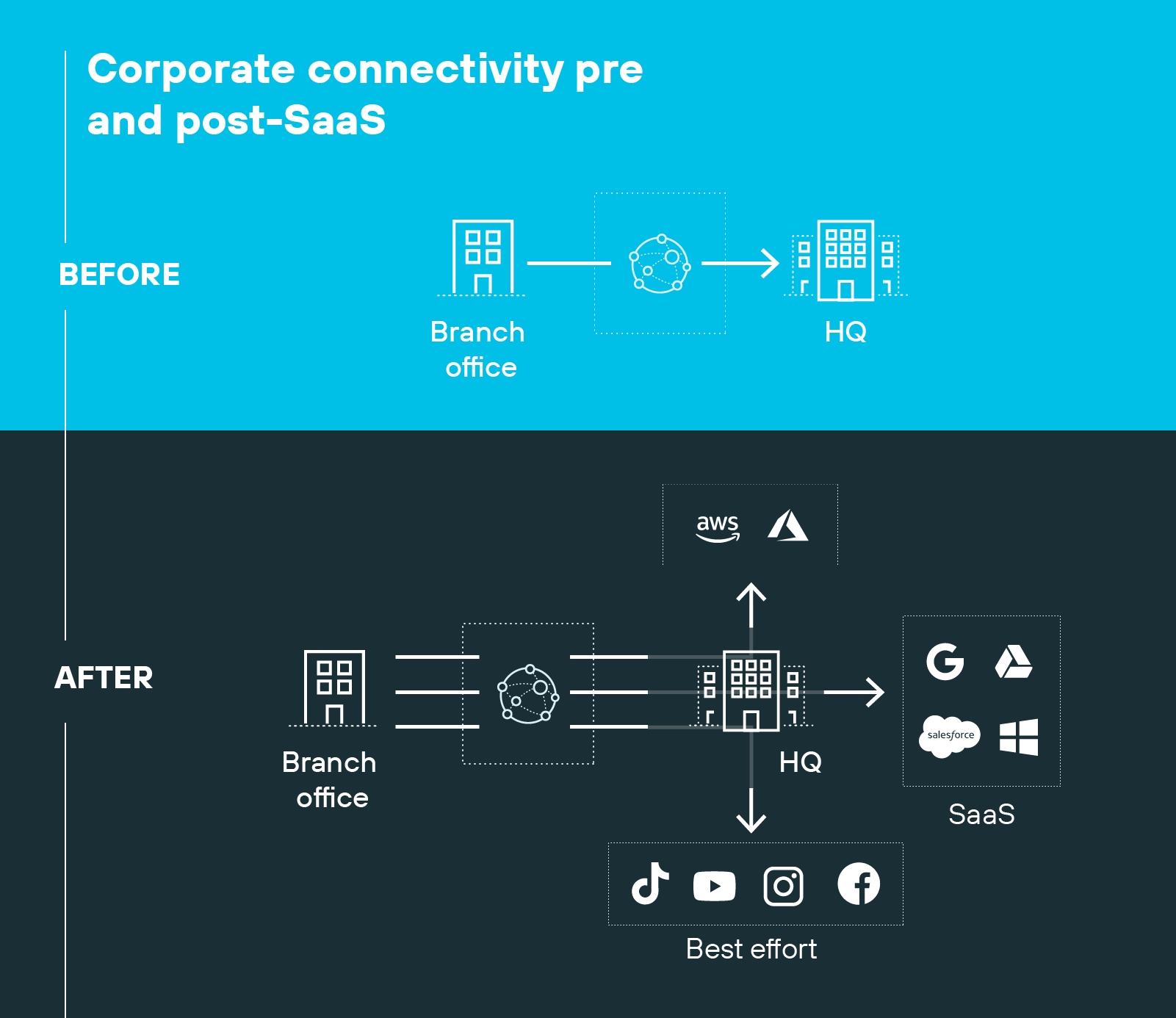
The most immediate driver is the dominance of cloud and SaaS.
Productivity, collaboration, and line-of-business apps now run almost entirely outside the data center. Backhauling that traffic over MPLS introduces latency and undermines performance.
And that's one of the major reasons SD-WAN adoption continues. Because direct, policy-based paths are essential for keeping SaaS and cloud services usable at scale.
Cost pressure is another factor.
MPLS circuits remain expensive and rigid. SD-WAN allows organizations to mix transports—broadband, LTE, or private lines. As well as use policy to steer traffic where it performs best. Which means network capacity can be scaled more flexibly and at lower cost than traditional WANs ever allowed.
Branch expansion and hybrid work also drive adoption.
