-
- What is the difference between personal and business VPNs?
- How does a VPN work?
- What does a VPN hide?
- What are VPNs used for?
- How secure are VPNs?
- Why do you need a VPN?
- What are the primary features of a VPN?
- What are the benefits of a VPN?
- What are the different types of VPNs?
- What are the different types of VPN protocols?
- What are the alternatives to a VPN for secure remote access?
- How to set up a VPN step-by-step
- How to choose the right VPN for your needs
- Comparing VPNs with other security technologies
- What is the history of VPNs?
- VPN FAQs
What Is a VPN? A Complete Guide to Virtual Private Networks
13 min. read
Table of Contents
A virtual private network, or VPN, is an encrypted connection that secures data transmission between devices over the Internet.
The encrypted connection protects sensitive information from potential threats and unauthorized access.
In corporate environments, VPNs facilitate secure connectivity to corporate resources, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. On personal devices, VPNs help protect data by encrypting internet traffic and masking the user's IP address.
What is the difference between personal and business VPNs?
Before we get into the nuts-and-bolts of virtual private networks, it’s worth taking a moment to make a distinction between personal and business VPNs (AKA enterprise VPNs).
Business VPNs vs. personal VPNs
| Parameter | Business VPN | Personal VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Primary use | Secure access to corporate networks and resources | Privacy, security, and unrestricted internet access for individuals |
| Management | Centralized, IT-managed | User-managed |
| Access control | Role-based access control | No role-based access |
| Security features | Advanced security (malware protection, DNS filtering, encryption) | Basic encryption, IP masking, protection on public Wi-Fi |
| Infrastructure | Dedicated servers and infrastructure | Shared servers |
| Scalability | Scalable for multiple users and teams | Limited scalability |
| Compliance | Complies with standards like GDPR and HIPAA | Not designed for regulatory compliance |
| Performance optimization | Optimized for secure, high-performance corporate environments | Not optimized for enterprise performance |
Personal VPNs are designed for individuals who want privacy, security, and unrestricted internet access. They encrypt internet traffic, mask IP addresses, and protect internet users on public Wi-Fi.
However: Since they’re designed for individual users, they obviously lack centralized control, role-based access, and enterprise-level security features.
Consumer-grade VPNs are typically managed by the user and rely on shared servers.
On the other hand:
Business VPNs provide secure access to corporate networks and resources. They offer centralized management, role-based access control, and dedicated infrastructure.
Enterprise-grade VPNs support many users organization-wide. And they need to be able to comply with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
They’re scalable, customizable, and equipped with advanced security features like malware protection and DNS filtering.
Unlike personal VPNs, business VPNs prioritize controlled access, security, and performance for corporate environments.
| Further reading: What Is a Business VPN?
How does a VPN work?
So, what does a VPN do?
A VPN encrypts internet traffic and routes it through a remote server, hiding the user’s IP address and securing data from unauthorized access.
But how does a VPN work?
The process differs slightly between business and personal virtual private network products.
Here’s how a business VPN works:
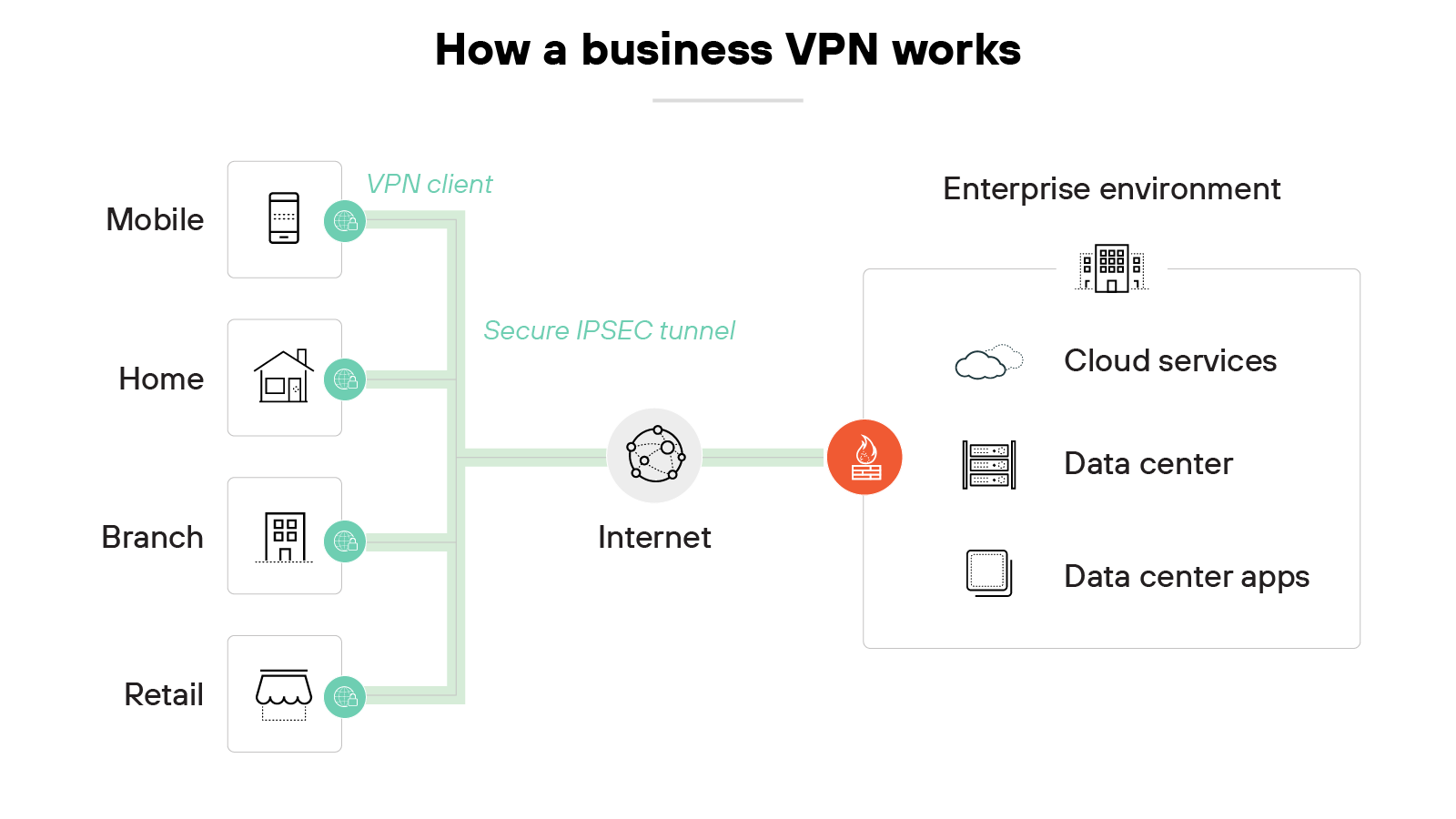
The VPN connects employees to a company’s internal network over an encrypted tunnel. It starts when a user logs in through a VPN client on their device.
That client establishes a secure connection to a VPN gateway managed by the organization.
From there, traffic is routed into the company’s private environment. Which means users can access internal tools, files, or systems as if they were physically on site.
The VPN continuously verifies the user’s identity and enforces access policies set by IT.
Enterprise VPN products are built for controlled, secure access—not general internet privacy.
In contrast:
Here’s how a personal VPN works:
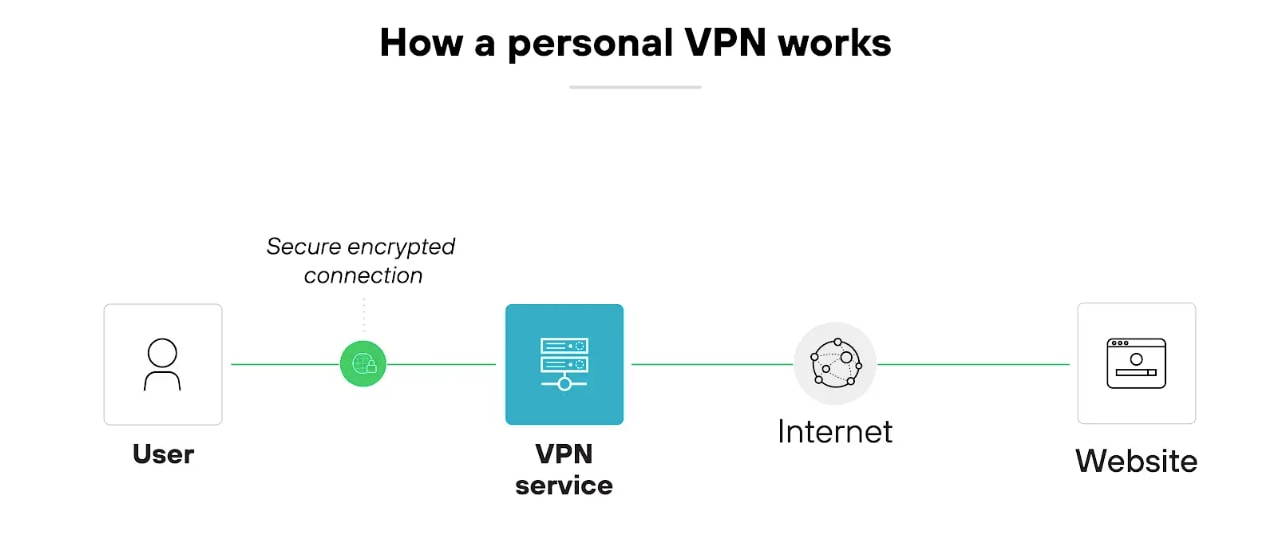
The VPN encrypts the user’s internet traffic and routes it through a remote server operated by the VPN provider.
The user installs an app, chooses a server location, and clicks connect.
Once the tunnel is established, the device’s traffic is sent to the VPN server before reaching any websites or services.
That server assigns a new IP address to the user’s device. Which helps obscure location and identity. The VPN also protects traffic from interception, especially on public internet.
Unlike corporate virtual private networks, personal virtual private networks don’t provide access to private networks. They focus on privacy, anonymity, and open internet access.
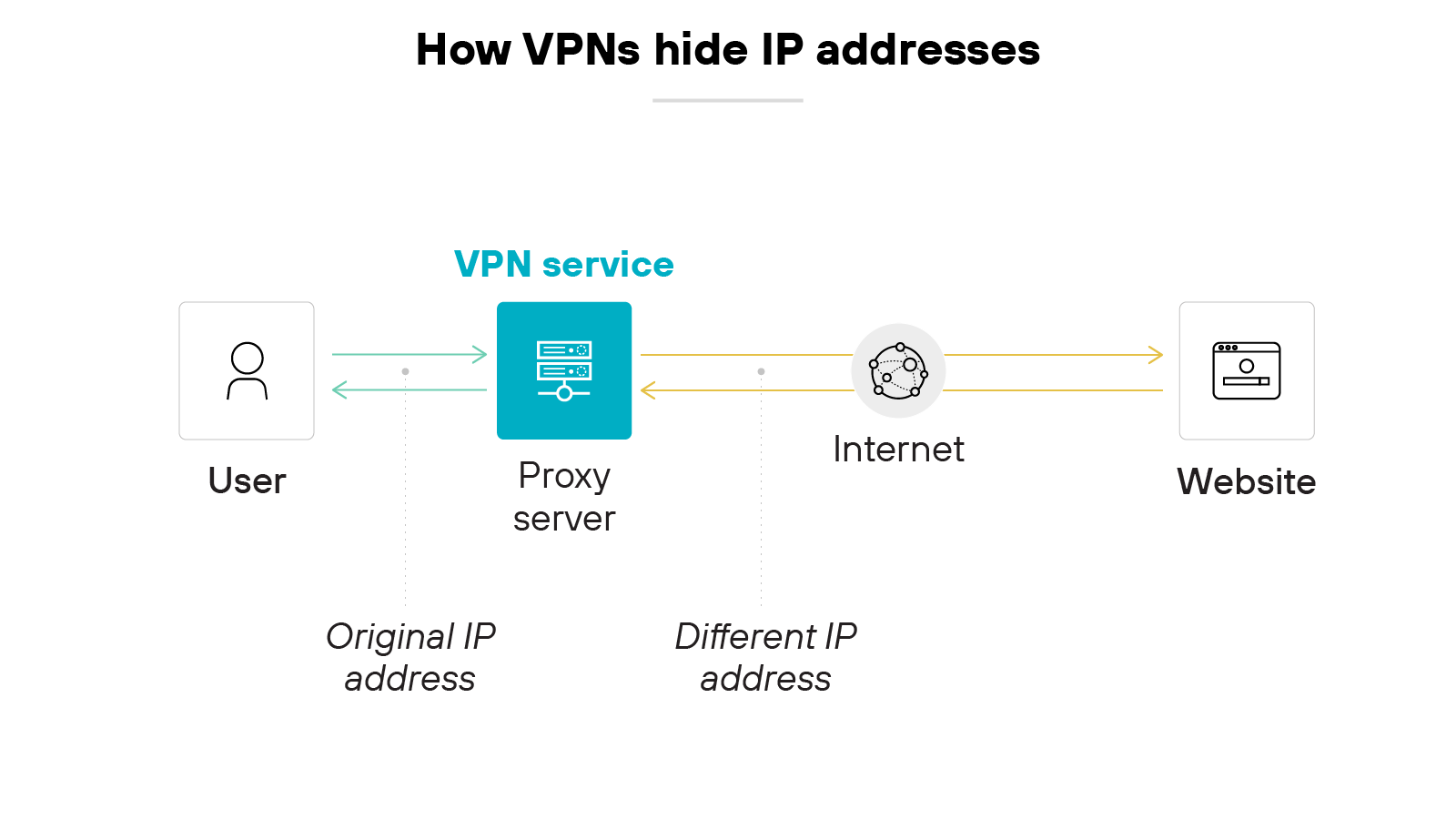
A virtual private network hides a device's original IP address by rerouting its traffic through a different server.
For consumer VPNs, this helps anonymize browsing activity. For business VPNs, this ensures secure access to corporate networks rather than general online anonymity.
As discussed, hiding the IP address makes the device appear as if it’s coming from the VPN's server location—not its actual location. This way, the actual connection source remains concealed. And that prevents adversaries from pinpointing the original device's location.
A virtual private network also hides the data it's sending and receiving using encryption. Even if someone intercepts the data, they can’t decipher its contents easily.
What are VPNs used for?
VPN use cases
| Business VPN | Personal VPN |
|---|---|
|
|
Business VPNs have two primary use cases: (1) secure remote access and (2) secure site-to-site connectivity. In the corporate world, virtual private networks focus on protecting sensitive data, compliance, and secure remote access to critical applications.
Personal VPNs, on the other hand, are often used to enhance online privacy, bypass content restrictions, avoid location-based tracking, and maintain security on public networks.
Let’s break down the use cases for both.
Business VPN use cases
Secure remote access
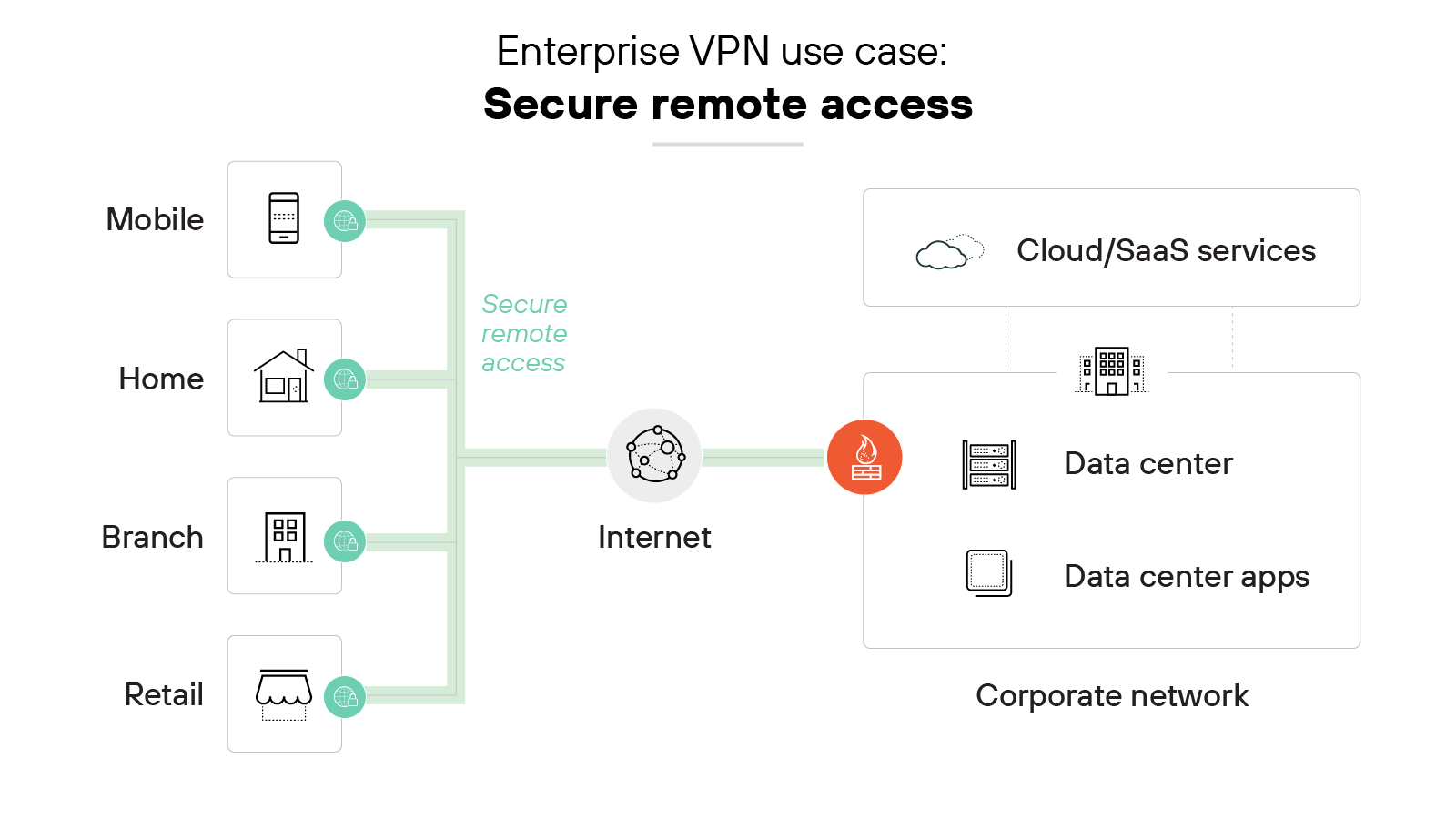
Remote access virtual private networks allow employees to access corporate networks from mobile devices, home offices and other remote locations.
They provide a safe way for remote users to access internal business applications and resources from any location without compromising security.
Secure site-to-site connectivity
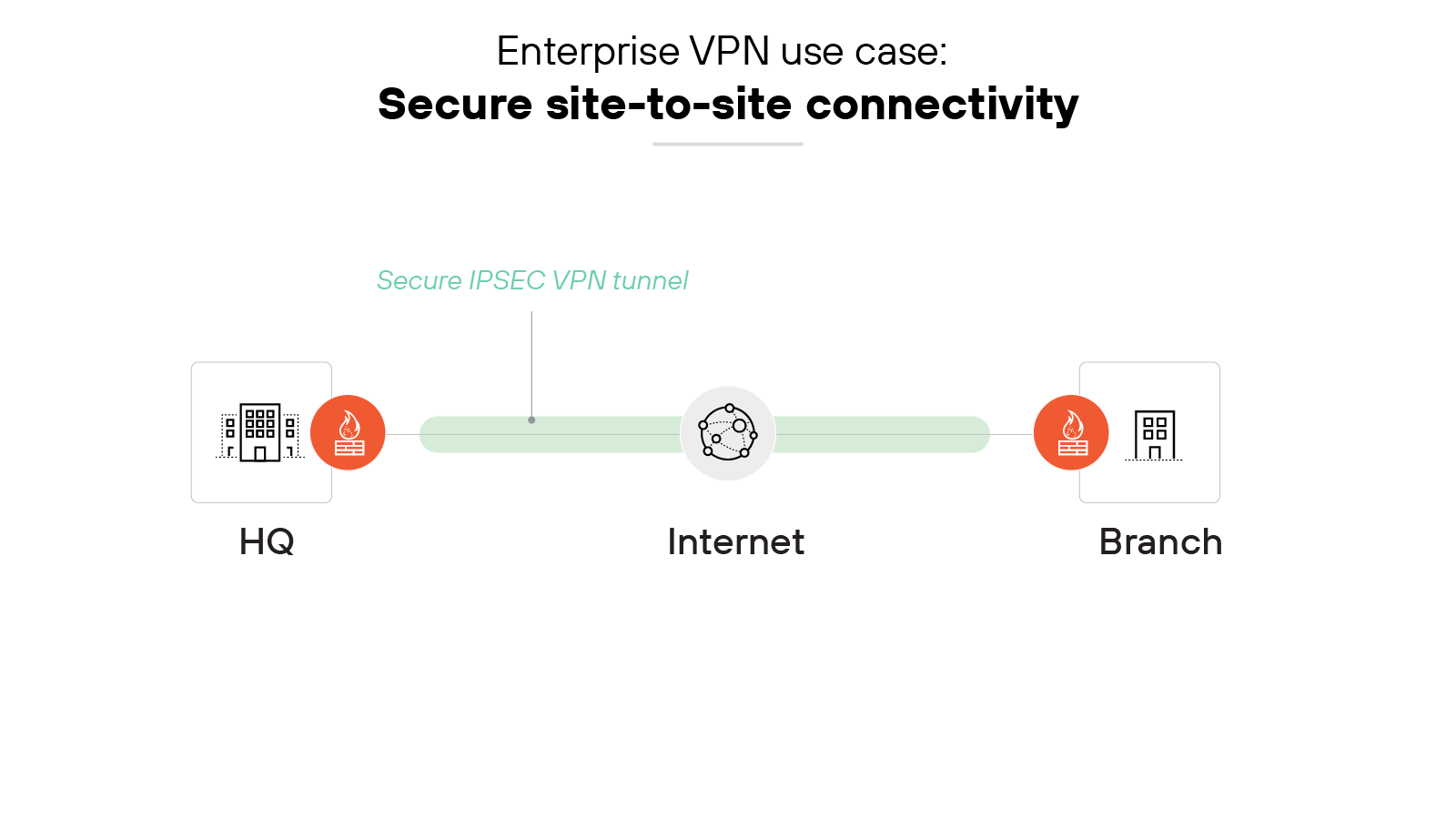
Site-to-site VPNs are used to create secure tunnels between sites rather than a specific user location or device. They also securely connect corporate headquarters, branch offices, data centers, and/or private, public, or hybrid clouds.
