What Is Network as a Service (NaaS)?
Network as a service (NaaS) is an enterprise infrastructure service that is offered as a cloud-delivered solution. This flexible means of consuming a network enables organizations to build better business agility, accelerate innovations, and improve performance with a cost-effective and scalable subscription-based model.
How Does Network as a Service (NaaS) Work?
NaaS eliminates organizations from the burden of procuring, deploying, and managing network infrastructure by offering cloud-based network services. With NaaS, businesses now can choose to purchase a subscription that provides access to the provider's network resources.
Customers may have a variety of options available to them:
- A managed service allows customers to pay for hardware subscriptions while the provider manages and maintains it.
- Rented hardware, owned by the provider and rented by the customer, is another option. As a result, customers are responsible for installing and operating the equipment themselves.
- Outsource complete operations including deployment, management, and day-to-day ops
With NaaS, organizations can replace legacy network configurations like virtual private networks (VPNs), multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) connections, and firewalls as well as On-Prem Controller networking hardware like load balancers and firewall appliances. NaaS has had a major impact on enterprise networking architecture due to its newer model of routing traffic and applying security policies.
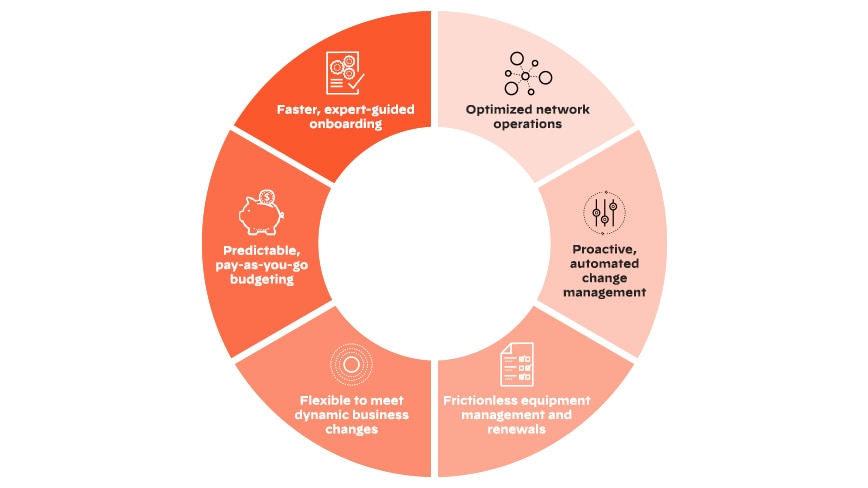
How NaaS Developed
A growing need for cost-effective and flexible network infrastructure led to the emergence of network-as-a-service (NaaS). In the past, enterprises had to invest heavily in physical networking infrastructure and hire specialized IT personnel to handle it. For enterprises with limited resources, this approach has proven expensive and time-consuming.
Cloud computing, however, has provided an opportunity to virtualize infrastructure and offer it “as a service.” Through a virtualized infrastructure, enterprises can access and use network resources and services on a pay-per-use basis.
The concept of NaaS is similar to other "as-a-service" models, such as software-as-a-service and platform-as-a-service (PaaS). Organizations can get the services they need without worrying about the infrastructure or maintenance.
Since its inception, NaaS has grown to include various networking services, including firewalls, VPNs, load balancers, and other networking tools. Using a centralized platform, customers can manage and monitor their network services, allowing them greater control and visibility.
Advantages of Network as a Service (NaaS)
NaaS can be an appealing option for companies that need to scale their infrastructure quickly, have limited IT resources, or require secure networking capabilities. Furthermore, NaaS allows customers to focus on their core competencies by reducing the complexity of managing and maintaining IT infrastructure.
In particular, NaaS provides the following advantages:
Scalability
NaaS allows organizations to scale their infrastructure to meet changing requirements. For companies experiencing seasonal fluctuations or sudden growth, this is especially important.
Cost-Effectiveness
With NaaS, organizations avoid the high upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining the physical infrastructure. The pay-per-use or subscription model allows them to scale their IT infrastructure more quickly and cost-effectively.
Improved Reliability
NaaS providers often have redundant network infrastructure in place, which can help ensure network reliability and reduce the risk of outages. Service providers might have multiple data centers located in different geographic regions, with automatic failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted customer service.
Increased Agility
NaaS allows organizations to provision and deprovision network resources and services quickly to meet changing business needs. This agility is particularly important for businesses that need to rapidly scale up or down their IT infrastructure.
Challenges of Naas
While NaaS offers several benefits, there are also some challenges that businesses need to be aware of:
Dependence on NaaS Provider
With NaaS, enterprises rely on third-party providers for their infrastructure and services, which may make them more vulnerable to outages or other issues caused by the provider's infrastructure. In addition, enterprises may have difficulty switching NaaS providers once they have adopted a particular provider due to the complexity of migrating infrastructure.
Security Concerns
NaaS providers are responsible for securing and protecting the data that is transmitted over their infrastructure. Customers need to ensure that their provider has adequate security measures in place to protect their data from unauthorized access or theft.