Remote sites and new offices need to be online in days, not months. SD-WAN's ability to provision and enforce policy centrally makes this possible without a large field workforce.
And as always, security remains a persistent challenge.
The attack surface has grown with more devices, more distributed traffic, and new classes of applications, including generative AI.
Which is why organizations need a consistent way to enforce encryption, segmentation, and access policies across every location and transport. SD-WAN provides that uniformity where legacy WANs fall short.
So:
While SD-WAN may not be brand new, adoption is still happening because the pressures haven't gone away. Cloud, cost, agility, and security continue to pull organizations toward SD-WAN today just as strongly as they did in its early years.
- Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: What Are the Differences?
- What is the Difference Between SD-WAN and MPLS?
- What Is SD-WAN Architecture? Components, Types, & Impacts
Application performance and reliability
Application performance is one of the clearest reasons organizations continue to adopt SD-WAN. Legacy WANs depend on fixed routes that often force traffic through data centers. And that design creates latency, plus makes application behavior unpredictable.
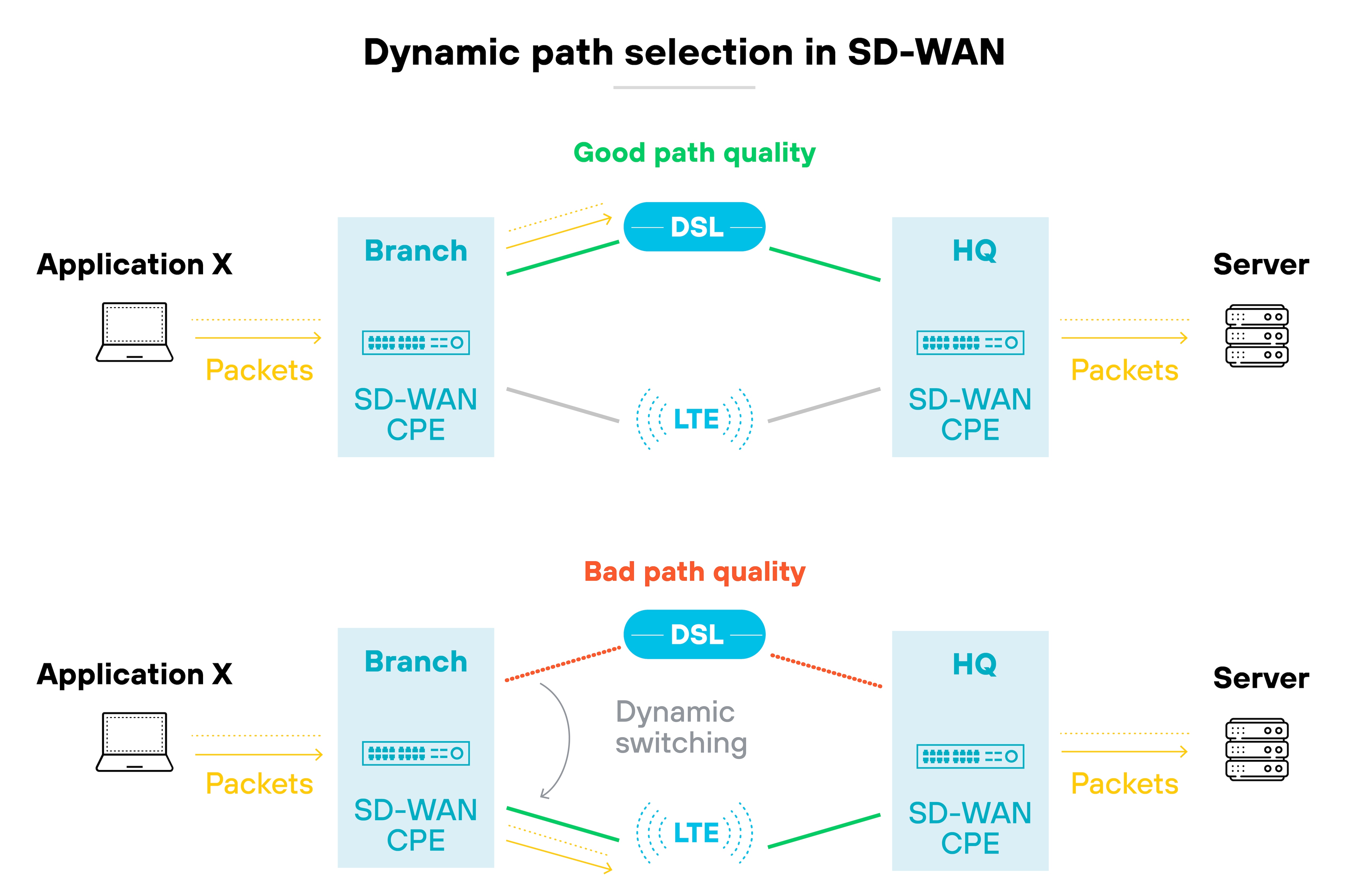
SD-WAN improves performance by using dynamic path selection.