A site-to-site virtual private network performs encryption/decryption of traffic in transit so that all inbound/outbound traffic from either site is secure.
Personal VPN use cases
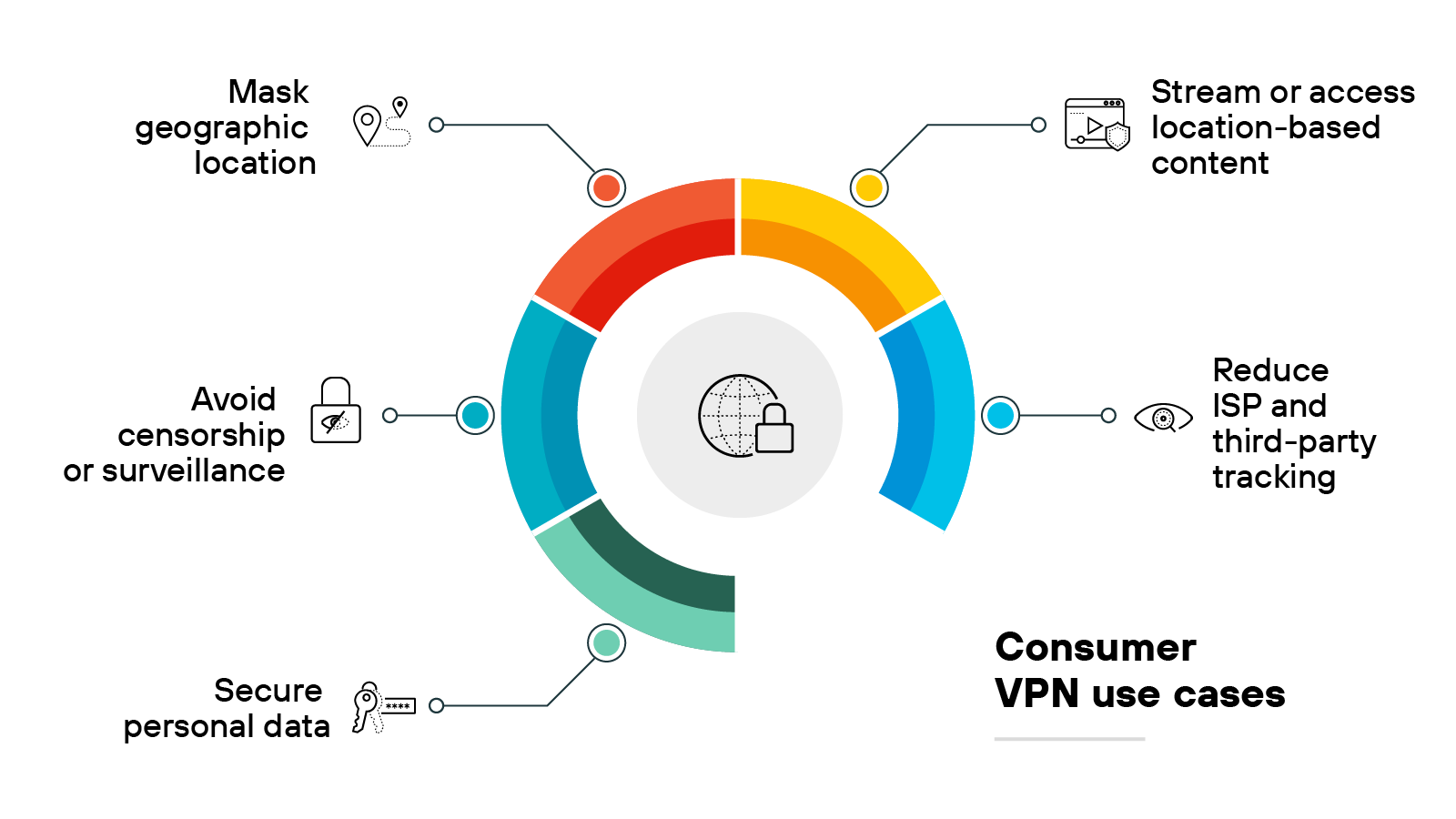
Secure personal data
A personal VPN encrypts personal data before it leaves the device. This helps protect sensitive information on unsecured networks, especially when using public Wi-Fi.
Stream or access location-based content
Some websites and streaming platforms restrict access based on geographic location.
A personal virtual private network allows users to route traffic through servers in other countries, which can make regional content available outside its intended location.
Avoid censorship or surveillance
Internet users in regions with restricted internet access may use a VPN to reach blocked sites.
The VPN masks traffic and origin, which can help bypass local filtering and monitoring systems.
Reduce ISP and third-party tracking
Internet service providers (ISPs) can log browsing activity and associate it with a user’s IP address.
Personal virtual private networks prevent this by routing traffic through external servers, which helps reduce the visibility of online behavior.
Mask geographic location
A VPN assigns a new IP address from the server location it connects to. This makes it appear as if the user is in a different place, which can help increase privacy or avoid location-based restrictions.
How secure are VPNs?
VPNs are generally safe for transmitting data over the internet but aren’t 100% secure. A VPN doesn’t constitute a complete network security strategy.
More specifically, virtual private networks don’t provide complete protection on their own.
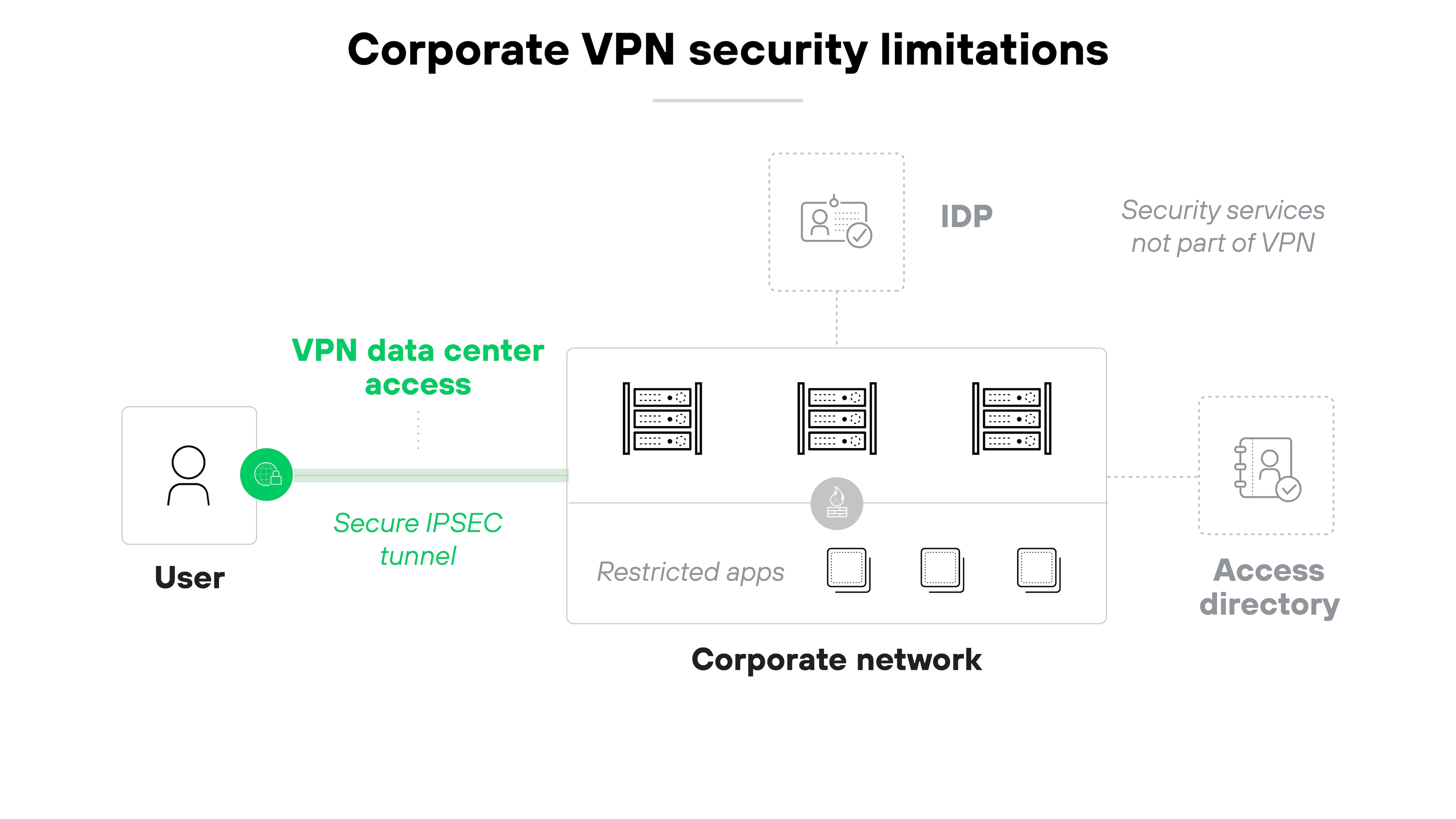
Here’s why:
As more users work outside the office and more apps move to the cloud, threats become harder to control. Which means traditional VPNs often need help from other security tools.
To address this, organizations should look for network security platforms that combine virtual private network capabilities with broader network protections. This makes it way easier to protect remote users and devices—especially when they operate beyond the traditional perimeter.
Consumer-grade VPNs are equally insufficient for personal security purposes.
Personal VPNs do help protect internet traffic by encrypting data and masking the user’s IP address. This at least prevents eavesdropping on public networks and makes browsing activity harder to trace.
However: A personal VPN doesn’t block malware, phishing attempts, or malicious downloads.
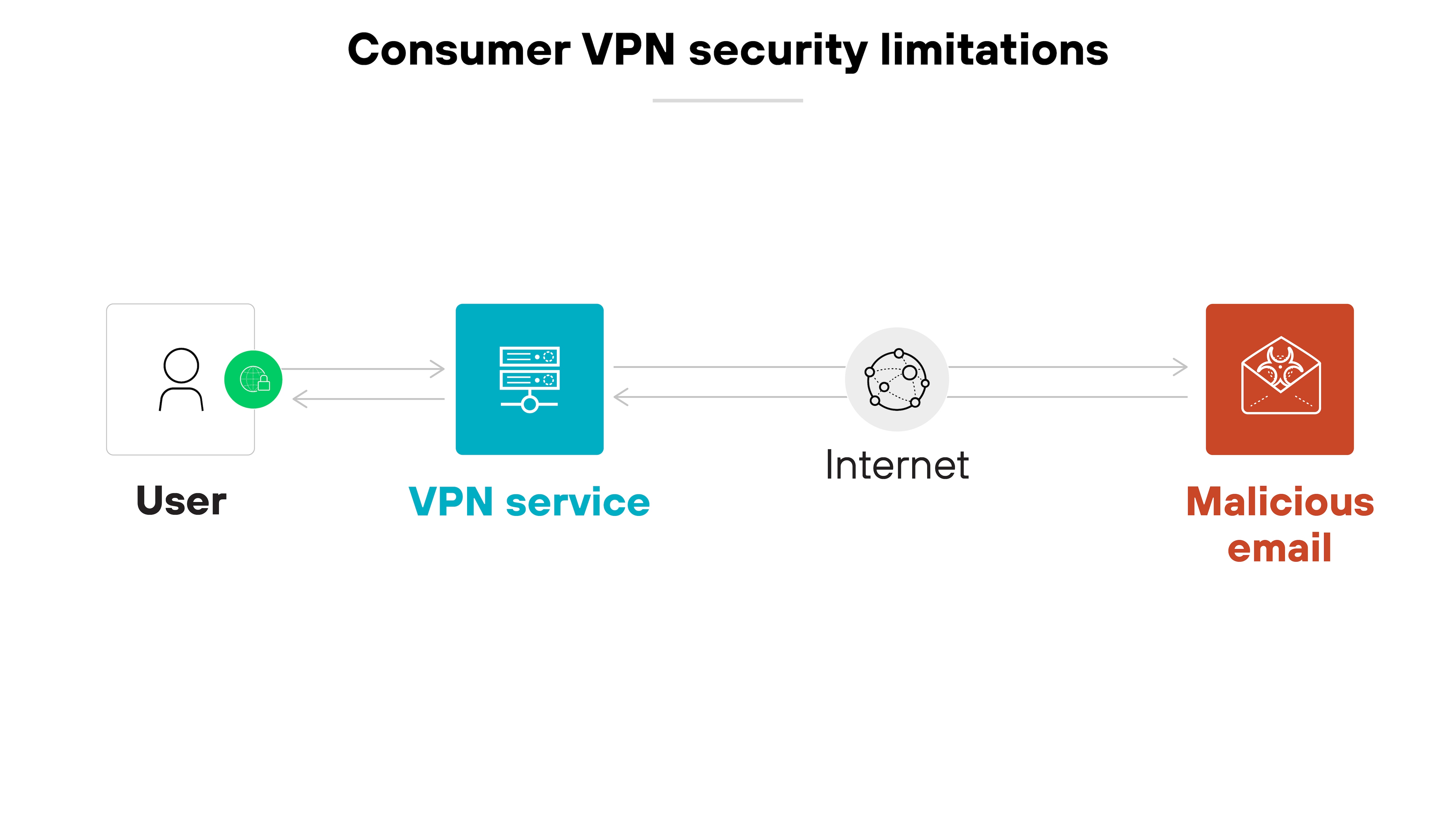
It also doesn’t control what happens after a device is compromised.
In other words: If a threat reaches the device, a VPN can’t stop it from stealing or damaging data. So for stronger protection, users should pair a virtual private network with antivirus software.
From a business perspective, you need a VPN to provide secure remote access to company systems and data. A business virtual private network extends the corporate network to employees working from home or traveling.
It also protects sensitive resources while maintaining work continuity for teams outside the office.
From a consumer perspective, you need a VPN to reduce exposure to unnecessary data collection. It does this by encrypting traffic and masking the device’s IP address.
Without a virtual private network, websites, apps, ISPs, and even public internet operators can see more than most people realize—like browsing habits, device identifiers, and location.
A VPN limits that visibility. Which helps keep your activity more private, especially in environments where tracking is common or unavoidable.
What are the primary features of a VPN?
VPN features
| Business VPN | Personal VPN |
|---|---|
|
|
A VPN includes a range of features that help protect data and manage access.
Some of these features are common across most virtual private networks. Others depend on whether the product is used for business or personal purposes.
Business VPNs tend to focus on centralized control, secure authentication, and support for multiple users.
Personal VPNs focus more on privacy, encryption, and usability on individual devices.
Let’s walk through the key features of each:
Business VPN features
Authentication and access control
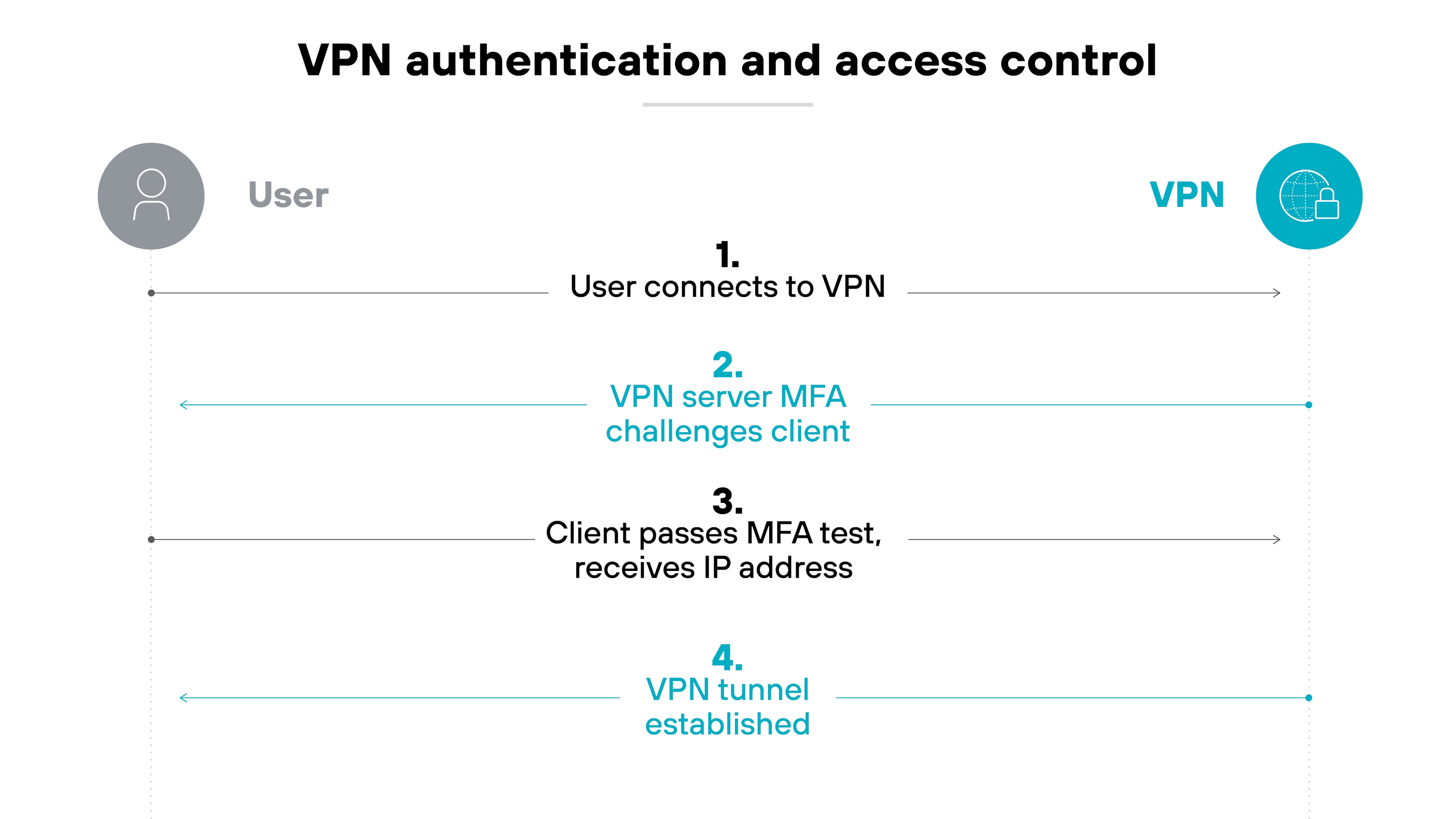
Authentication helps control who can access the VPN.
Before a user connects, the VPN checks their identity. This step verifies that the right person is trying to access the network.
Many virtual private networks support methods like Kerberos, RADIUS, LDAP, or SAML 2.0. These allow organizations to choose what fits their environment.
Once the user is verified, the VPN links their identity to an IP address. That mapping helps track activity and apply access controls.
Some providers also support multifactor authentication. Which adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a password.
In some cases, cookie-based authentication can keep users signed in between sessions. This can reduce friction for repeated access.
Host/endpoint information
Host information profiles check details about the device before granting access. They can see the device type, software versions, encryption settings, or whether backups are enabled.