Limited Customization
NaaS providers usually offer a standard set of network services, which may not meet the specific needs of some enterprise customers. This could limit the customer's ability to customize its infrastructure to meet its unique requirements.
How NaaS Relates to SASE
NaaS and secure access service edge (SASE) are related concepts often used in enterprise network architecture.
SASE combines software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) with network security functions, all offered via a single cloud service provider. Its integrated functions, such as secure web gateways (SWG),Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), and firewall as a service (FWaaS), offer a comprehensive approach to network security.

Through SASE, enterprises can access and manage their network infrastructure more easily and efficiently due to a comprehensive set of security and networking services delivered from the cloud.
For those enterprises thinking about NaaS, a SASE architecture may provide a better alternative, enabling them to control their networking and security stack and driving down overall risk.
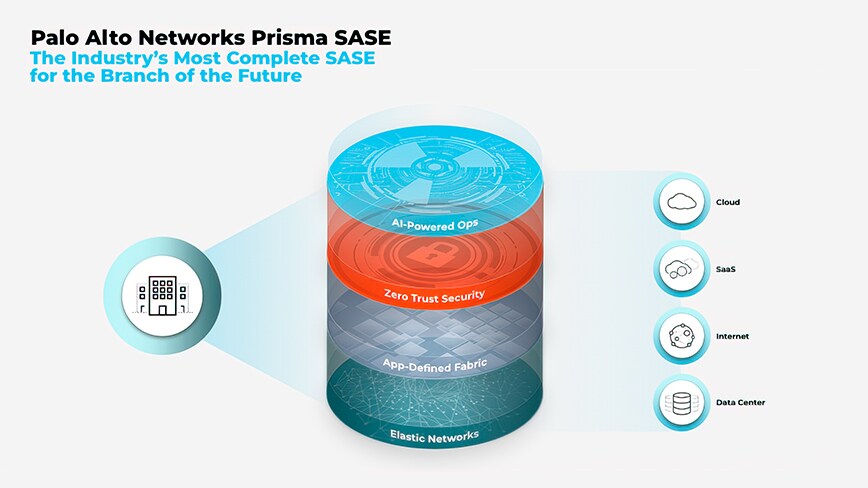
Prisma SASE with next-generation SD-WAN delivers the following differentiated capabilities:
- Elastic networks flexibly support multiple WAN connections, like 5G, MPLS, broadband, and satellite, in an active/active model. Unlike every other SD-WAN solution, Prisma SD-WAN ensures that a single device failure does not result in the loss of any WAN capacity. Prisma SD-WAN’s centralized controller-based architecture seamlessly builds, manages, and updates the network with no routing complexity.
- App-defined fabric provides direct-to-app access that ensures an exceptional user experience for all applications, including SaaS, cloud, and private applications. Unlike Gen 1 SD-WAN solutions that only provide traffic engineering for data center applications, Prisma SD-WAN delivers SLAs and the best user experience for all applications.
- Zero Trust security with zero compromises for your branch office means that all apps, people, and things have to be secured. Prisma SD-WAN is natively integrated with Prisma Access for a unified SASE solution. Prisma Access provides ZTNA 2.0 as a highly distributed service that secures your branch office. Deep integration between Prisma SD-WAN and Prisma Access provides the industry’s first integrated IoT security that identifies all IoT devices, views security policy recommendations, and enforces these policies. Prisma SASE is the only solution that can secure all your applications and things without additional products needing to be deployed.
- AI-powered operations leverage native Autonomous Digital Experience Management (ADEM) to provide deep observability and AIOps to help organizations automate complex and manual Day 2 IT operations. Prisma SASE is the only solution that captures and analyzes real traffic and synthetics from the user to the application to proactively analyze issues, automate troubleshooting, and prevent outages.
Is Network as a Service (NaaS) Right for My Enterprise?
Business objectives, current infrastructure, and IT budget all play a role in determining whether NaaS is suitable for your enterprise. If you are considering NaaS, here are some key considerations:
- Business goals: Identify your goals and how NaaS can help you achieve them. NaaS provides greater flexibility and scalability, enabling you to respond to changing business requirements quickly, and can reduce upfront costs associated with purchasing and maintaining the physical infrastructure.
- Network infrastructure: Determine if your network infrastructure can meet your current and future business requirements. A NaaS solution may be a good option if you have outdated or inadequate infrastructure.
- IT staff: Consider your IT expertise and whether you have the resources to manage and maintain your network infrastructure. You can reduce the burden on your internal IT department by using NaaS providers for managed services and support.
- Security: Assess whether NaaS providers can meet your security requirements. Security features such as intrusion detection and prevention, data encryption, and identity and access management are typically available through NaaS providers. Still, you should make sure that they meet your specific needs.
- Costs: Analyze the cost of NaaS compared to purchasing and maintaining the physical network infrastructure. Pay-per-use or subscription-based pricing models can reduce upfront costs but also come with ongoing operational costs.
The advantages of NaaS for enterprises include greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Considering the potential challenges and evaluating your specific requirements before deciding whether NaaS is right for your company is essential.