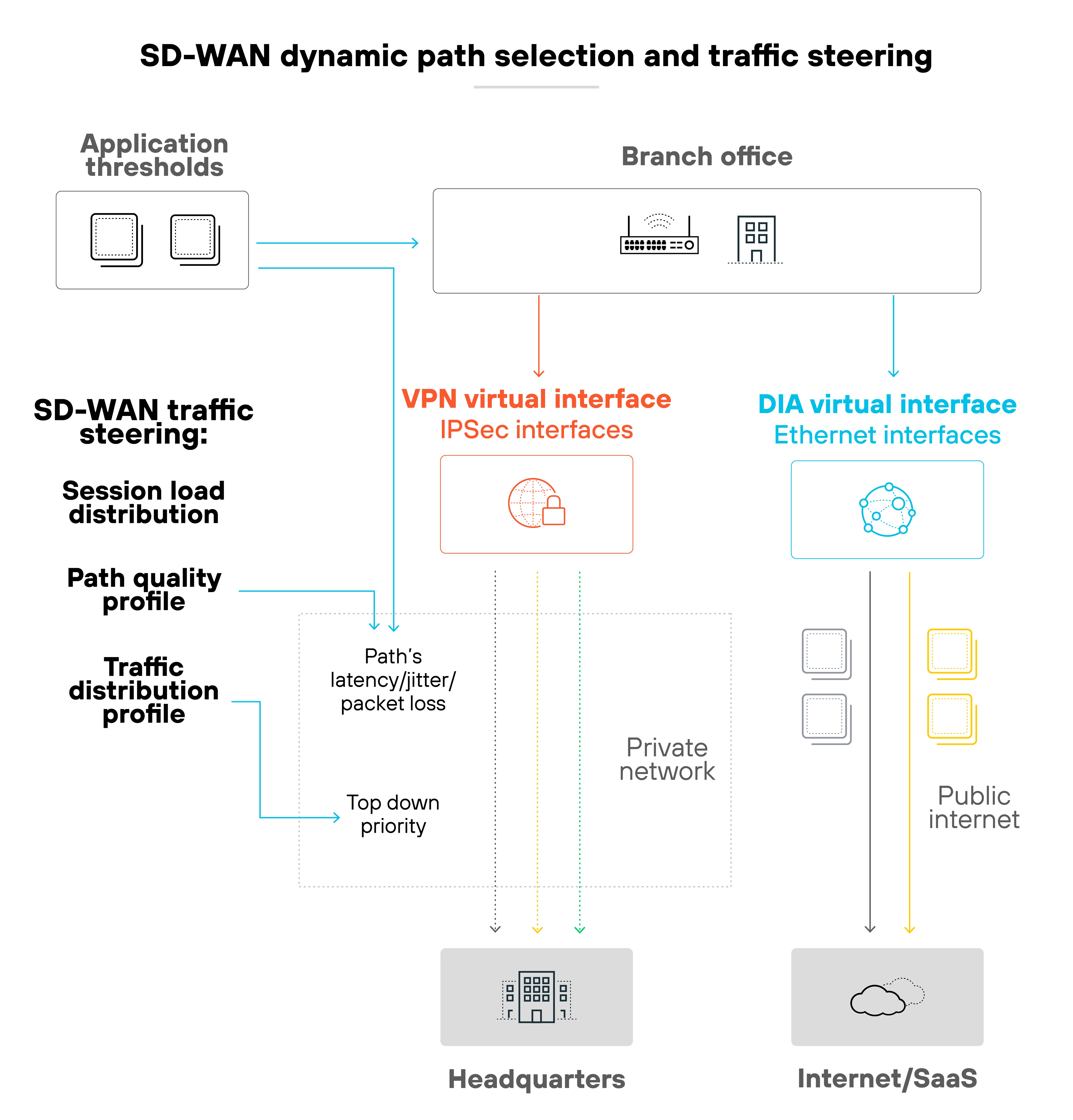
The system monitors available transport links in real time. So traffic can be shifted automatically to the link that best meets the application's needs.
Reliability is another outcome.
Active/active failover keeps sessions alive even when one circuit fails. This approach reduces brownouts and makes outages far less disruptive. In other words, workloads don't collapse because a single link degrades.