Like this:
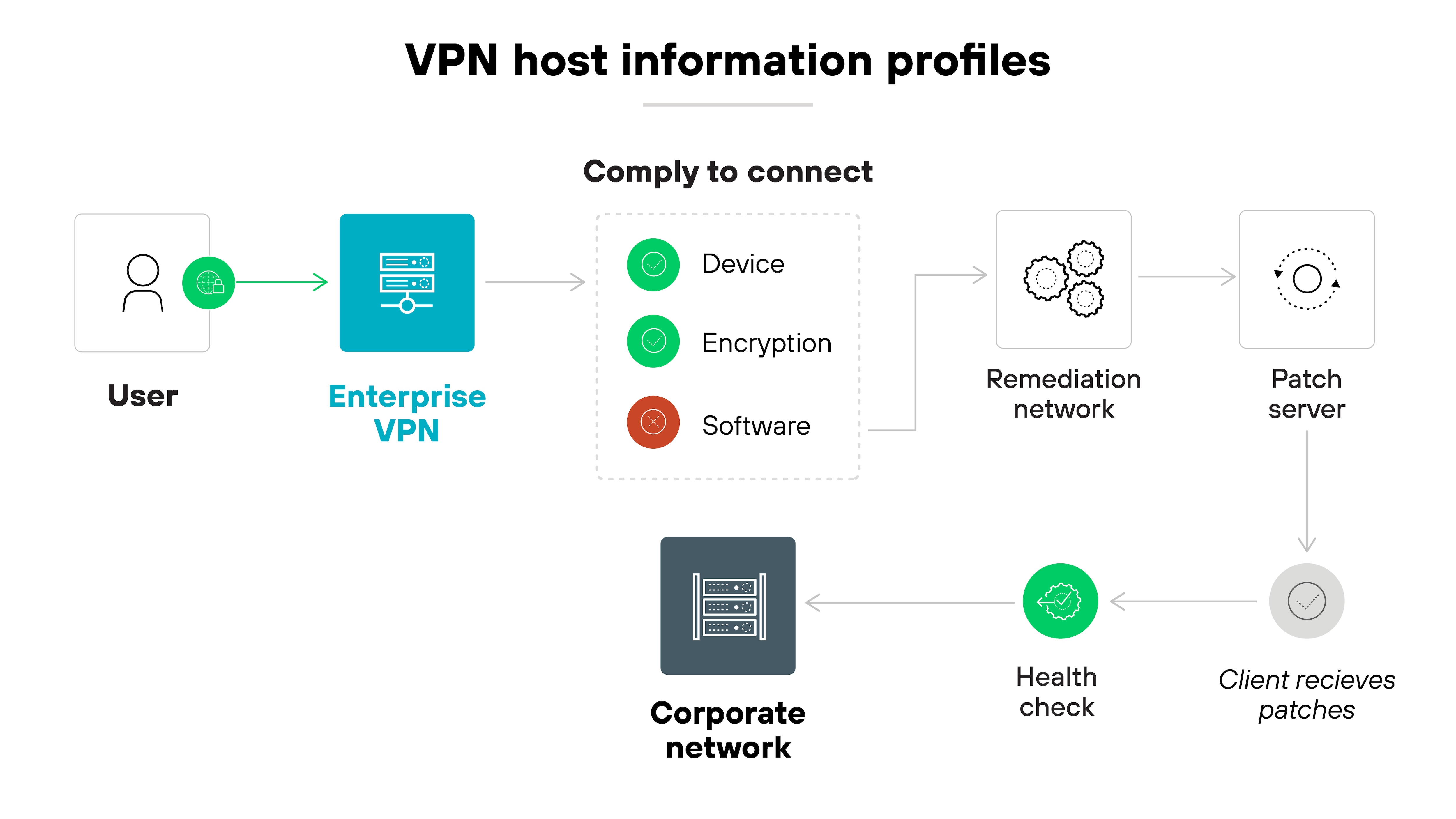
This allows the virtual private network to enforce access policies based on each device’s security posture. Only endpoints that meet specific requirements are allowed to connect.
Flexibility
Some VPNs offer always-on protection. Others allow exceptions for certain use cases.
For example: Latency-sensitive traffic can bypass the virtual private network based on specific apps, domains, or routes.
Like so:
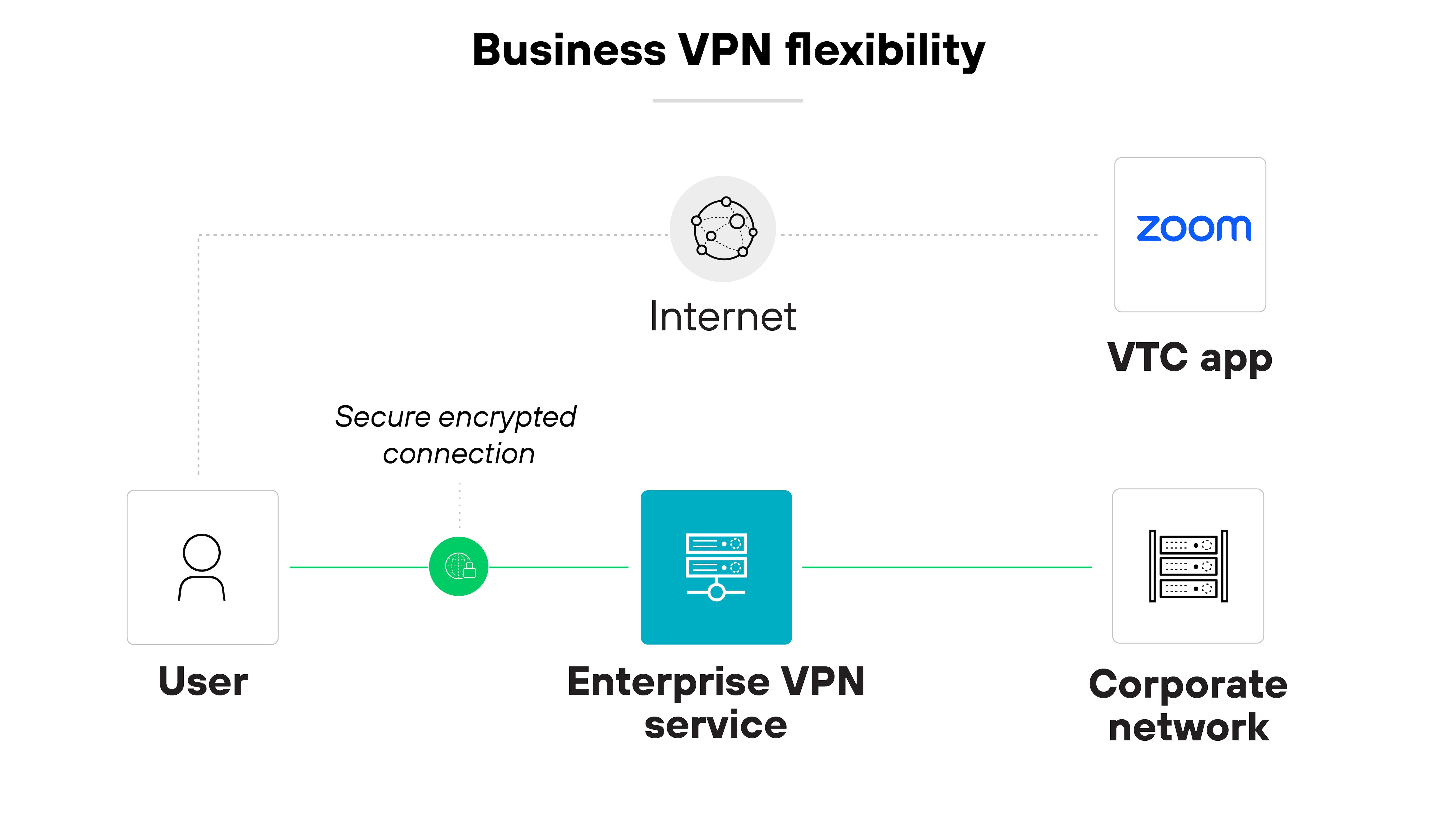
This level of flexibility can help balance security and performance in more complex environments.
Cloud-based gateways
Cloud-based VPN gateways can scale automatically. They adjust to changing traffic loads without manual intervention.
Here’s how it works:
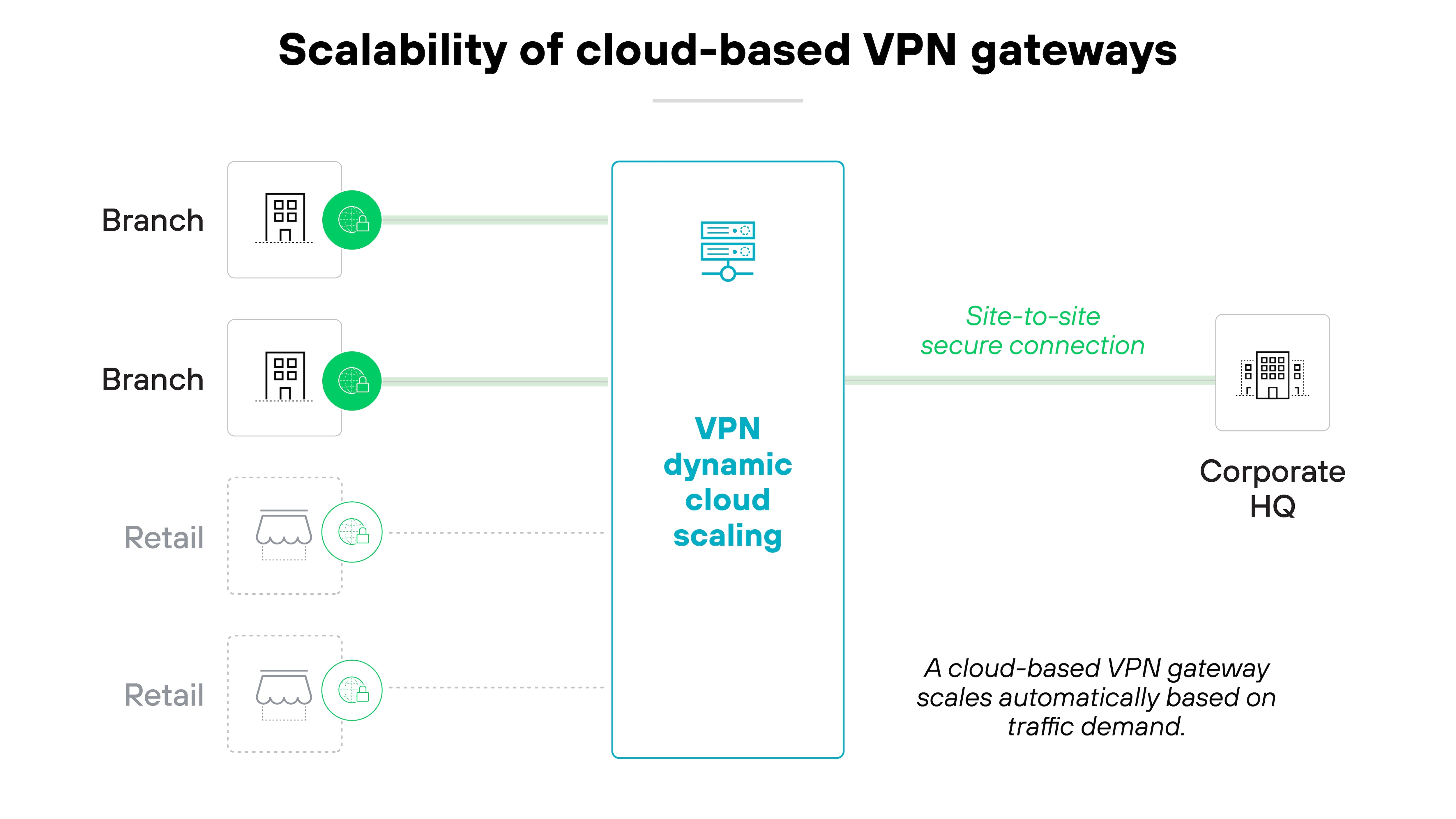
This helps maintain stable performance as demand shifts. It also supports remote work and distributed teams by reducing reliance on fixed, on-prem infrastructure.
Personal VPN features
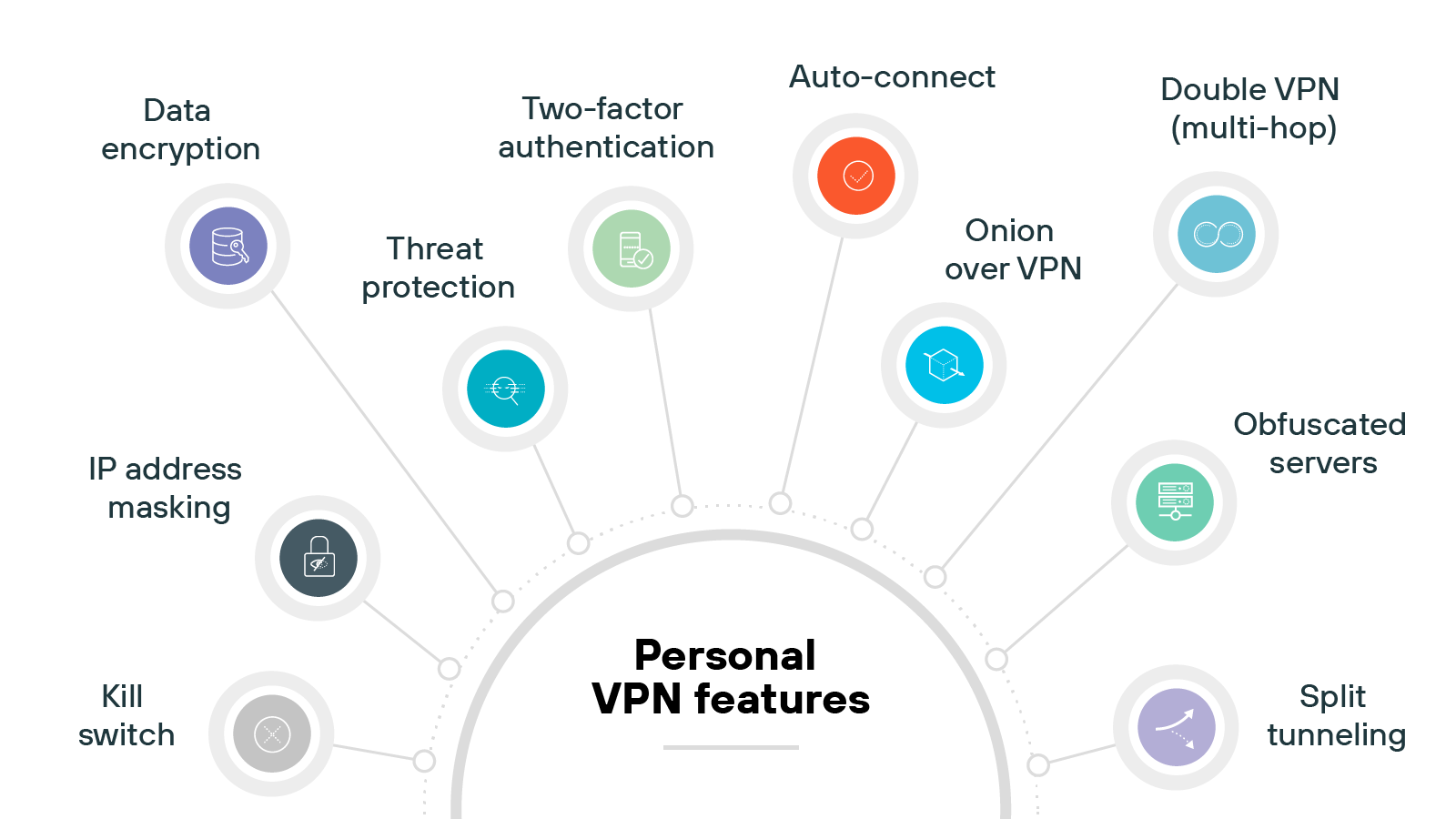
IP address masking
The primary feature of a personal is hiding your device’s real IP address by assigning a different one from the VPN server. This helps obscure your location and makes online activity more difficult to trace.
Data encryption
Encryption is a core function of any VPN. It protects the data moving between your device and the VPN server, making it unreadable to third parties.
While all VPNs use encryption, the strength and type can vary depending on the provider and protocol.
Kill switch
Some VPN providers offer a kill switch to protect your data if the connection fails.
When enabled, it immediately cuts off internet access until the VPN reconnects. This prevents your device from defaulting to an unprotected connection.
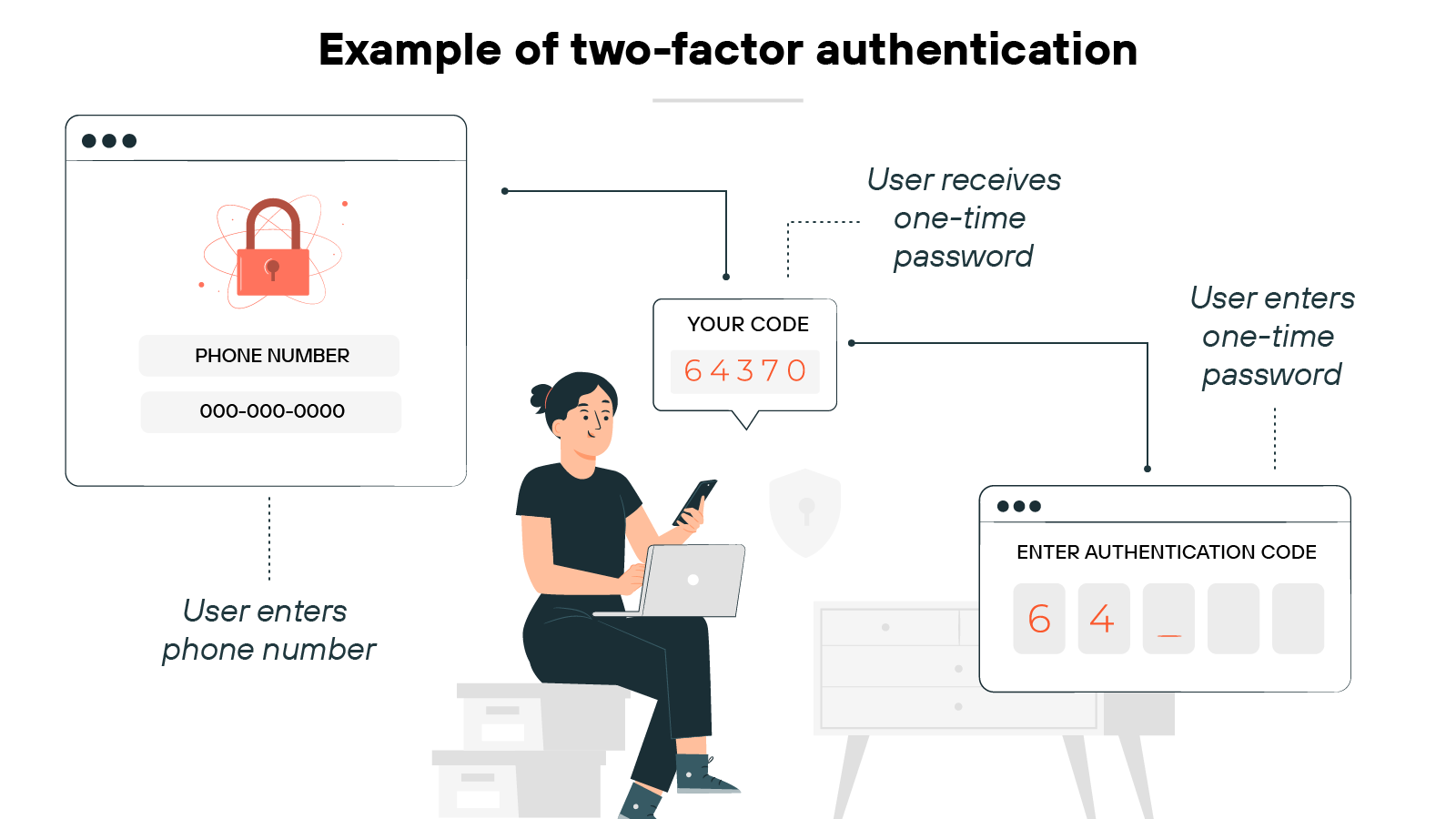
Two-factor authentication
A few VPNs support multi-factor authentication (MFA) at login.
This adds a second verification step—like a code sent to your phone—on top of your username and password. It’s a simple way to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Split tunneling
Not all VPNs offer split tunneling, but when they do, it gives users more control.
You can route specific apps or services through the virtual private network while keeping the rest of your traffic on a direct internet connection.
This can help maintain speed for lower-risk tasks.
Auto-connect
Many VPNs let you configure auto-connect rules. This ensures it turns on automatically when you start your device or join an unfamiliar network.
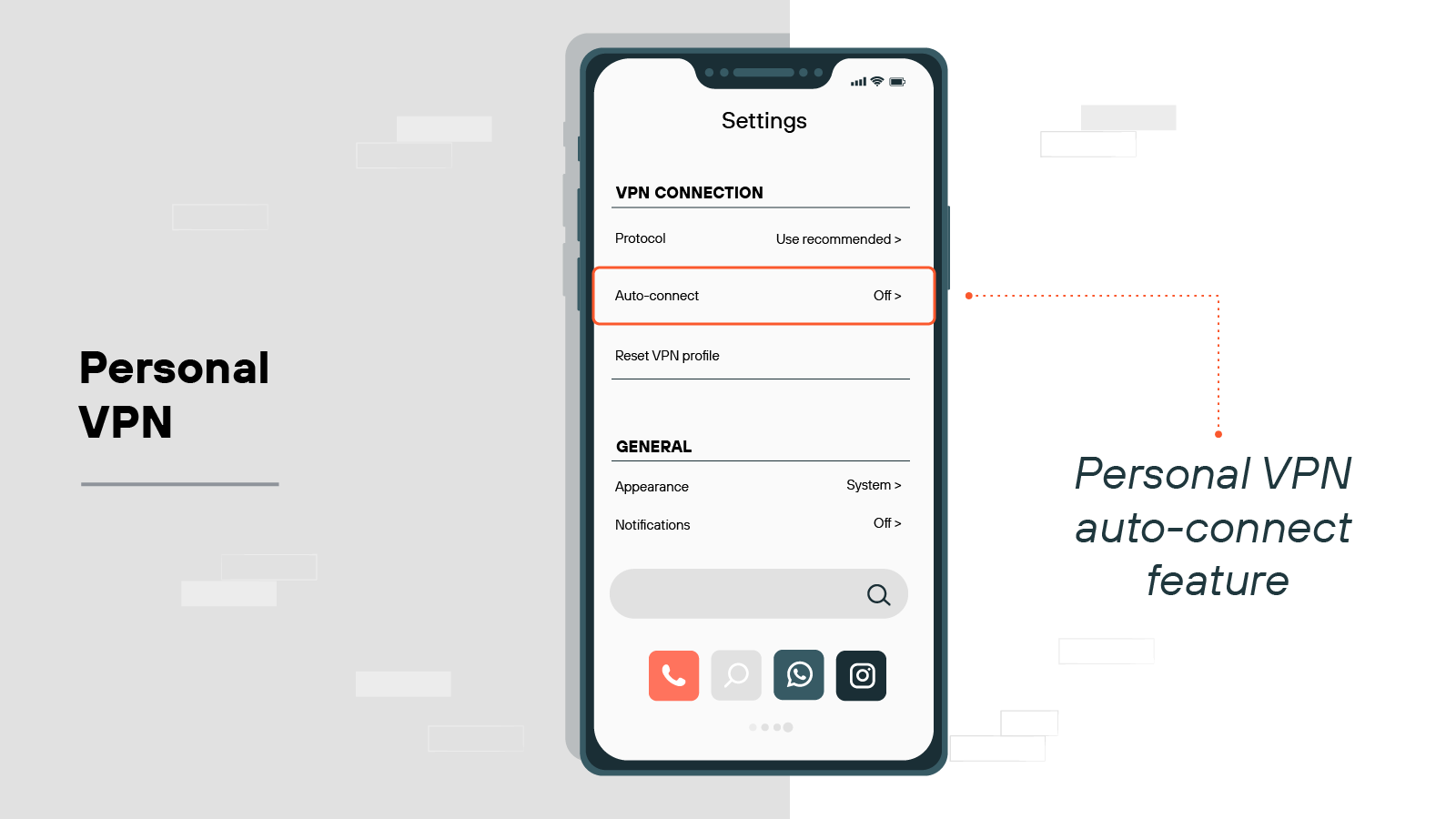
It helps maintain consistent protection, especially if you frequently use public Wi-Fi.
Obfuscated servers
Some providers include obfuscated servers as an optional feature. They’re designed to disguise VPN traffic as regular HTTPS traffic.
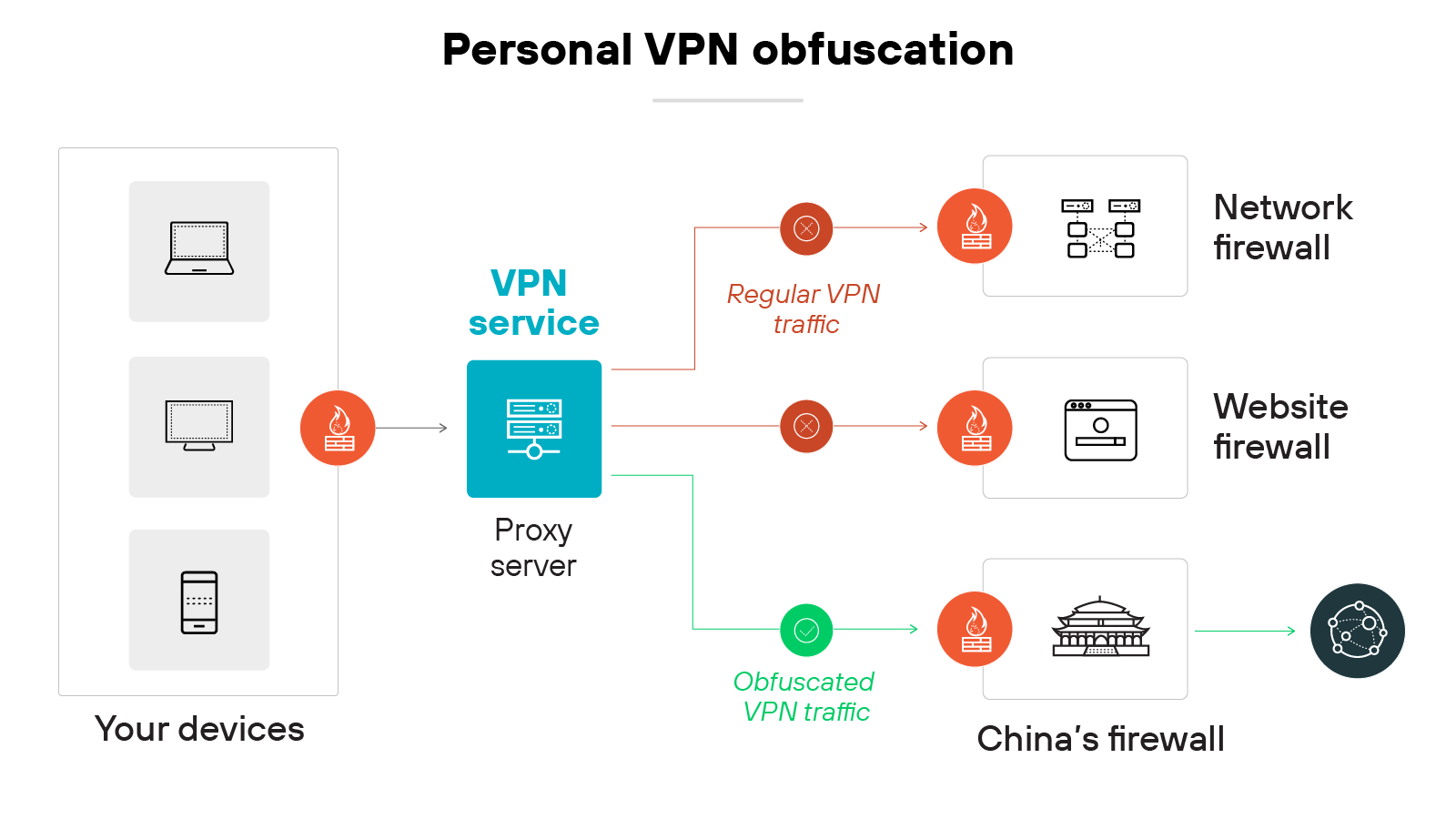
That makes it harder for networks or governments to detect that you’re using a virtual private network, which can be helpful in restrictive regions.
Double VPN (multi-hop)
Double VPN is typically available in premium VPN plans.
It routes your traffic through two VPN servers instead of one. Which adds an extra layer of privacy by separating your entry and exit points. And that makes it more difficult to trace your activity.
Onion over VPN
A few VPNs offer the ability to route traffic through the Tor network after encryption.
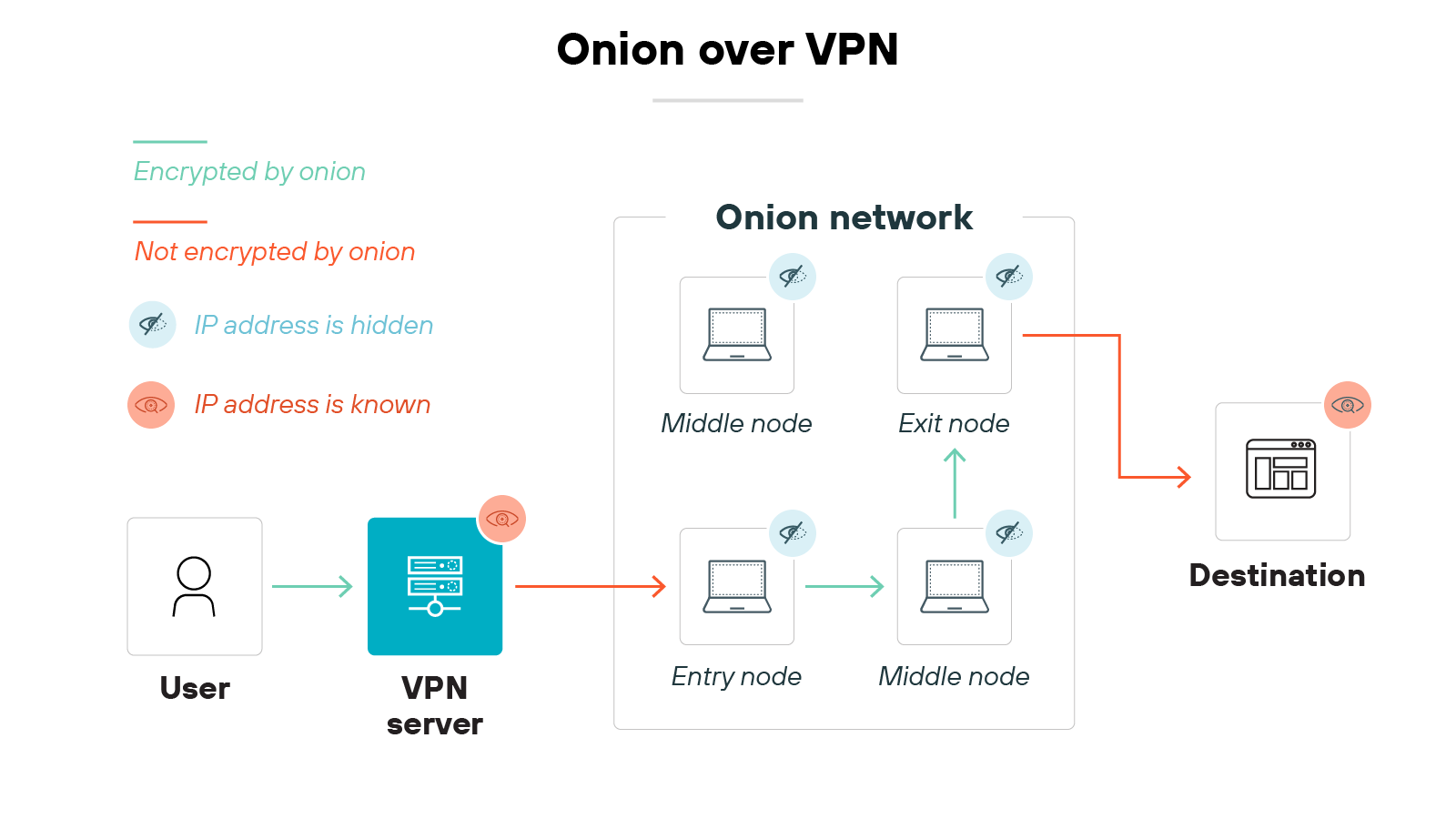
This is known as Onion over VPN. It’s designed for internet users who want maximum anonymity, but it may reduce browsing speed due to the extra layers of routing.
Threat protection
Some VPNs bundle in threat protection tools. These may block ads, prevent trackers, or stop you from visiting known malicious sites.
It’s not a full antivirus solution, but it can help reduce your exposure to basic web-based threats.
What are the benefits of a VPN?
VPNs offer different types of value depending on how and where they’re used.
VPN benefits
| Personal VPN | Business VPN |
|---|---|
|
|
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages of VPNs in both corporate and consumer scenarios.
Business VPN benefits
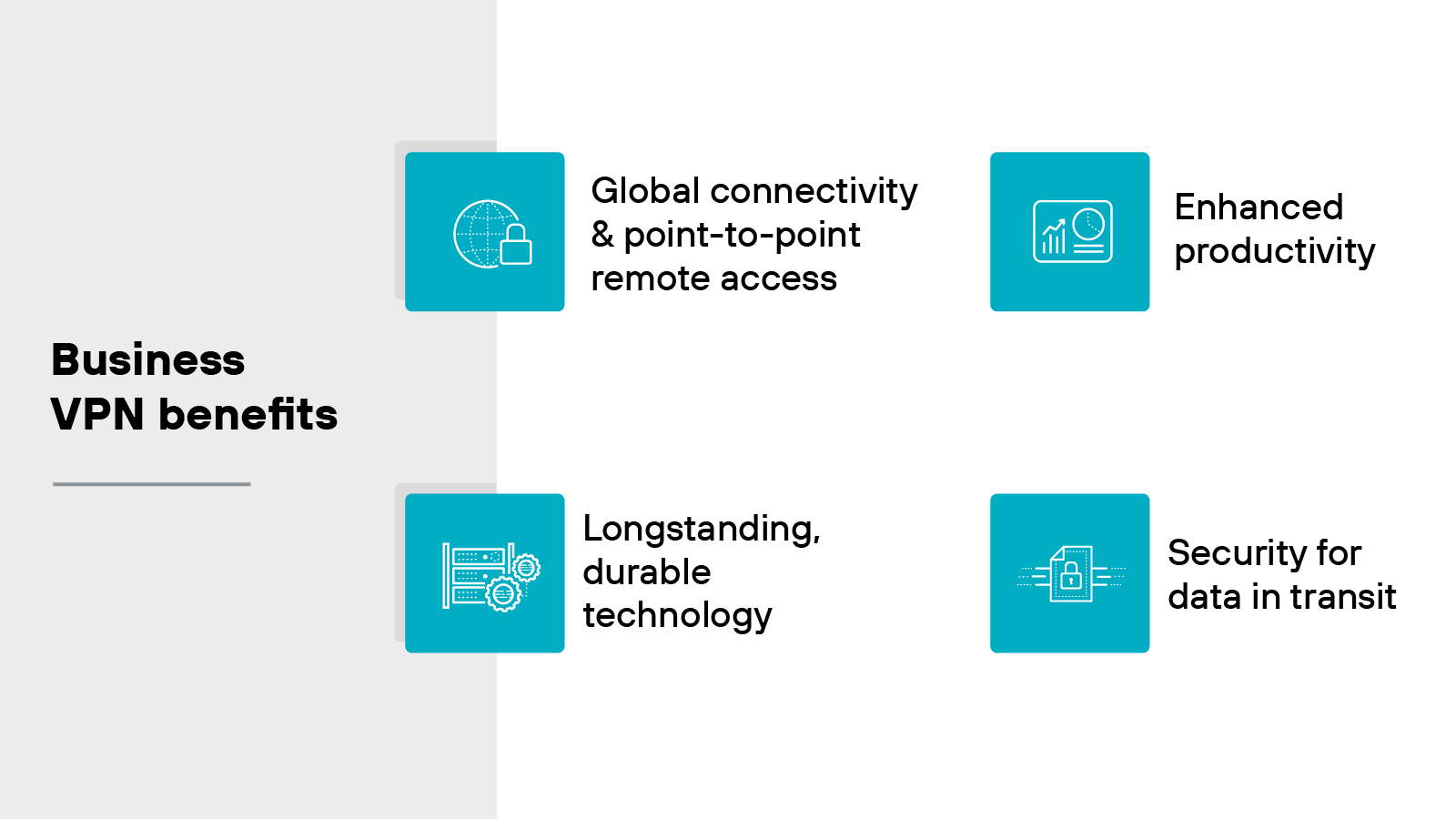
Global connectivity and point-to-point remote access: Business VPNs help extend access to internal resources across multiple regions. This allows remote employees to securely connect to applications and data regardless of location. So teams can stay connected without needing to be physically present in the office.
Enhanced productivity: VPNs support flexible work environments. Employees can log in from home, while traveling, or from other remote locations. The flexibility is helpful for productivity and ensures access to the systems people rely on.
Security for data in transit: VPNs encrypt the data moving between user devices and corporate systems. And that reduces the chance that sensitive information can be intercepted during transmission. It’s especially important for remote access scenarios where connections may pass through public or untrusted networks.
Longstanding, durable technology: VPNs have been in use for decades. The reason so many businesses rely on them is because the core technology is well understood and widely supported. However: Older solutions may lack the protections needed for today’s cloud-first environments. So it’s worth reviewing whether your current setup still meets security and performance needs.
Personal VPN benefits
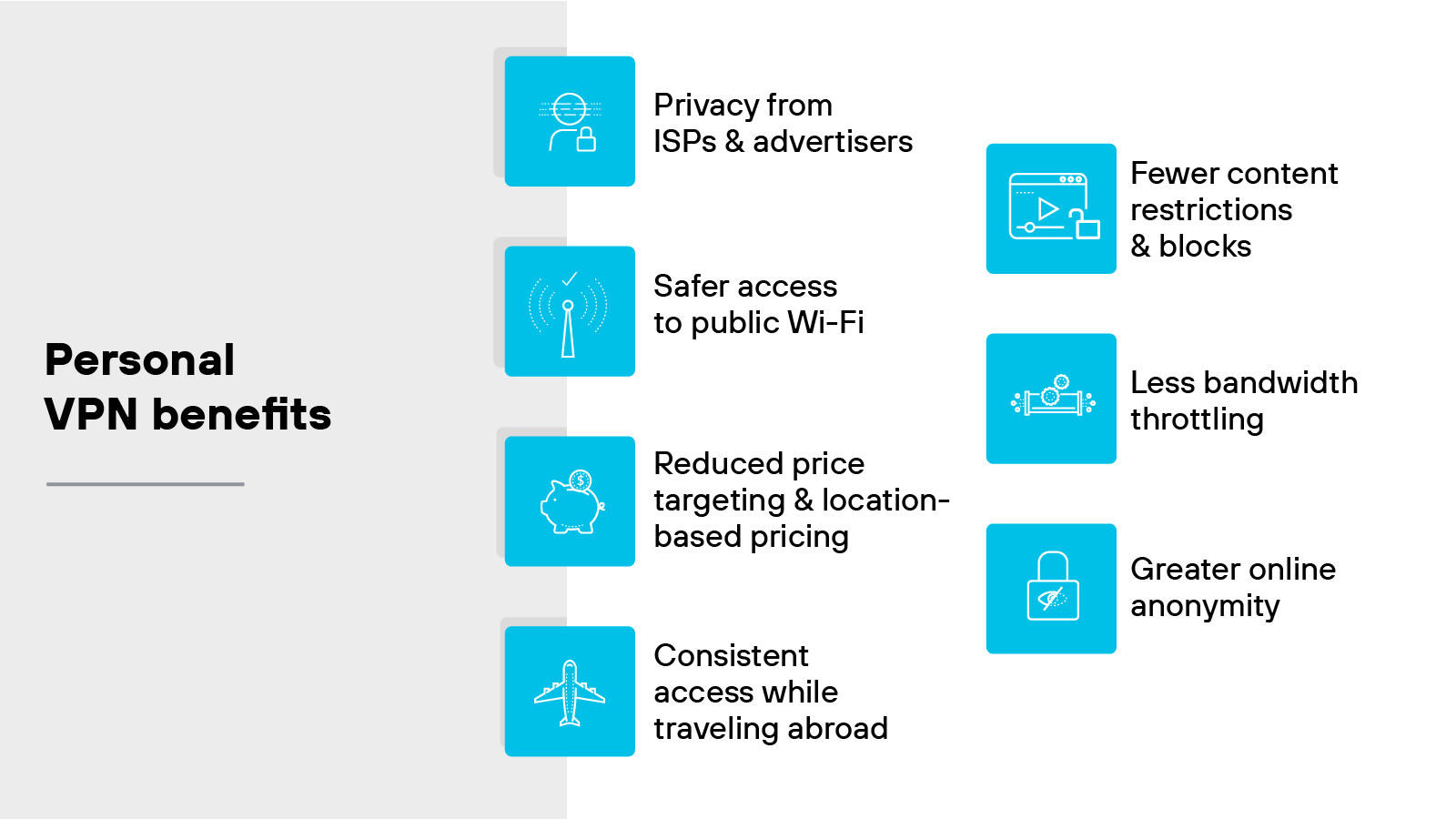
Privacy from ISPs and advertisers: A VPN helps limit how much visibility internet service providers and ad platforms have into your browsing activity. It does this by masking your real IP address and encrypting your traffic. So it’s harder to connect your activity back to you.
Safer access to public Wi-Fi: Public networks are often unsecured. That makes it easier for attackers to intercept data. A VPN helps reduce that risk by encrypting your traffic before it leaves the device.
Reduced price targeting and location-based pricing: Some sites adjust prices based on your location. With a VPN, you can appear to be in another region. That may let you view alternate pricing or compare deals without geographic bias.
Consistent access while traveling abroad: You might lose access to familiar apps or sites while outside your home country. A VPN can help maintain access by routing your connection through a home-region server.
Fewer content restrictions and blocks: Some networks or countries block access to specific websites or services. A VPN can help bypass those restrictions by masking the true source of your connection.
Less bandwidth throttling: Some ISPs slow down certain types of traffic. For example: Video streaming or gaming. A VPN can make your activity harder to detect, which may help avoid throttling in some cases.
Greater online anonymity: VPNs reduce the amount of personal information exposed during a session. That includes your IP address and browsing activity. While not fully anonymous, it does help limit how much can be tracked.
| Further reading: What Are the Benefits of a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
What are the different types of VPNs?
Here’s a breakdown of the most common types of VPNs:
Site-to-site VPN
Remote access VPN
Cloud VPN
SSL VPN
Double VPN
Remember: Not all VPNs work the same way.
Some connect entire networks. Others support individual users. Some are built for cloud access or rely on browser-based encryption.
The best option depends on what the VPN is being used for. For example: A branch office connecting to headquarters may need a site-to-site VPN. But an employee working from home usually connects through a remote access VPN.
And not all options offer the same level of control, flexibility, or performance.
Let’s take a look at how each one works.