Service-level agreements can also be enforced.
SD-WAN continuously measures packet loss, latency, and jitter against defined thresholds. If a link no longer meets the SLA, traffic is rerouted to a healthier path.
Today, this is critical because SaaS, video, and AI-driven workloads dominate enterprise traffic. It's not just about avoiding dropped calls. It's about keeping business applications like Slack, Zoom, Salesforce, and inference-heavy AI models stable across global sites.
The outcome is simple. Less jitter. Fewer brownouts. Reliable performance for latency-sensitive applications. SD-WAN provides the transport intelligence to maintain these standards in ways that legacy WAN architectures cannot.
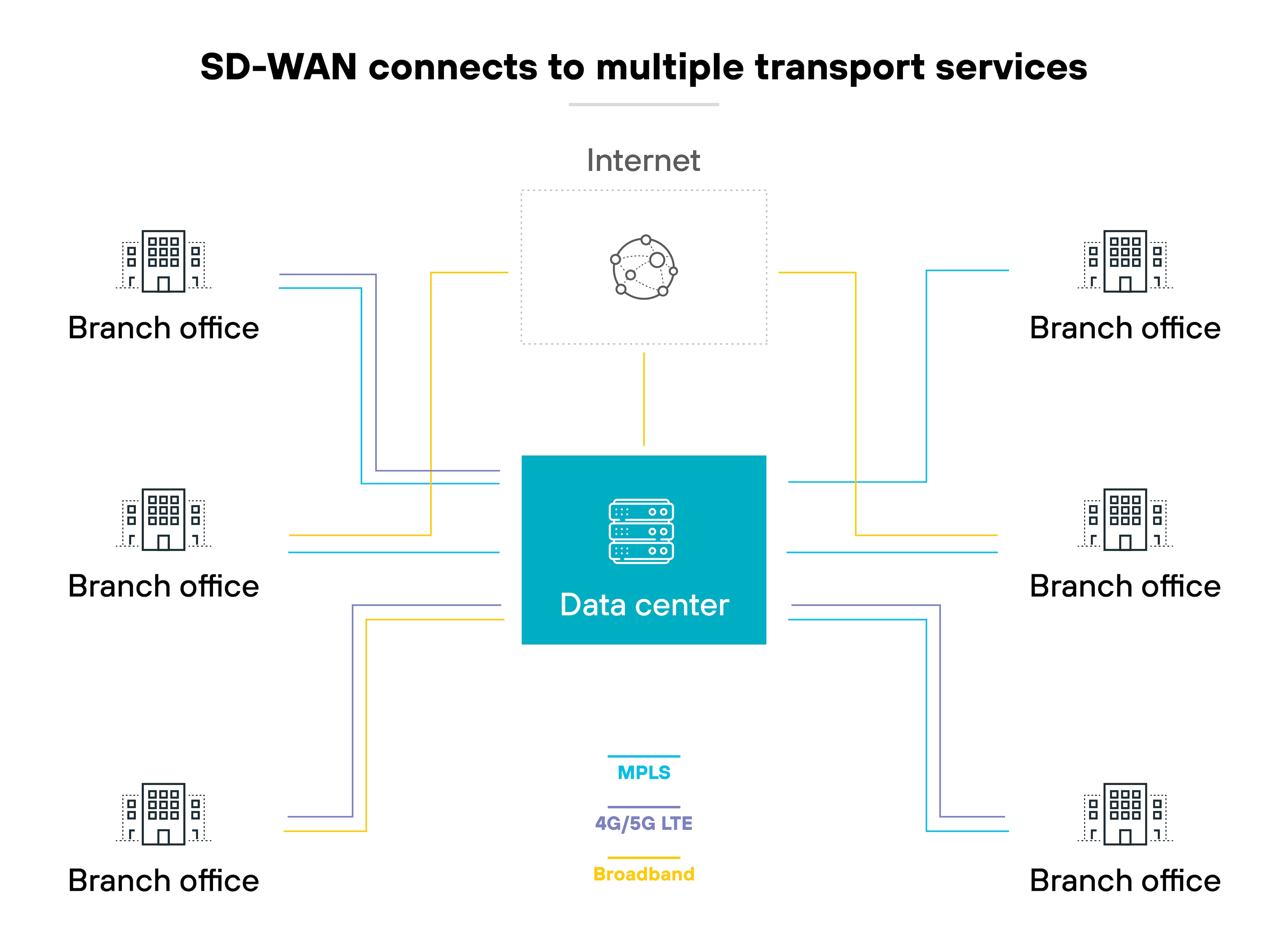
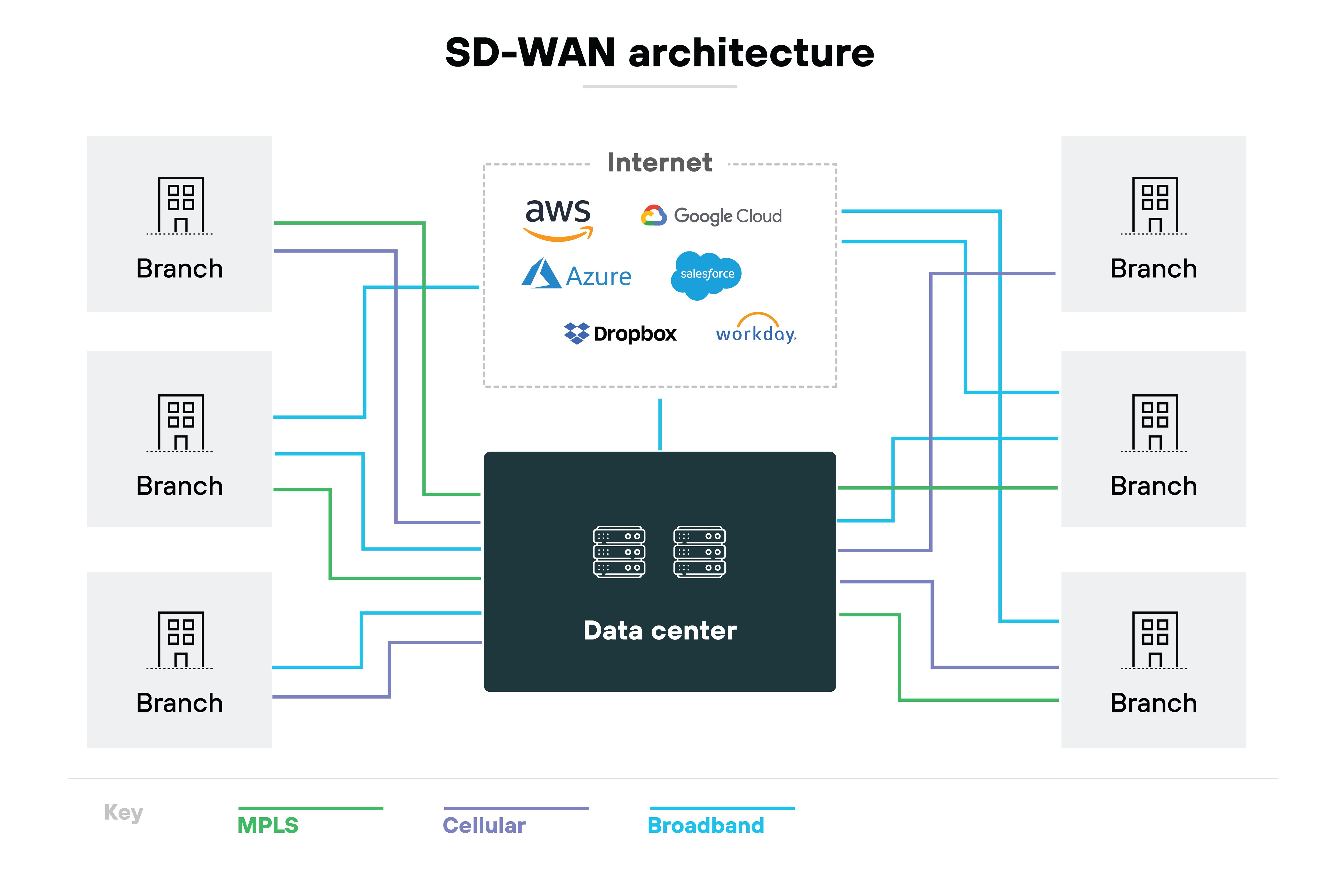
Reduced connectivity and operational costs
Cost remains one of the strongest reasons organizations adopt SD-WAN. Traditional WAN models often rely on MPLS circuits. Those circuits are reliable but expensive and slow to provision.
SD-WAN introduces flexibility.
It can combine broadband, LTE, or DIA links with existing MPLS. Which means: organizations can choose the most cost-effective option at each site. The result is lower recurring connectivity spend and less dependence on long-term MPLS commitments.
Operational savings add to this picture.
With centralized management and automation, IT teams make fewer site visits. Truck rolls become rare. Configuration changes happen once at the controller and propagate everywhere. In other words, the network requires less day-to-day labor.
Capex and opex are both affected.