Site-to-site VPN
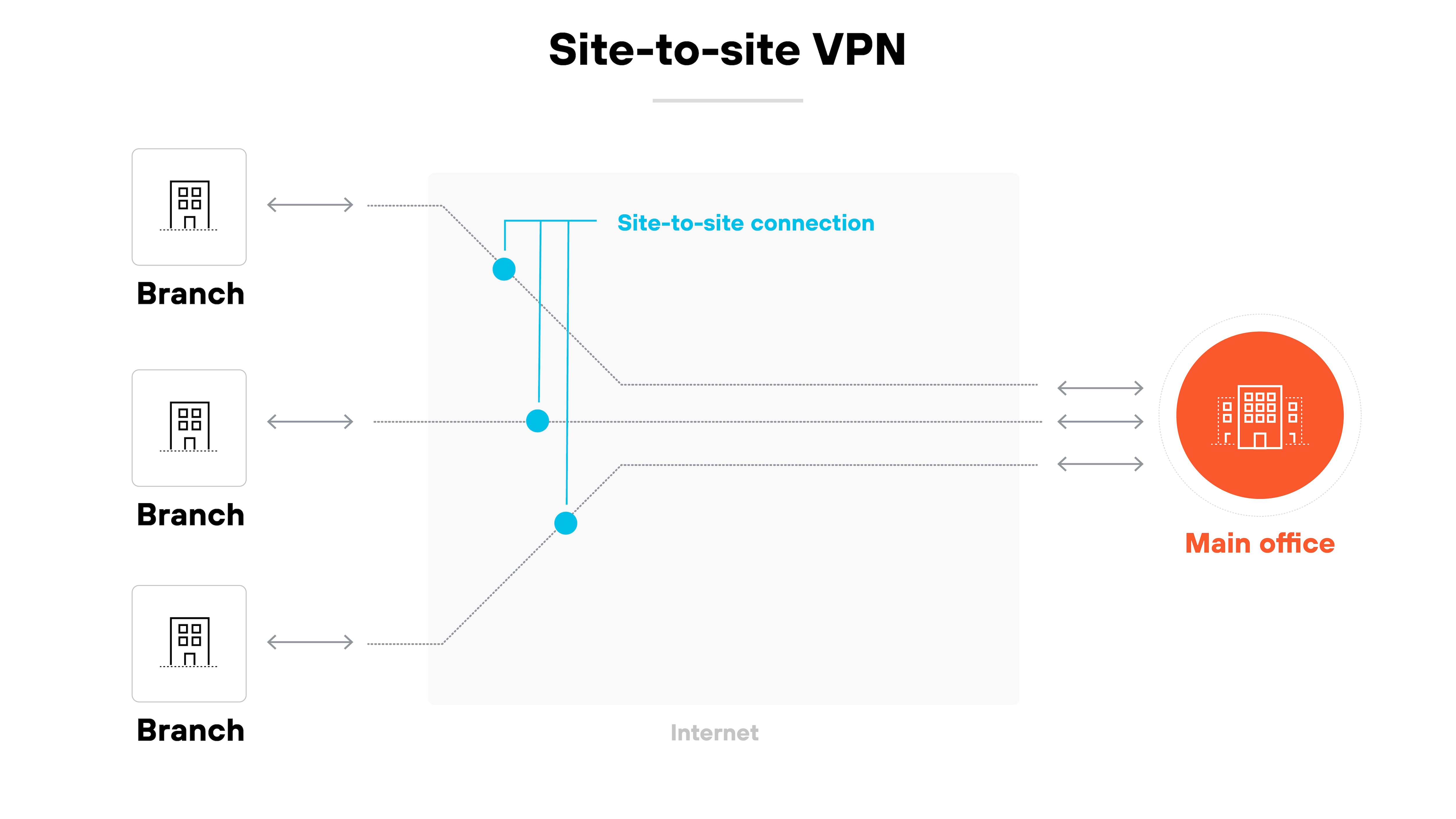
A site-to-site VPN connects two or more networks over the internet.
It’s typically used to link a company’s main office with its branch offices.
Site-to-site virtual private networks create a secure tunnel between sites so that traffic can move between them without being exposed.
Remote access VPN

Remote access VPNs let individual users connect securely to a company network from outside the office.
The virtual private network encrypts all data sent between the user’s device and internal systems. This allows remote employees to access apps, files, and services as if they were on the corporate network.
Cloud VPN
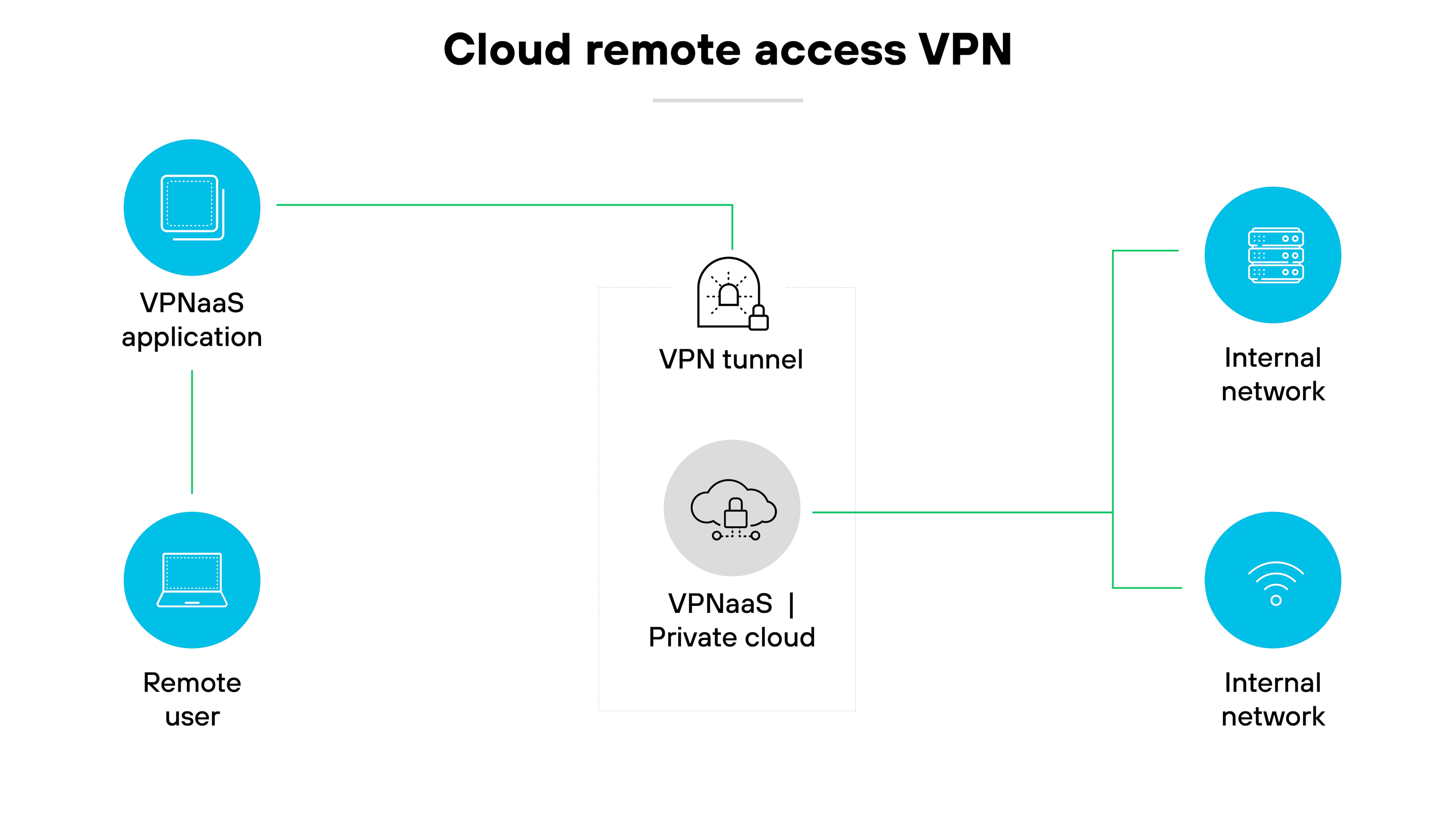
A cloud VPN—also called VPN as a service (VPNaaS)—is designed to support access to cloud-based resources.
It allows users to connect securely to applications and data hosted in the cloud.
Most services are accessed through a client app or browser-based login.
SSL VPN
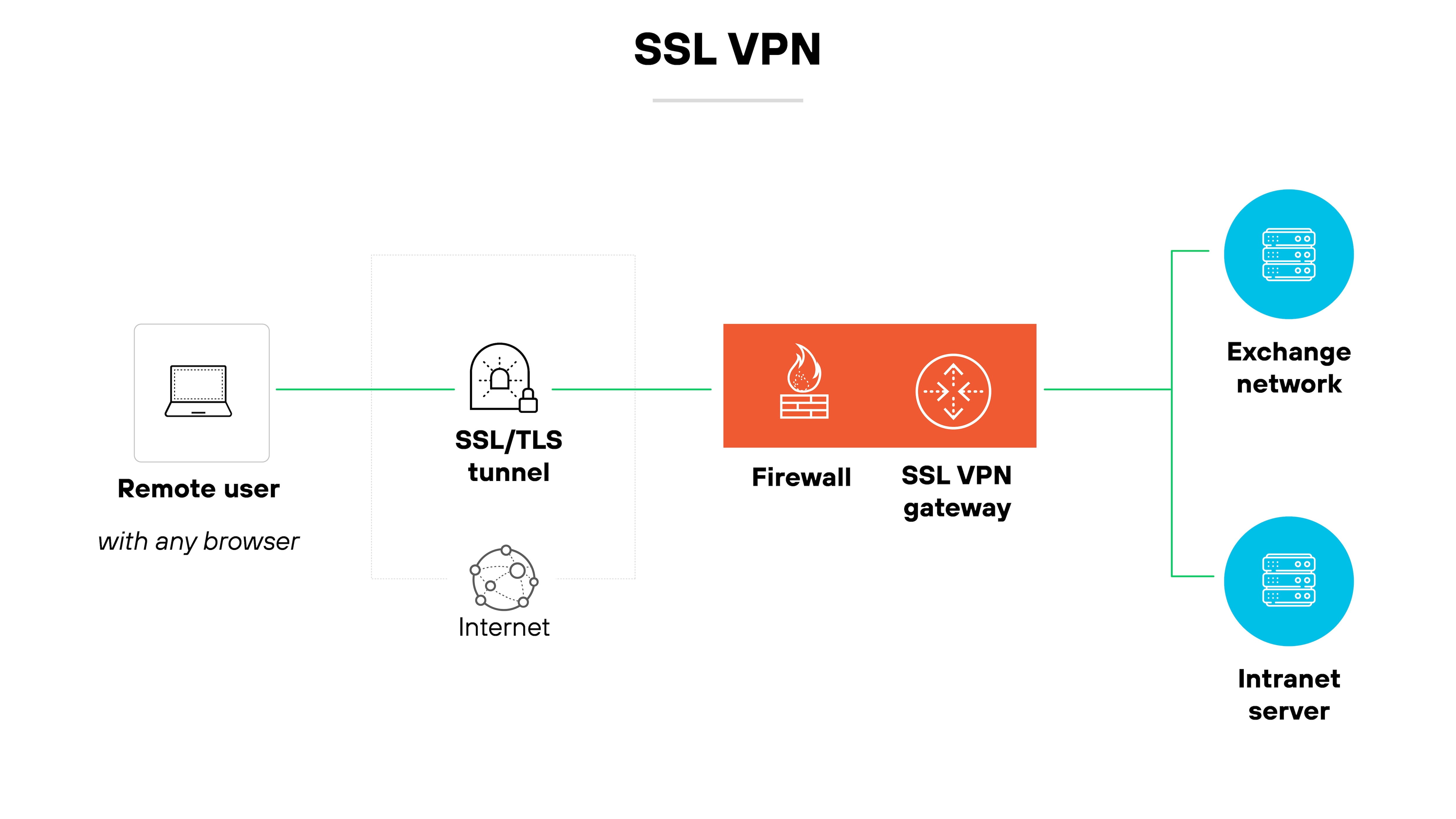
An SSL VPN uses the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol to encrypt browser-based connections.
It doesn’t always require a separate client, which can make it easier to use.
There are two types:
SSL portal VPNs give access to a single web page or application.
SSL tunnel VPNs allow connections to multiple network services—not just web apps.
Double VPN
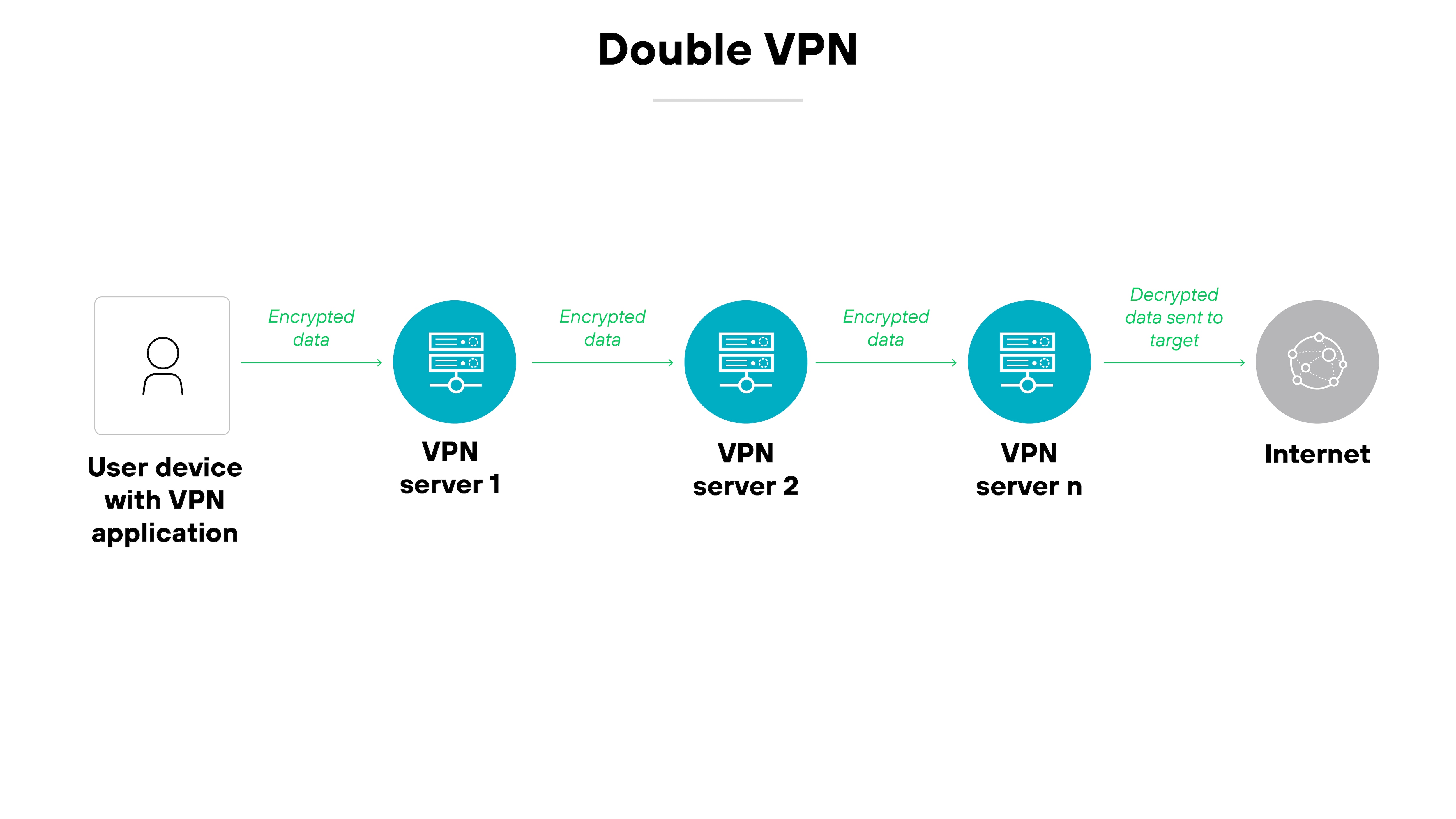
A double VPN routes your internet traffic through two servers instead of one, encrypting data twice.
The added layer of encryption increases privacy, but it may also reduce speed—especially if the servers are far apart.
Note:
A double VPN is more of a configuration versus a type of VPN technology.
| Further reading:
What are the different types of VPN protocols?
The main types of VPN protocols include:
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
WireGuard
OpenVPN
SoftEther
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
VPN protocols determine how data moves between your device and the VPN server.
Each protocol uses different methods to create a secure tunnel. Some prioritize speed. Others focus on compatibility or encryption strength.
The protocol you choose also affects the performance, security, and reliability of the connection.
Certain protocols are better suited for business environments. Others remain popular for personal use. Legacy options may still be supported but are gradually being replaced by newer standards.
Below is a breakdown of each.
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
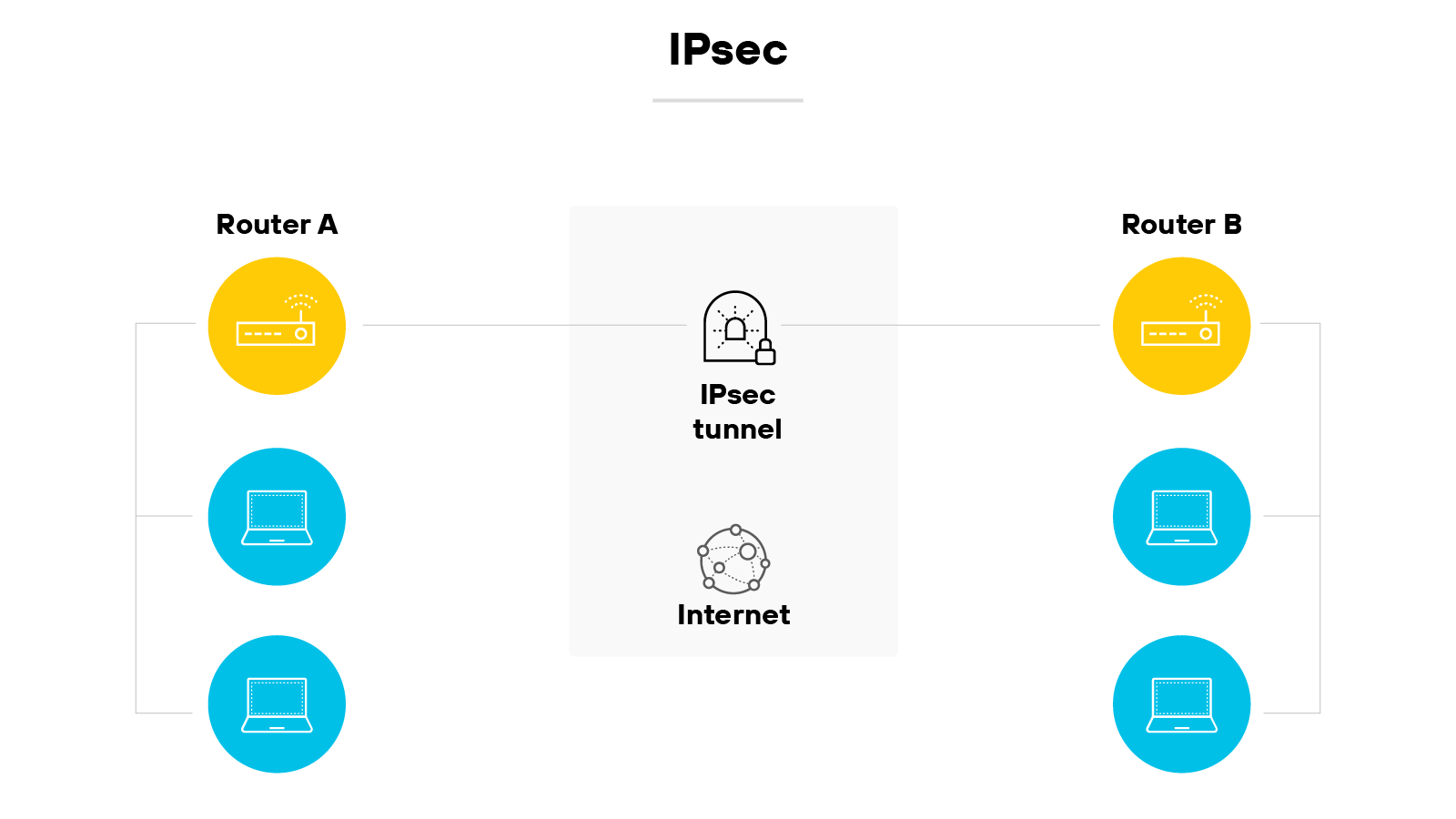
IPsec is a widely used VPN protocol suite designed to secure IP traffic.
It does this by encrypting and authenticating each packet that travels between two endpoints.
IPsec includes components like authentication header (AH) and encapsulating security payload (ESP), which help verify data integrity and confidentiality.