Fewer dedicated appliances lower capital expense. Reduced management time and the use of more affordable circuits lower operating expense. That combination makes it easier to predict ongoing costs. And to calculate a faster return on investment.
It's worth noting, though, that many organizations aren't abandoning MPLS entirely. Instead, they run hybrid underlays that balance MPLS, broadband, LTE, and sometimes 5G. The benefit here isn't just cutting costs. It's being able to scale bandwidth up or down more fluidly while keeping spend under control.
In practice, this adds up to: Reduced reliance on costly private circuits. Lower administrative overhead. More predictable operating budgets. And faster site ROI.
CALCULATE POTENTIAL SAVINGS WITH SD-WAN
Estimate your organization's ROI in minutes.
Try the ROI calculatorAgile branch and site deployment
Legacy WAN provisioning has always been slow. Adding a new branch often meant waiting months for MPLS circuits, hardware, and manual configuration.
SD-WAN changes that timeline. With zero-touch provisioning and virtualized CPE overlays, a branch can be turned up in days instead of months. So new sites no longer stall because the network isn't ready.
The impact goes beyond speed. As organizations expand globally, pursue mergers and acquisitions, or stand up hybrid workforce hubs, agility becomes critical.
Traditional WANs create delays during restructuring. SD-WAN reduces that friction by centralizing deployment, enforcing templates, and scaling configurations without heavy rework.
Why does this matter?
Because business growth is unpredictable. One quarter may require opening multiple branch sites across regions. Another may mean integrating a newly acquired company. SD-WAN's centralized model keeps provisioning consistent no matter the scenario.
There's also a reliability angle.
Automated deployment reduces human error, which lowers the chance of outages during setup. And by extending the same policies everywhere, IT teams spend less time reconfiguring devices site by site.
Here's what organizations get. Faster branch launches. Lower operational overhead. And smoother transitions when business priorities shift.
Consistent security posture
SD-WAN isn't a security platform. Its role is networking. But its architecture introduces controls that strengthen how security policies are applied across a distributed WAN.
Encrypted tunnels are at the core.
Every site can connect over public or private links with traffic protected end to end. And that means sensitive data isn't left exposed when branches use broadband or LTE instead of MPLS.
Segmentation is another building block.
With SD-WAN overlays, IT teams can isolate traffic for different users, applications, or devices. For instance, a guest Wi-Fi network can be kept separate from internal business systems. And that reduces the chance that a compromised endpoint spreads risk laterally.
Centralized enforcement ties it together.
Policies are defined once and pushed everywhere. No more device-by-device configuration drift at remote branches. The outcome is a uniform security posture whether traffic rides over fiber, 5G, or broadband.
Why is this important now?
Because the attack surface has expanded. Remote workers, IoT endpoints, and AI-driven applications all demand consistent protection. A single weak site can open a gap. SD-WAN helps by applying encryption and segmentation everywhere without exceptions.
Plus, this aligns with Zero Trust principles.
Access is least-privileged, and policies follow users and applications across the network. Basically, every branch, hub, and remote site operates under the same rules.
The result is network-wide uniformity. Organizations reduce gaps that often appear in distributed environments. And IT can ensure that growth—whether new branches or new workloads—doesn't dilute the overall security posture.
- What Is SD-WAN Security? | SD-WAN Security Considerations
- Top 7 SD-WAN Challenges: SD-WAN Risks, Issues, & Solutions
Centralized visibility and control
Legacy WANs were managed device by device. Each router or appliance had to be configured separately, often through a command line. And that made policies inconsistent and troubleshooting slow.
SD-WAN replaces that approach with a single management plane.
Policies are defined once and pushed everywhere. Analytics and telemetry are built in. The effect: IT teams can see how applications perform across the entire network without logging into each site individually.