It also uses Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to establish encryption keys between devices.
| Further reading:
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
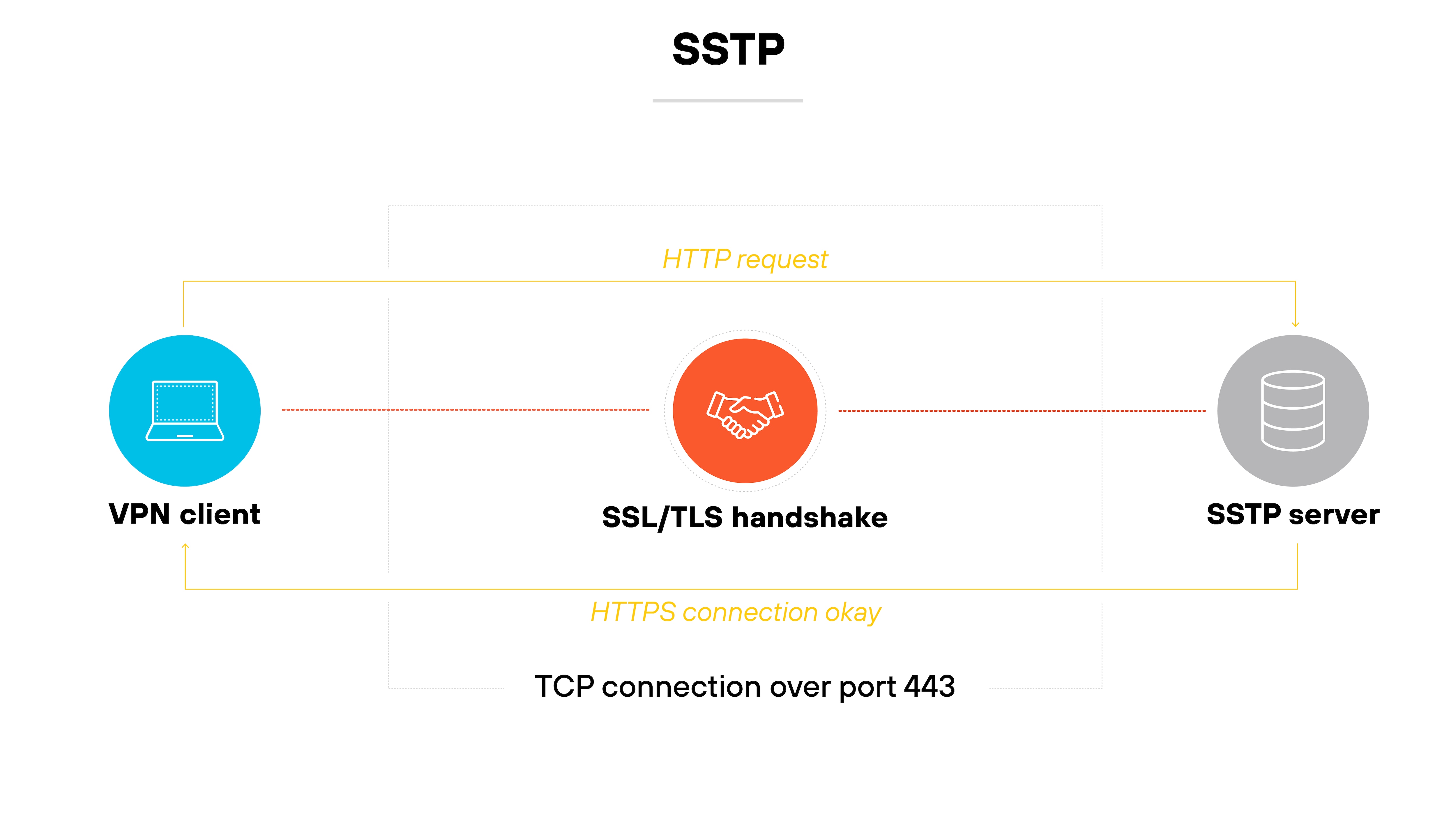
SSTP is a VPN protocol that Microsoft developed.
It establishes a secure tunnel using SSL/TLS encryption.
Because it relies on the same port used for HTTPS traffic, it can pass through most firewalls without issue.
It’s typically used in Windows environments and offers better security than legacy options like PPTP and L2TP.
WireGuard
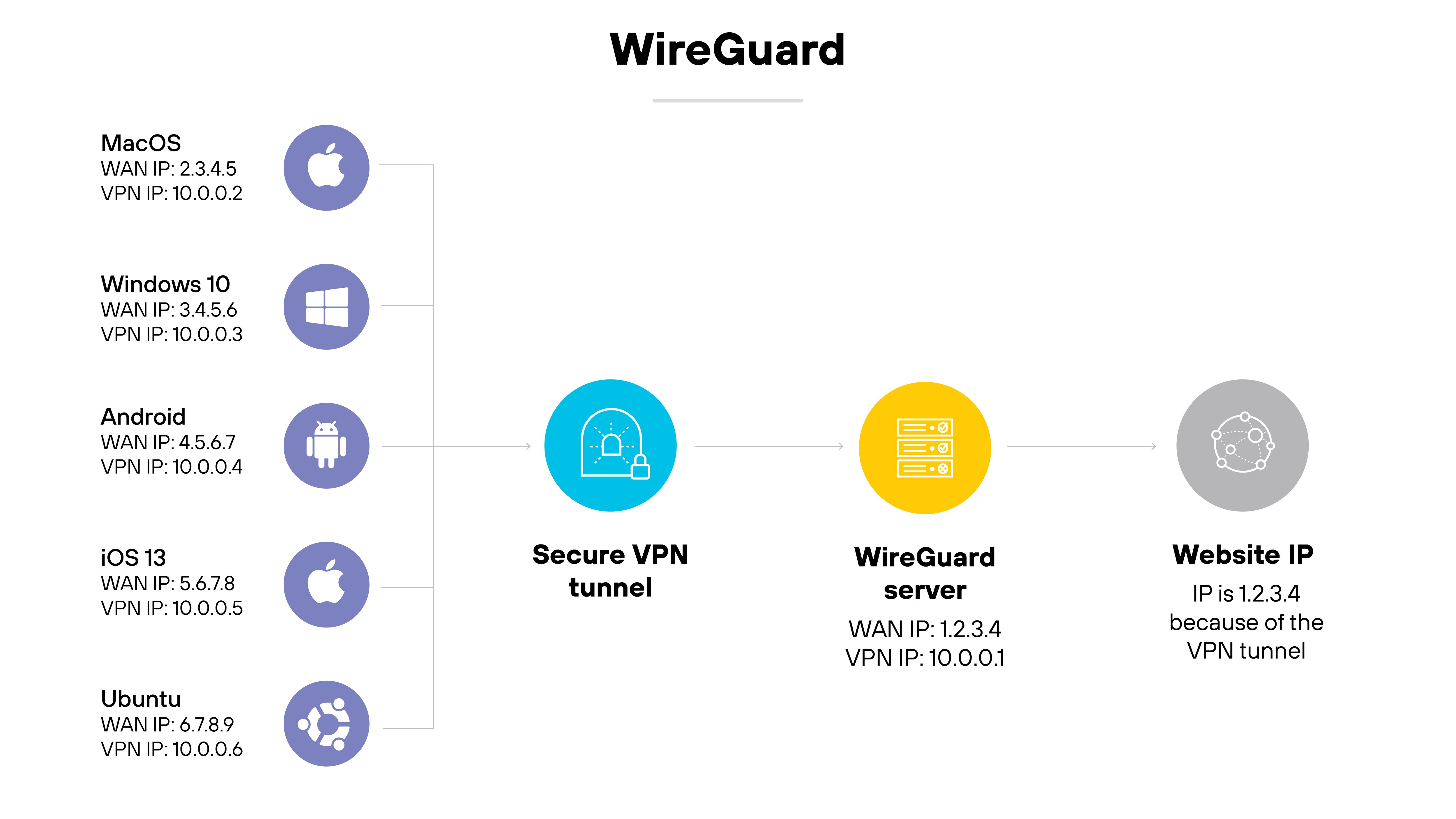
WireGuard is a modern, open-source VPN protocol known for its streamlined design and strong cryptographic foundation.
It uses UDP for fast, low-latency communication and aims to be simpler and easier to audit than older protocols.
WireGuard is supported by many consumer VPN providers and is gaining traction in business environments as well.
OpenVPN
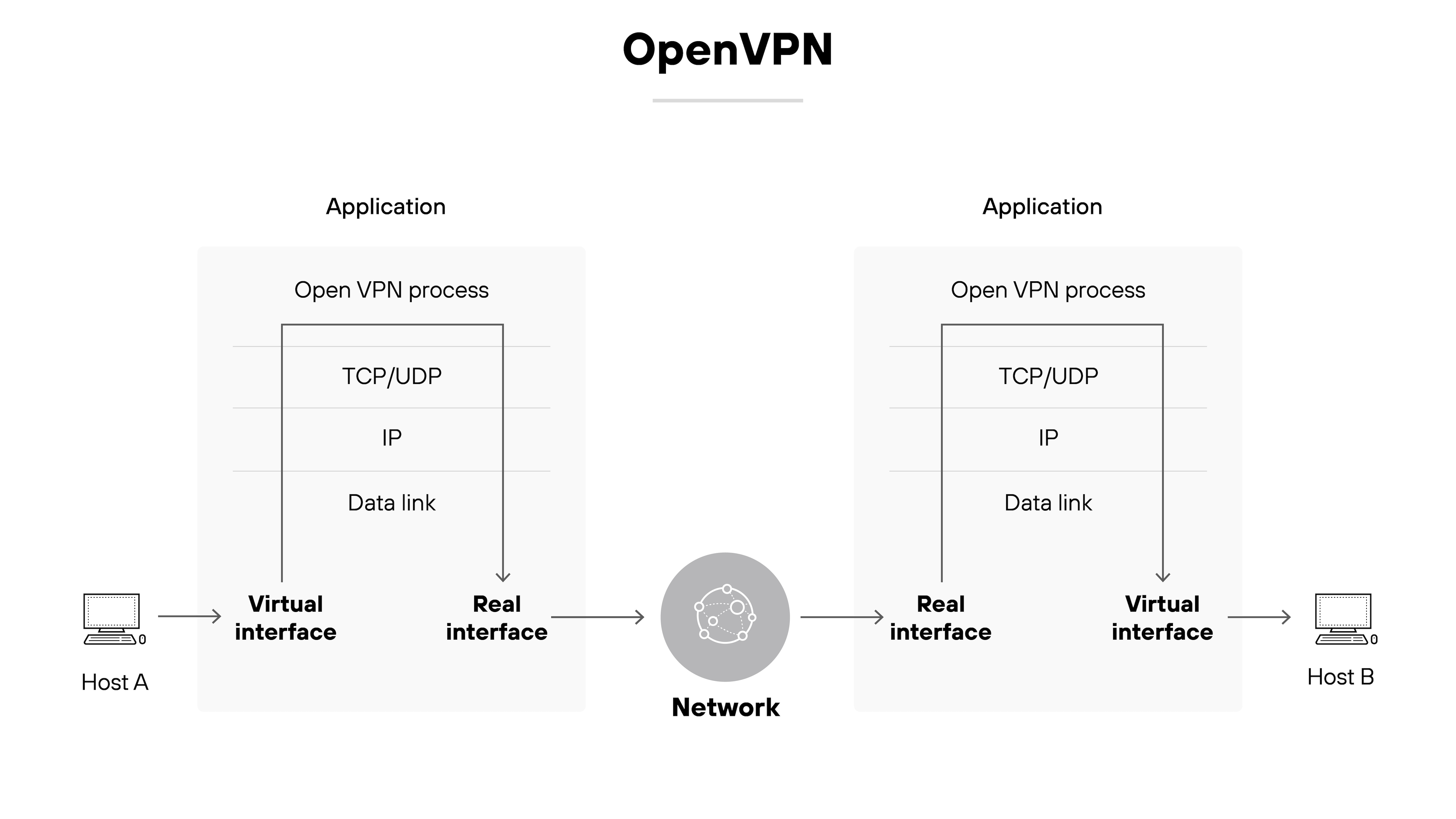
OpenVPN is a flexible open-source protocol that supports both site-to-site and remote access VPNs.
It can operate over either UDP or TCP and works with a wide range of configurations.
Many VPN providers support OpenVPN because it’s reliable and well-tested, though setup can be more complex than with newer protocols.
SoftEther
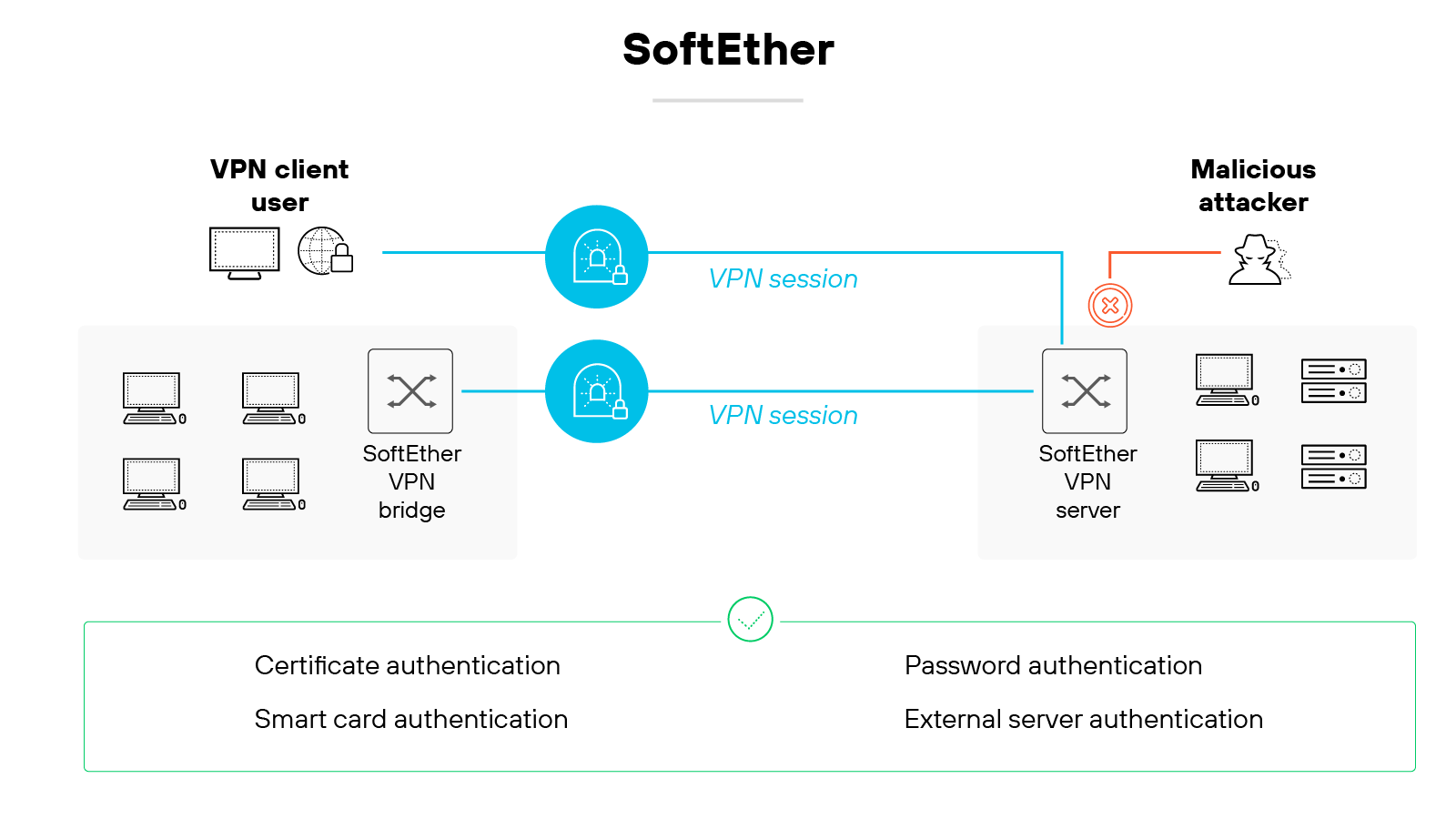
SoftEther is a multi-protocol VPN solution that allows encrypted communication between VPN clients, servers, and bridges.
It uses TCP/IP and can support multiple VPN protocols, including its own.
It’s often used in academic and experimental settings due to its flexibility and broad feature set.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
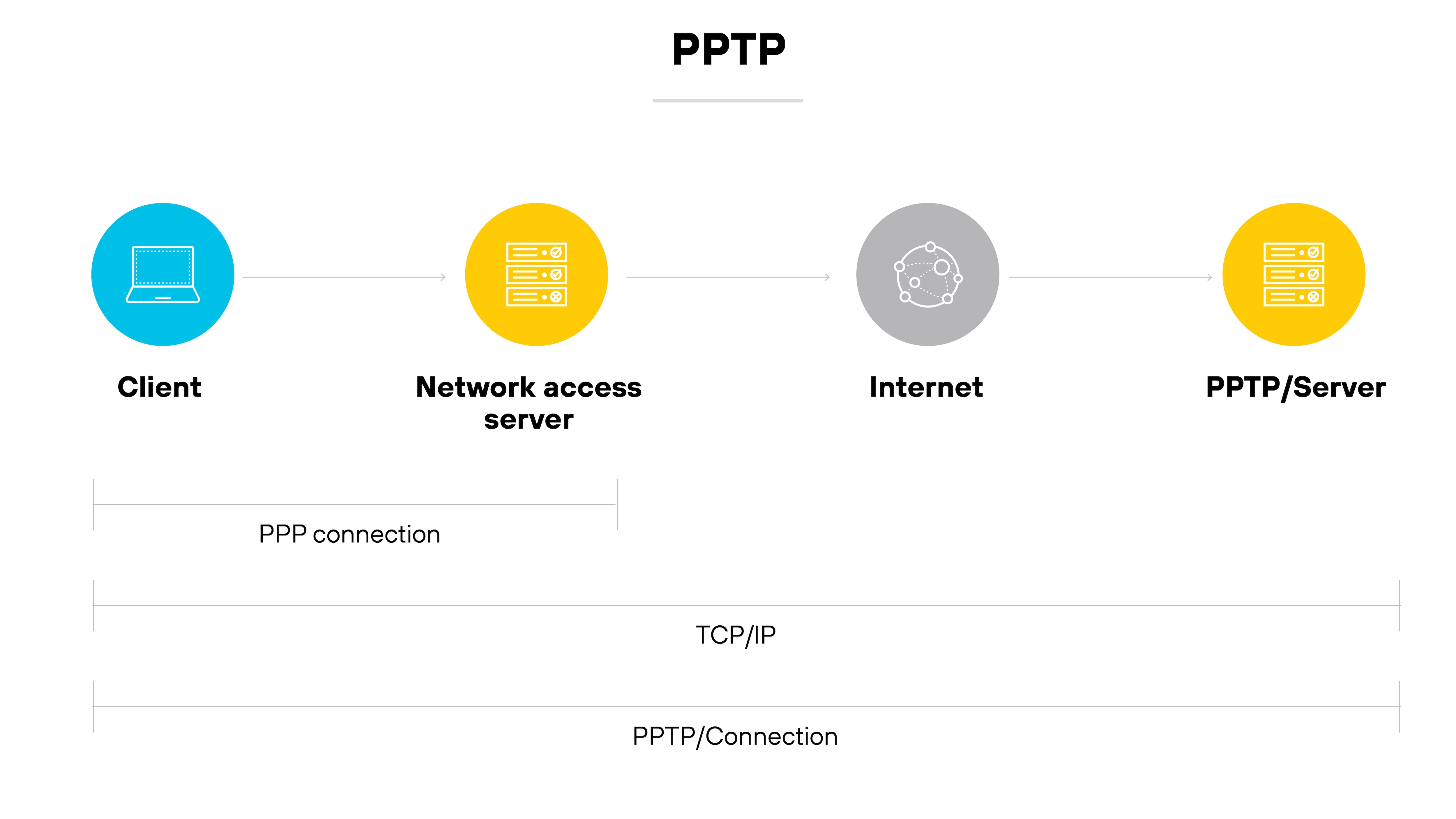
PPTP was one of the earliest VPN protocols available.
It works by encapsulating PPP traffic over IP networks.
However, it’s now considered obsolete due to significant security vulnerabilities. Most modern VPN services have phased it out in favor of more secure alternatives.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
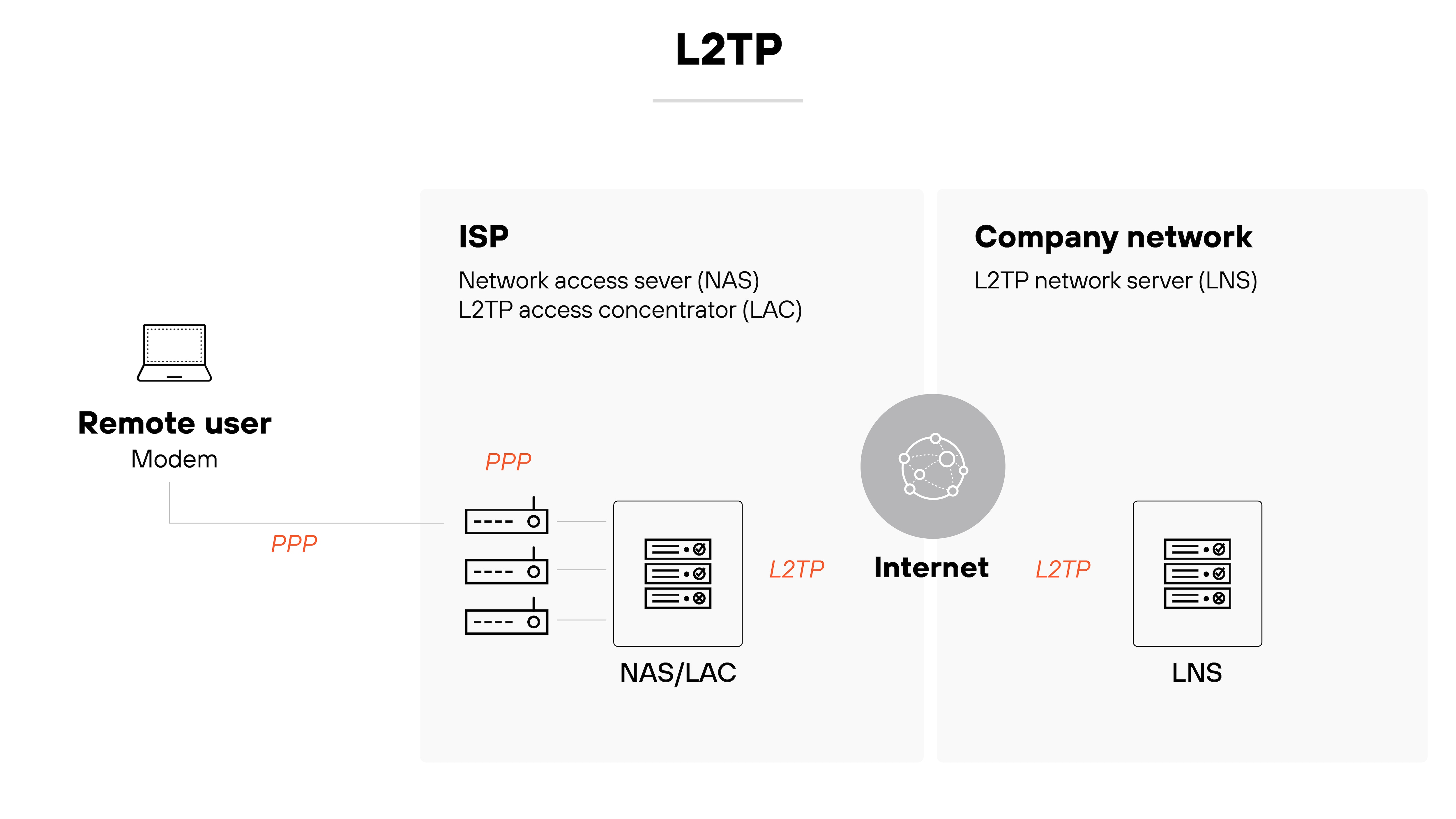
L2TP is a tunneling protocol used to support VPNs.
It doesn’t provide encryption on its own but is often paired with IPsec for security.
Like PPTP, it has largely been replaced by newer, more secure options. It’s still found in some legacy systems, though.
| Further reading:
What are the alternatives to a VPN for secure remote access?
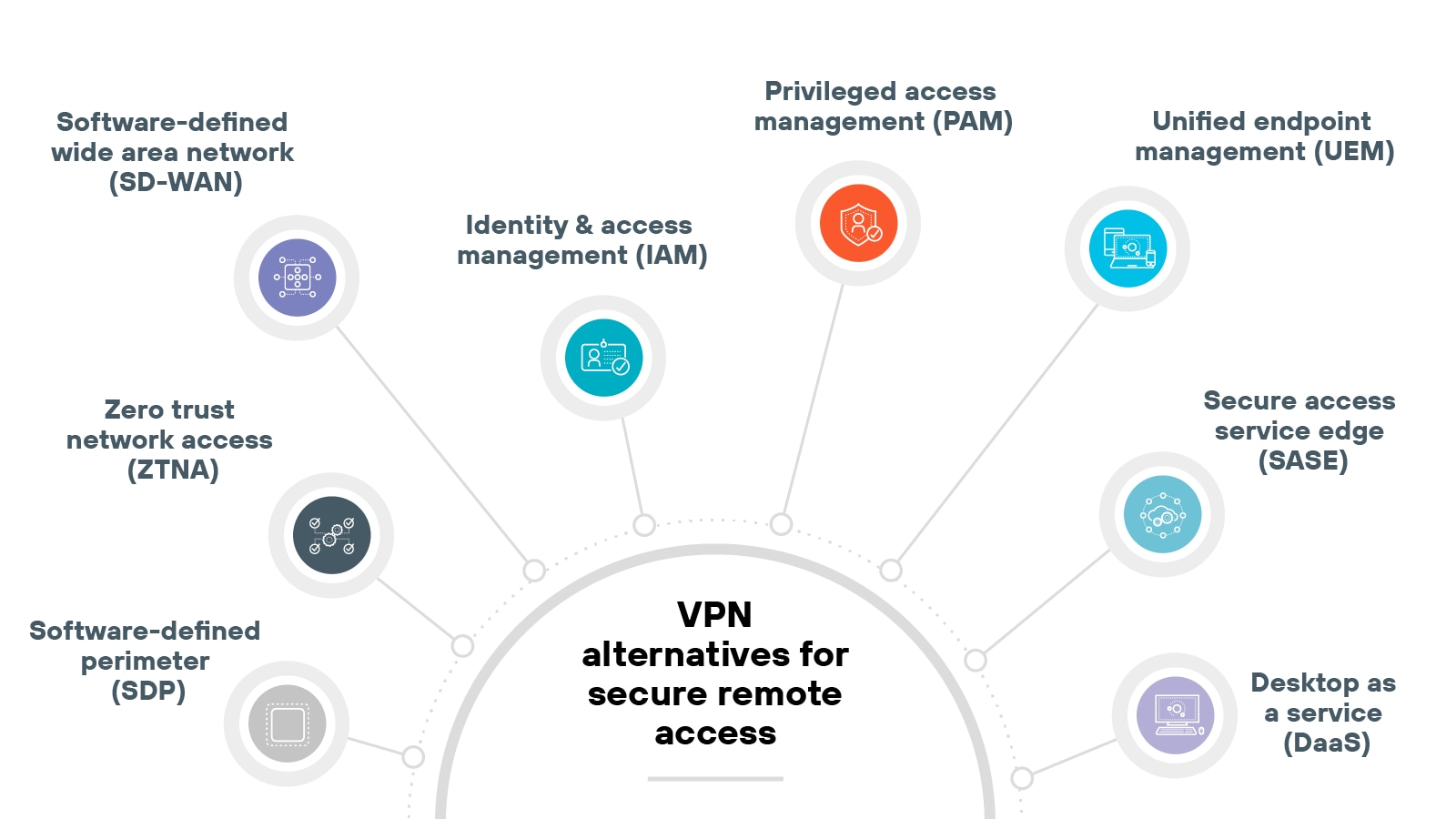
Commonly used alternatives to VPNs for secure remote access include:
Software-defined perimeter (SDP)
Privileged access management (PAM)
Unified endpoint management (UEM)
Desktop as a service (DaaS)
Traditional virtual private networks have long been a staple for remote access. But they weren’t designed for today’s cloud-first, hybrid work environments.
Organizations today are now exploring other ways to secure remote connectivity that better match current needs.
These alternatives focus more on identity, context, and direct-to-app access. They can help reduce attack surface, improve performance, and simplify management.
Each one has its own focus and trade-offs.
Some replace VPNs entirely. Others are used alongside them to strengthen security or improve the user experience.
VPN setup varies depending on the environment. Business deployments typically require more components and configuration than personal use.
Some steps may also change based on the provider, device type, or network policies in place.
The next sections outline a typical setup process—first for organizations, then for individual users.
Business VPN setup process
Business VPN setup typically involves multiple components. The exact steps can vary depending on the platform, provider, and IT environment.
So while this outline can help guide the process, it’s important to refer to your provider’s documentation for service-specific requirements.
Align essential VPN components
Start by identifying the key elements.
You’ll need a VPN client, a VPN server, and a compatible router. The client enables user connections; the server handles those connections.
Note:
Some routers may have VPN clients built in.
Prepare the network
Remove outdated or conflicting VPN clients. These can interfere with installation or cause errors.
If possible, limit the number of unused devices on the network to streamline setup.
Install the VPN client
Download and install the software from your VPN provider.
Choose versions based on operating systems and prioritize installation on the systems that need access first.
Follow configuration guidance
Not all providers offer native apps for every platform. If no software is available, check the vendor’s site for device-specific configuration instructions.
Connect to the VPN
Open the client and log in using your assigned credentials. In most cases, the VPN will connect automatically to the closest available server.
Choose a VPN protocol
VPN protocols determine how data is encrypted and transmitted. Pick a protocol that fits your organization’s security and performance goals.
Note:
Some providers select a default for you.
Troubleshoot if needed
If you run into issues:
Restart the VPN client or device
Check for conflicting VPN software
Update the client and drivers
Re-enter credentials
Try a different server or protocol
Verify no other tools are blocking the connection
Customize settings
Adjust settings based on how the VPN will be used.
Enable auto-connect if users rely on the VPN daily.
Set default servers for speed.
Review logs or dashboards if monitoring is needed.
Personal VPN setup process
Setting up a personal VPN is usually simple. Most providers offer apps that walk you through the process.
The majority of personal VPN products follow a similar setup pattern—even if the details vary by provider.
Here’s what it typically involves:
Choose a VPN provider
Start by selecting a trusted provider.
Look for strong encryption standards, clear privacy policies, and a wide range of server locations. These factors help ensure a more secure and reliable experience.
Create an account and select a plan
Next, create an account.
Then choose a plan that fits your needs.
Note:
Many providers offer monthly or annual options. Some include a free trial or money-back guarantee.
Download and install the VPN app
Install the official app from the provider’s website or your device’s app store.
Tip:
Avoid third-party sources. They may not be secure or up to date.
Log in and open the VPN app
Open the app and sign in with your credentials. Some services also require a verification code or multi-factor authentication.
Select a server location
The app might connect you to a recommended server. Or you can pick one manually. Choose based on your location or what you plan to do—like streaming or staying anonymous.
Connect to the VPN
Click the connect button. Once active, your traffic is encrypted and routed through the VPN server.
Adjust settings as needed
Explore the settings menu. You can enable features like auto-connect, kill switch, or split tunneling. You can also change the VPN protocol if needed.
Confirm the VPN is working
Make sure the VPN is active. Check for a confirmation in the app or visit an IP checker site to confirm your new IP address.
| Further reading: How to Set Up a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
How to choose the right VPN for your needs
Choosing a VPN isn't a one-size-fits-all proposition. The right option depends on how it fits into your environment and what you need it to support.
Business VPNs need to scale, integrate cleanly, and deliver strong administrative control.
Personal VPNs should focus more on ease of use, privacy protections, and compatibility across devices.
The sections below break down what to consider in each case.
Business VPN selection process
Evaluate your infrastructure and compatibility
Start by assessing how the VPN integrates with your existing IT stack. Check compatibility with your operating systems, devices, and cloud environments.
Prioritize enterprise-grade security
Look for strong encryption standards like AES-256, along with support for secure protocols such as IPsec, OpenVPN, or WireGuard.
Choose a provider that demonstrates ongoing adherence to industry compliance standards.
Tip:
Don’t just check for support of strong protocols—confirm they’re the default settings. Some VPNs include outdated protocols for compatibility but don’t disable them by default.
Look for centralized management
Effective enterprise VPNs offer centralized dashboards, role-based access, and logging for administrative oversight. These features help reduce errors and streamline management.
Tip:
Ask vendors for a demo of their admin console before committing. A platform that looks good on paper can still be clunky in practice if the UI is unintuitive or lacks search/filtering options.
Confirm scalability and uptime
Ensure the VPN can scale with your business. Look for providers that guarantee high uptime and have geographically distributed servers to maintain performance.
Review support for BYOD and remote work
If employees use personal devices, make certain that the VPN supports BYOD policies and includes features like mobile OS compatibility and device-level security enforcement.
Inspect provider transparency and data policies
Check for independent audits, a clear privacy policy, and details on how the provider handles logs and user data.
Transparency matters when third parties are securing your traffic.
Weigh the cost against capabilities
Business VPNs vary widely in price. Compare plans based on feature sets, available support, and long-term cost.
Watch for hidden fees related to setup or user scaling.
Tip:
Consider the total cost of ownership—not just monthly pricing. That includes the time your team spends on setup, maintenance, and support. A cheaper plan that’s harder to manage may cost more in the long run.
Personal VPN selection process
Define your primary use case
Are you focused on privacy, content access, travel, or public internet safety? Clarifying your goal helps narrow down providers with the right strengths.
Check for strong privacy policies
Look for VPNs with verified no-log policies and independent audits. This helps reduce the risk of your data being stored or sold.
Tip:
Go beyond the marketing claims. Look for VPNs that have completed independent third-party audits verifying their no-log policies. Bonus: Check whether those audits are recurring, not one-time.
Look into encryption and protocol options
Choose a VPN that offers up-to-date encryption (like AES-256) and supports secure, modern protocols like WireGuard or OpenVPN. These impact both speed and protection.
Verify device and OS support
The VPN should work on all devices you use—Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and others.
Some providers also allow router installs for home-wide protection.
Tip:
If you’re planning to use the VPN on smart TVs, gaming consoles, or routers, check whether the provider offers setup guides or dedicated apps for those platforms. Native support saves a lot of hassle.
Compare server count and locations
More server options usually mean better performance and flexibility for region-based browsing.
It also helps distribute traffic to avoid congestion.
Assess ease of use
Choose providers with straightforward apps and simple connection steps. Setup should be fast, and switching servers shouldn’t require advanced knowledge.
Be cautious with free VPNs
Free services often come with tradeoffs—like slower speeds or questionable data practices.
Consider a paid option with a trial period or money-back guarantee.
Tip:
Look for signs of monetization. If the service is free, ask yourself: Are they showing ads? Logging activity? Reselling bandwidth? A trustworthy VPN will disclose how they support their free offering.
Test performance and customer support
Run speed tests and evaluate support availability.
Look for 24/7 chat or helpful documentation in case of issues.
Comparing VPNs with other security technologies
Let’s take a moment to compare VPNs with a few adjacent network and security technologies.
These tools may overlap in some use cases but are built to solve different problems.
VPN vs. SD-WAN
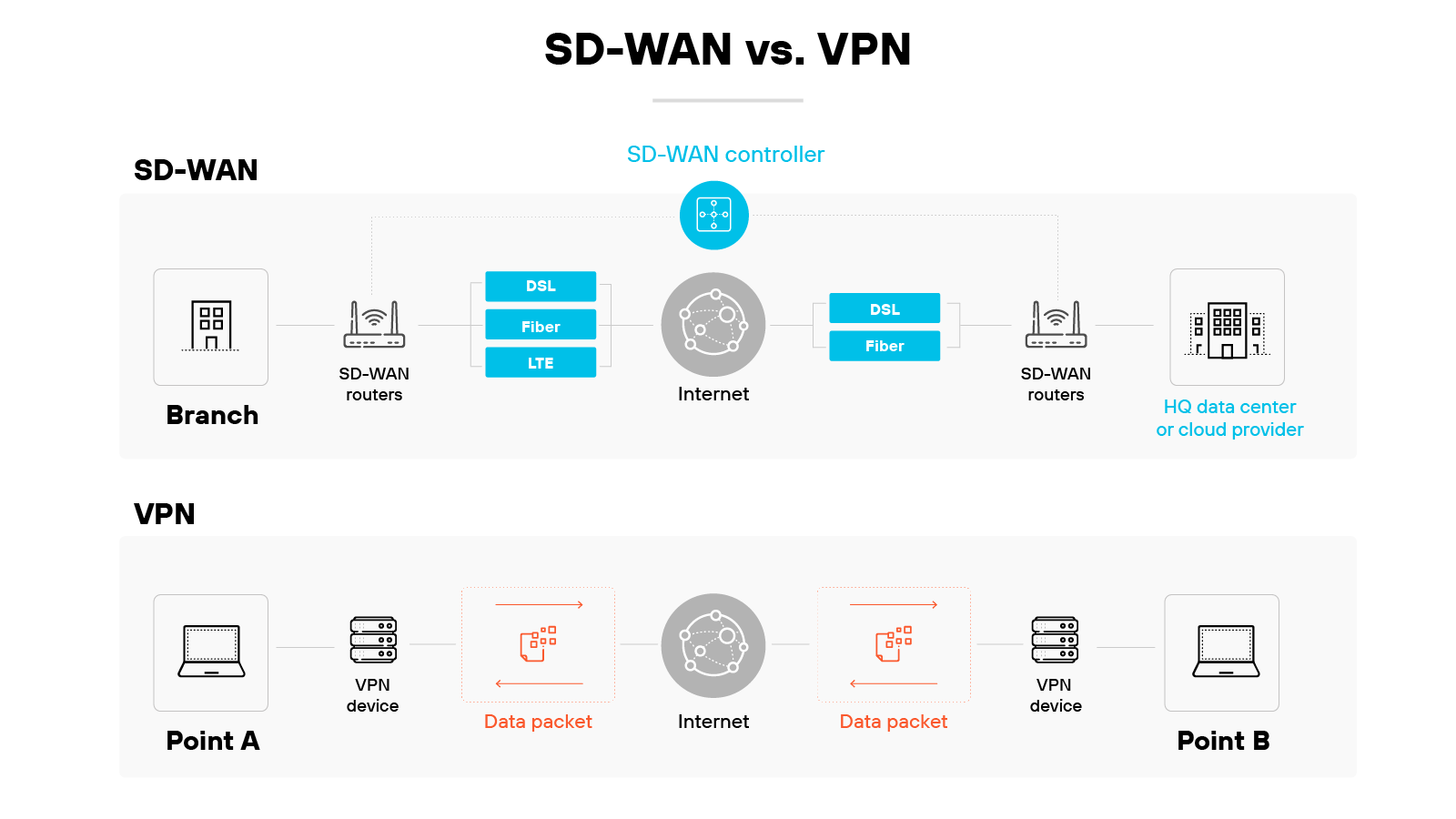
SD-WAN and VPNs both support secure remote connectivity. But they do it in very different ways.
VPNs create a secure, encrypted tunnel between a user and a network. This helps protect data in transit and supports private access from one point to another.
Most virtual private networks rely on a single, fixed connection path.
SD-WAN takes a broader approach. It uses software to dynamically route traffic across multiple connection types.
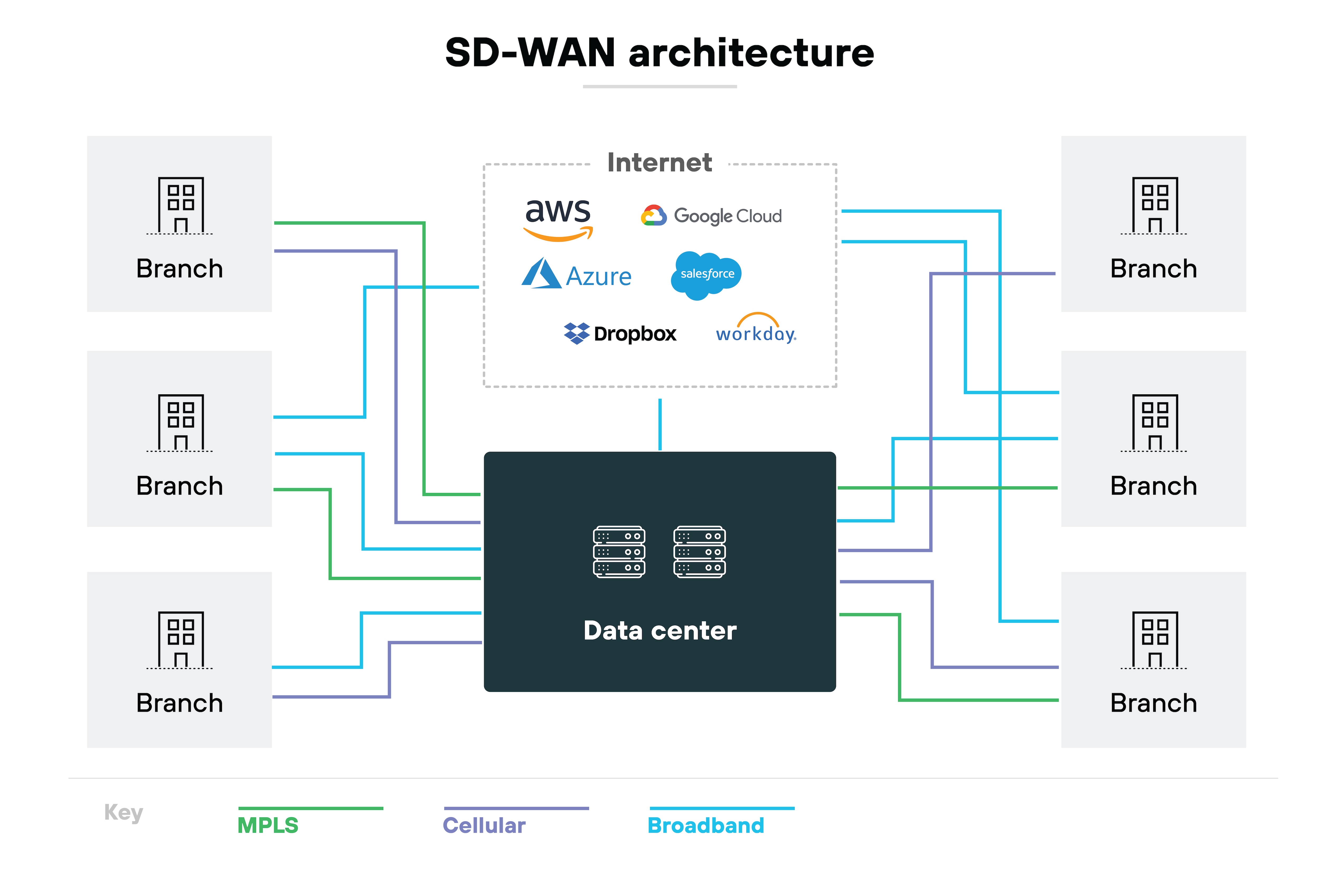
It can adjust based on real-time conditions, traffic type, or policy.