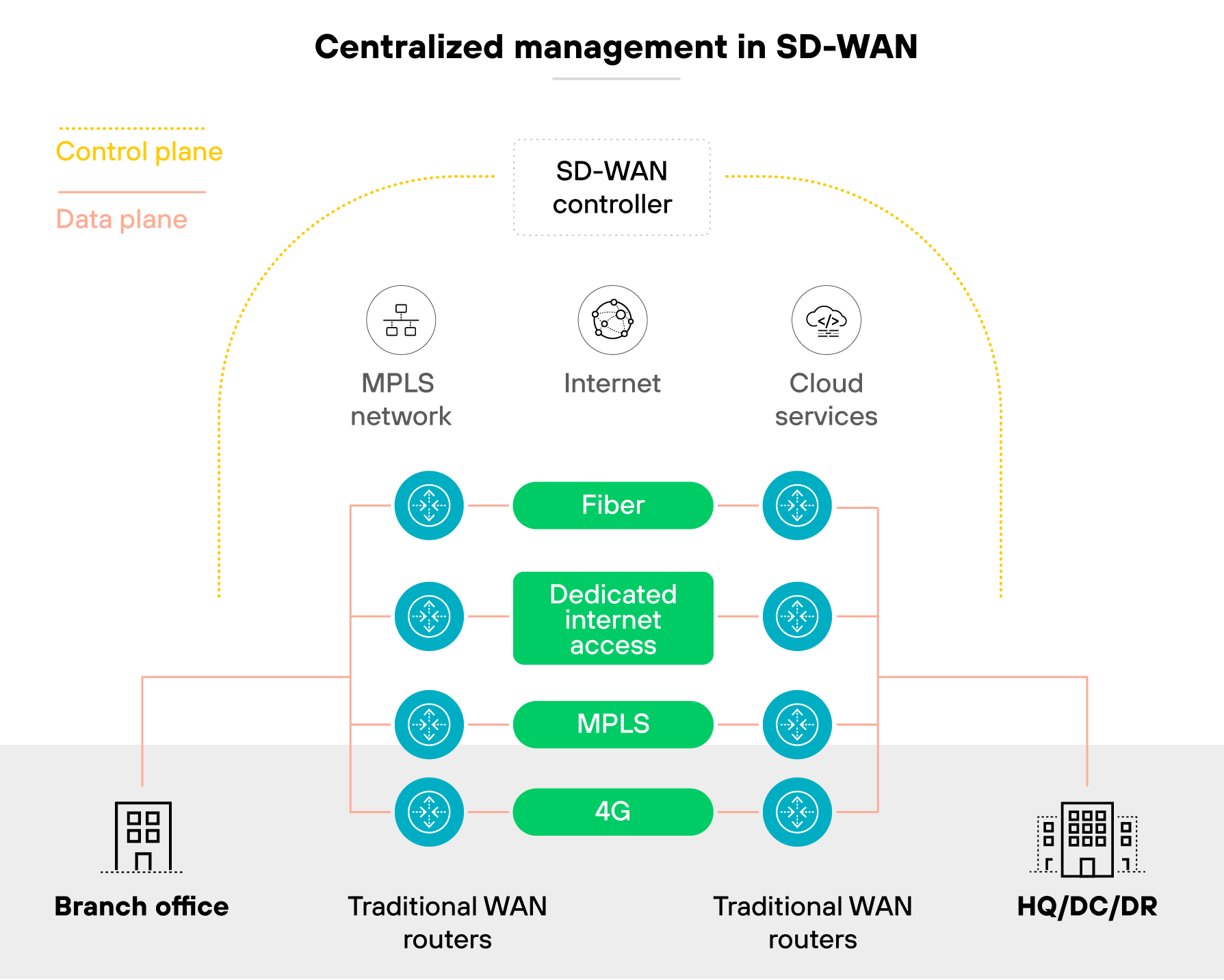
This shift reduces complexity.
Instead of juggling different consoles and vendor tools, administrators work from one interface. For example, a change in application policy can be deployed to hundreds of branches at once. And the outcome is fewer errors and faster time to resolution.
Plus, today, visibility demands have grown majorly.
Organizations now support multi-cloud environments, remote users, and thousands of IoT or AI-driven connections. Centralization helps keep this from overwhelming IT. It filters operational noise and surfaces meaningful alerts instead of raw data.
So, why is this significant?
Because faster troubleshooting means shorter outages. A standardized policy model also improves compliance. So that organizations can demonstrate that governance is consistent everywhere, no matter the transport or geography.
Ultimately, IT teams can manage networks at scale without being buried in manual tasks. They can troubleshoot issues faster, keep outages contained, and prove that policies are applied consistently across every site and connection type.
Optimized access to cloud and SaaS applications
As mentioned, traditional WANs often backhauled traffic through data centers before reaching cloud services. And that extra hop degraded SaaS performance, added latency, and frustrated end users.
SD-WAN eliminates that bottleneck.
It allows for direct-to-cloud connectivity, steering traffic over the best available path instead of forcing it through a fixed hub. And SaaS traffic reaches cloud services without unnecessary detours that add latency or degrade performance.