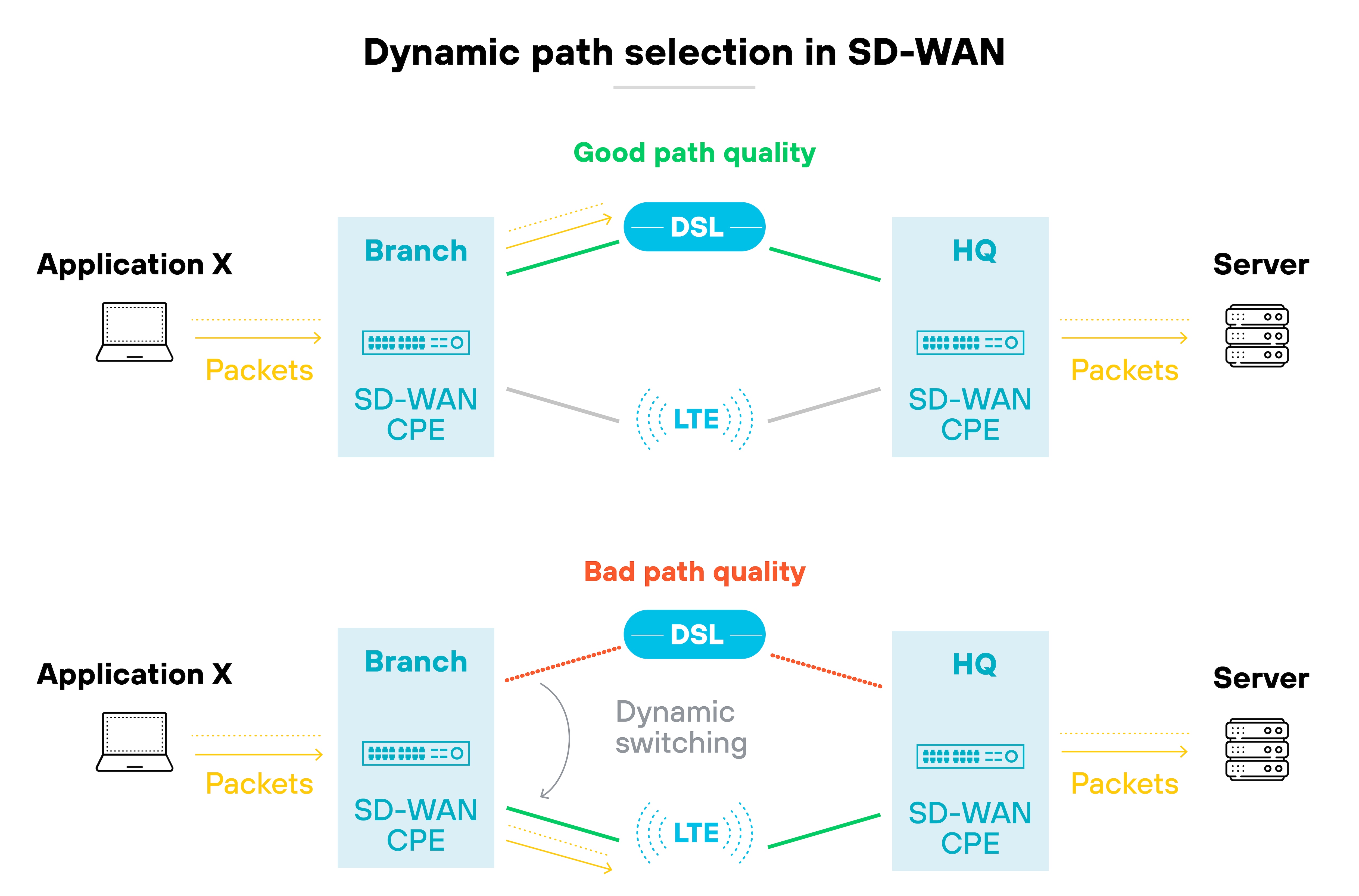
This allows for greater flexibility, better performance, and centralized control—especially across distributed environments.
| Further reading: SD-WAN vs. VPN: How Do They Compare?
VPN vs. VPS vs. VPC
VPN, VPS, and VPC comparison
| Category | VPN | VPC | VPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Secures online data exchange. | Private cloud within public infrastructure. | Virtual machine acting as a server. |
| Deployment | Connects remote users to networks. | Scalable hosting for cloud services. | Dedicated resources for hosting. |
| Scalability | Ideal for individual connections. | Highly scalable with cloud services. | Less scalable, but resource-dedicated. |
| Control | Limited network control. | Extensive cloud network control. | Server control within host limits. |
| Customization | Basic security settings. | Custom network configurations. | Configurable server settings. |
VPN, VPS, and VPC sound similar—but they serve very different purposes.
A VPN is a security tool. It encrypts internet traffic between your device and a remote server. The goal is to keep data private and protect online activity from monitoring or interception.
A VPS is a virtual private server. It’s a virtualized environment that runs on a physical machine and acts like a dedicated server. VPSs are commonly used to host websites or applications and offer more control than shared hosting.
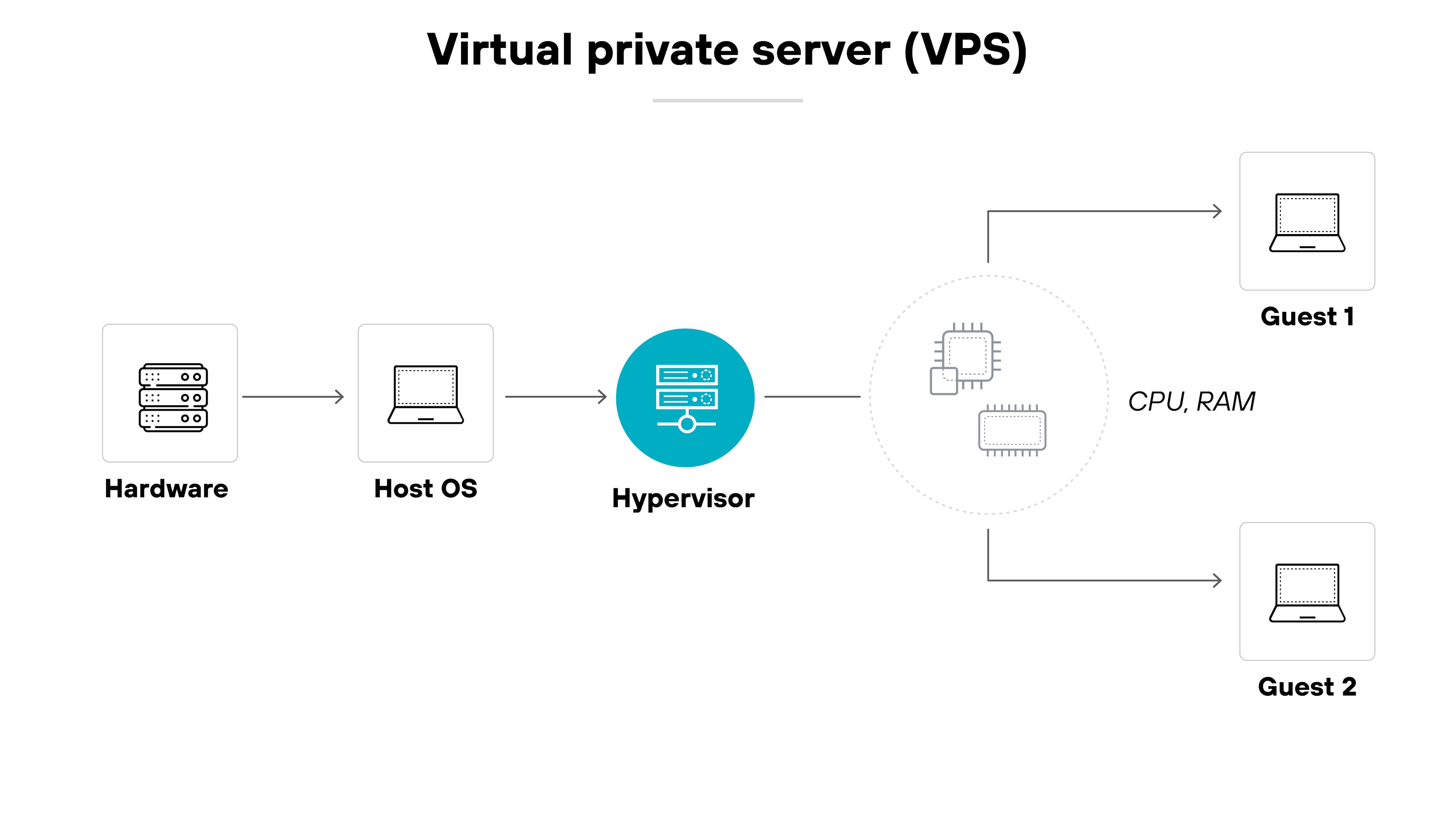
A VPC, on the other hand, is a virtual private cloud. It’s a private segment of a public cloud provider’s infrastructure.
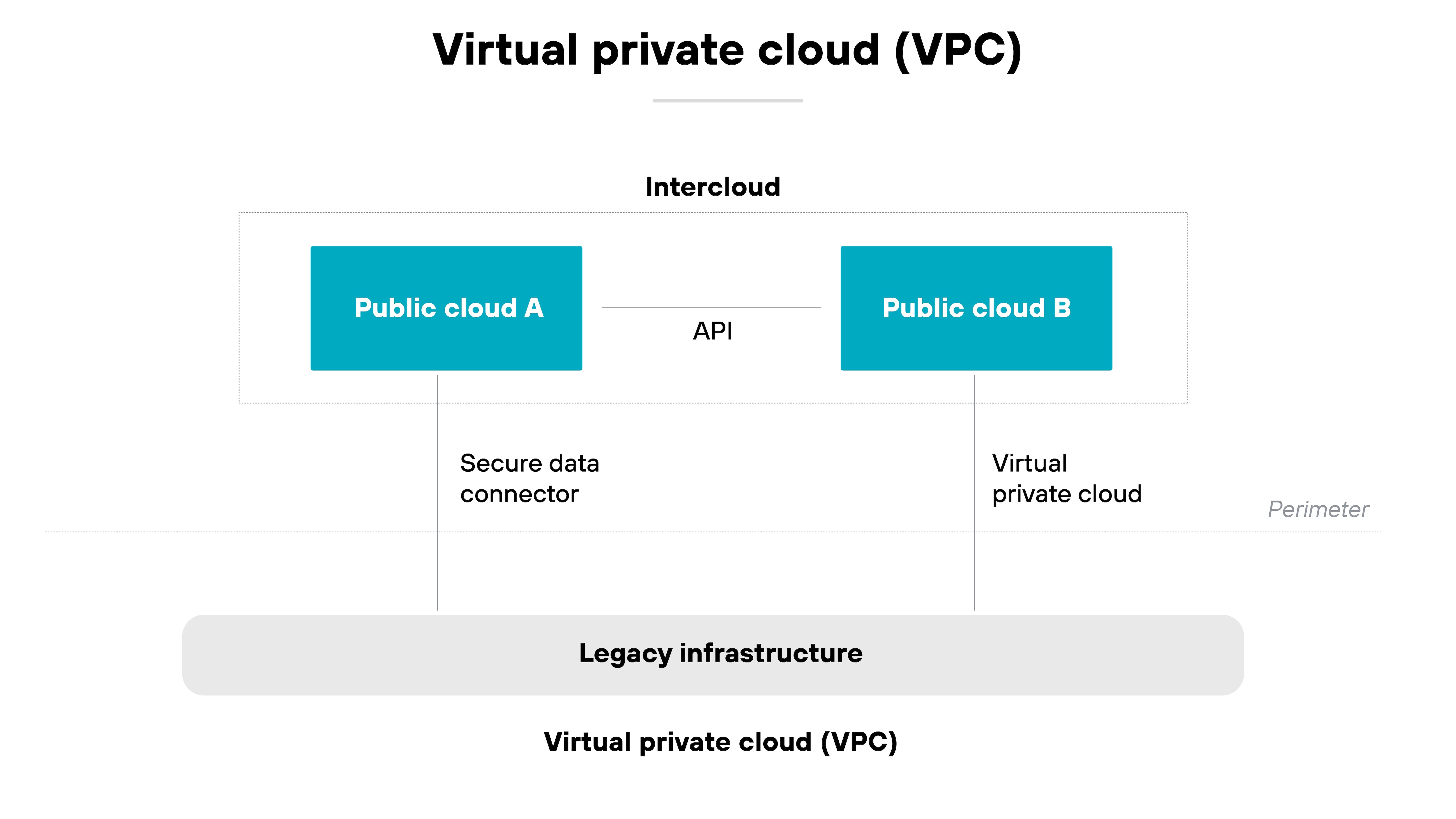
It gives organizations an isolated network environment where they can run cloud-based resources securely and with more control over configuration.
| Further reading: VPC vs. VPN vs. VPS: What Are the Differences?
What is the history of VPNs?
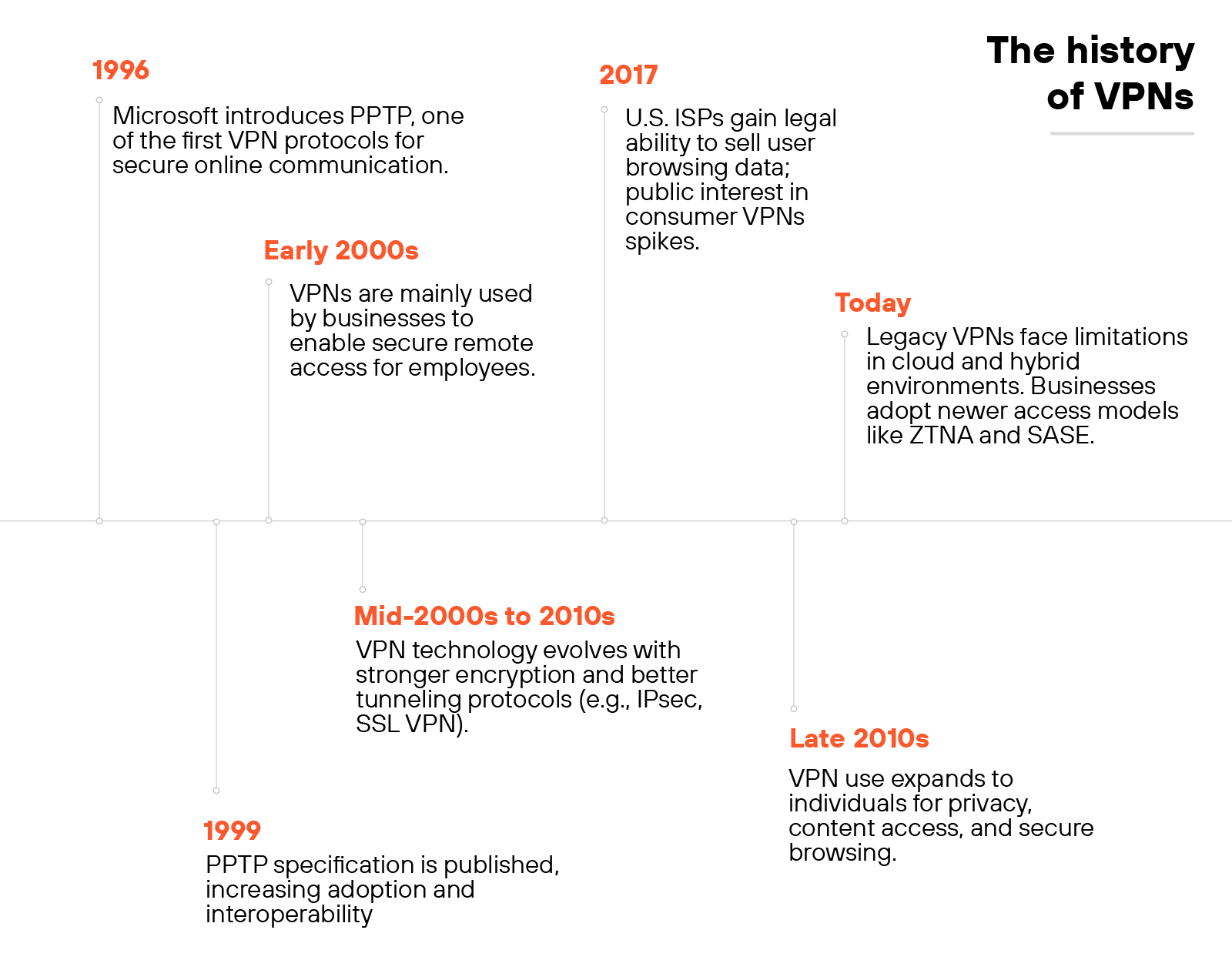
Microsoft introduced the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) in 1996. This early protocol marked the beginning of modern VPNs by enabling encrypted internet connections between user devices and networks. By 1999, the PPTP specification became publicly available.
In the early 2000s, virtual private networks were primarily used by businesses. Organizations deployed them to give remote employees secure access to internal systems and files.
The connection acted as an extension of the corporate network, making it easier to share resources across locations.
As internet use expanded, VPN protocols evolved. New standards offered stronger encryption and more reliable tunneling. These improvements addressed growing concerns around online threats, data interception, and privacy.
Public interest in VPNs grew in response to major privacy events.
In 2017, news broke that U.S. internet service providers could legally sell users’ browsing histories. That moment brought broader attention to VPNs as a privacy tool.
While national net neutrality protections were rolled back, some U.S. states responded with local legislation. As a result, VPNs became more common among individual users—not just businesses.
Today, traditional VPNs don’t always meet the needs of hybrid or cloud-first environments.
Many lack the flexibility to connect users directly to applications without increasing risk or slowing down performance.
Organizations are now looking to simpler, more integrated solutions that combine access and security in a single product.
| Further reading: What Is the History of VPN?
A VPN encrypts internet traffic and hides your IP address. It helps protect personal data on public Wi-Fi and reduces tracking. For businesses, it secures remote access to corporate resources and supports secure site-to-site communication.
VPN stands for virtual private network, which allows users to create a secure connection to another network over the internet.
The definition of “VPN” is: a technology that establishes a secure connection over a public network, such as the internet, allowing enterprises to access their private networks remotely.
VPN protection refers to the enhanced security and privacy features provided by a Virtual Private Network.
VPN security refers to the suite of protocols, encryption standards, and practices that ensure operation is secure.
Virtual private networks are valuable security tools that encrypt data and mask users' IP addresses, enhancing online privacy and safety. However, while they contribute significantly to a layered security approach, they do not offer complete protection on their own. it is essential to complement usage with other security measures for comprehensive defense.
"VPN access" refers to the ability to connect securely to a remote network or system using a virtual private network.
In business, a VPN’s purpose is to establish a secure, encrypted connection, allowing companies to protect data and enable remote access. There are also consumer-facing services, usually consisting of a VPN app designed to hide your IP address.
Virtual private networks (VPN) are useful for secure remote access, advanced threat protection, url filtering, BYOD policies, and Zero Trust implementation.
Yes, virtual private networks are necessary to safeguard sensitive data, provide secure remote access to internal resources, enhance online privacy, and ensure consistent access to global content, especially in environments where data security and privacy are paramount.
VPNs are critically important to ensuring company data security.
A business VPN establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a company's network and remote users. It allows employees to access internal resources safely from anywhere, masking their IP address and protecting data transfers from eavesdropping. The server verifies user credentials, ensuring only authorized personnel can connect, thus maintaining the organization's cybersecurity and data integrity.
A VPN connection works by establishing an encrypted tunnel between a user's device and a virtual private network server. Data sent through this tunnel is encrypted, ensuring privacy and security. The user's IP address is masked, appearing as the server's address, which safeguards the user's identity and location.
No, not all VPNs work the same. While the core principle of encrypting data and masking IP addresses is consistent, virtual private networks can differ in terms of protocols used, encryption standards, server locations, and features offered.
For businesses, the type of virtual private network to use depends on specific needs. To connect remote employees to company resources, a remote access solution is ideal. For linking multiple office locations, a site-to-site solution is recommended.
The most popular types of virtual private networks for businesses are site-to-site and remote access. Site-to-site VPNs connect entire networks to each other, commonly used to link branch offices to a central office. Remote access VPNs allow individual users to connect to a business network from remote locations. The choice depends on business needs, such as remote worker support or inter-office connectivity.
Choose a reputable VPN provider, sign up for a plan, then download and install the app on your device. After logging in, select a server and connect. You can also configure VPNs manually on supported operating systems.
Some VPNs are free, but they often have limitations like slower speeds or less privacy. Many free providers monetize data or include ads. Paid services usually offer stronger privacy protections, better performance, and more features.
VPNs do not provide full security on their own. They don’t block malware or stop threats after they reach a device. Some services may also reduce internet speed or have unclear logging policies, especially free options.
Prices vary by provider. Consumer VPNs typically cost around $10 per month, with discounts for annual plans. Business VPN pricing depends on features, scale, and support needs, often with additional costs for setup or user volume.
A personal VPN can help protect your data on home networks, reduce ISP tracking, and support access to restricted content. While not required, it can improve privacy and security, especially for users concerned about online visibility.