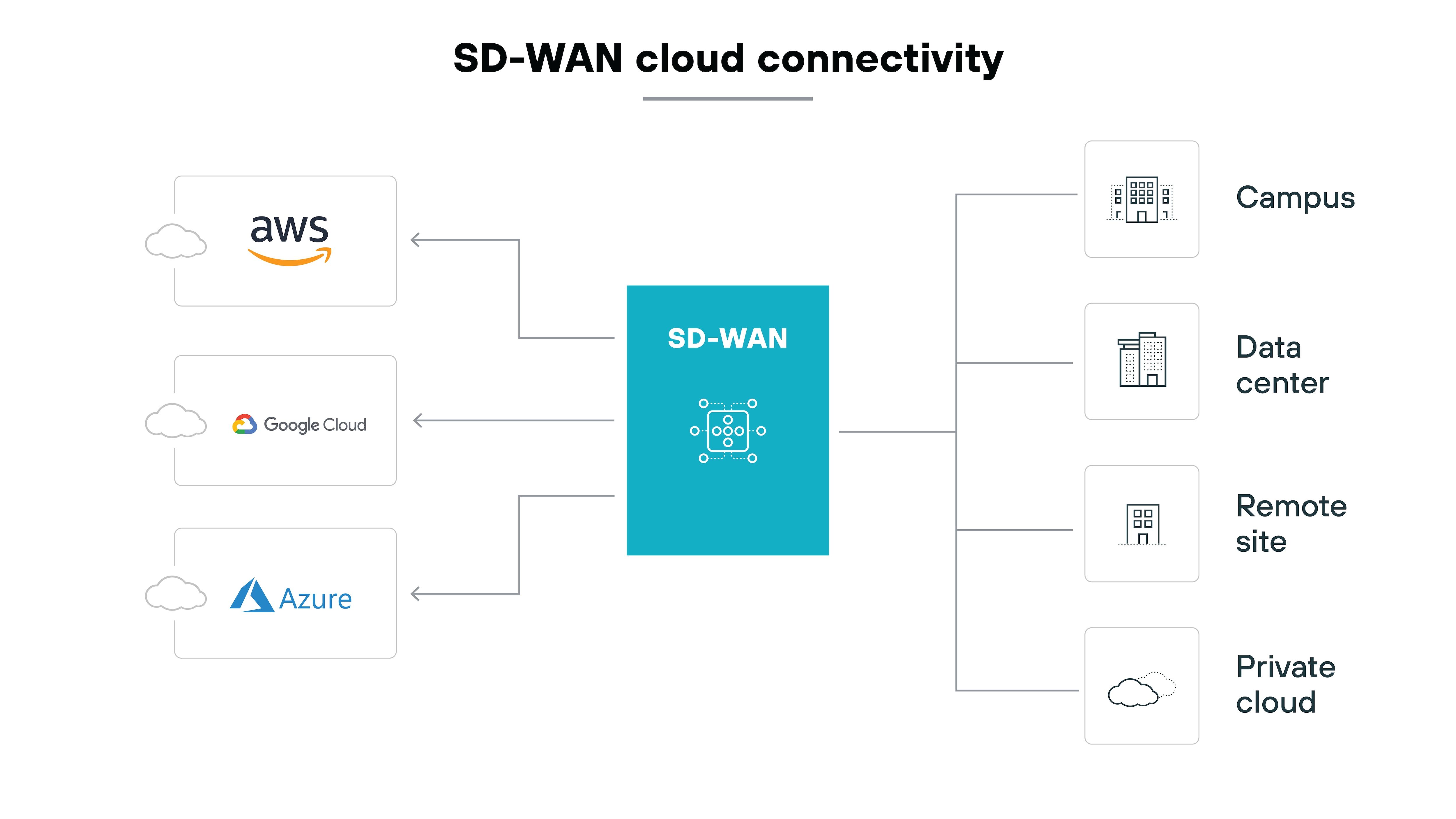
The difference is especially clear for distributed and hybrid workforces.
Users no longer depend on a single centralized entry point. Instead, they can connect directly from branch offices, remote sites, or even temporary hubs to whichever cloud services they need.
Plus, these days cloud-first isn't aspirational — it's the default.
Enterprises run workloads across multiple providers, while employees rely on SaaS tools daily. SD-WAN supports this shift by enabling multi-cloud access and managing application paths in real time. And users get a stable experience regardless of geography, while IT avoids the overhead of maintaining custom routes for each provider.
It's not just about faster connections. It's about reliable user experience.
SD-WAN reduces packet loss and jitter, which translates into fewer video call interruptions and smoother application sessions. Organizations can adopt cloud services at scale without worrying that performance will drag.
Ultimately, SD-WAN ensures that cloud and SaaS adoption scales without compromising performance. Organizations gain predictable application behavior, users stay productive, and IT teams maintain control over how traffic flows across providers and regions.