- 1. Do enterprises still need MPLS in the age of SD-WAN?
- 2. How does SD-WAN differ from MPLS in architecture and operation?
- 3. Which is more reliable, MPLS or SD-WAN?
- 4. How secure is SD-WAN compared to MPLS?
- 5. Is SD-WAN really cheaper than MPLS?
- 6. Can SD-WAN replace MPLS, or do they coexist?
- 7. What's the future of SD-WAN vs. MPLS?
- 8. SD-WAN vs. MPLS FAQs
- Do enterprises still need MPLS in the age of SD-WAN?
- How does SD-WAN differ from MPLS in architecture and operation?
- Which is more reliable, MPLS or SD-WAN?
- How secure is SD-WAN compared to MPLS?
- Is SD-WAN really cheaper than MPLS?
- Can SD-WAN replace MPLS, or do they coexist?
- What's the future of SD-WAN vs. MPLS?
- SD-WAN vs. MPLS FAQs
SD-WAN vs. MPLS: Reliability, Security, Cost, and the Future
- Do enterprises still need MPLS in the age of SD-WAN?
- How does SD-WAN differ from MPLS in architecture and operation?
- Which is more reliable, MPLS or SD-WAN?
- How secure is SD-WAN compared to MPLS?
- Is SD-WAN really cheaper than MPLS?
- Can SD-WAN replace MPLS, or do they coexist?
- What's the future of SD-WAN vs. MPLS?
- SD-WAN vs. MPLS FAQs
The difference between MPLS and SD-WAN is that MPLS forwards traffic with label switching over carrier circuits, while SD-WAN directs traffic with software-defined policies across diverse links.
MPLS achieves reliability through reserved network paths and carrier quality of service. SD-WAN achieves flexibility through centralized control, dynamic path selection, and integration with cloud applications.
Do enterprises still need MPLS in the age of SD-WAN?
MPLS became the backbone of enterprise WANs in the early 2000s.
It offered predictable latency, high availability, and strong quality of service. Service providers built global backbones on MPLS because enterprises needed private, reliable connections for voice, video, and business-critical applications.
For many years, this made MPLS the default WAN choice.
It delivered performance guarantees that the public internet could not match. Carrier SLAs reinforced this reliability, and global reach gave large enterprises confidence in using MPLS for their distributed operations.
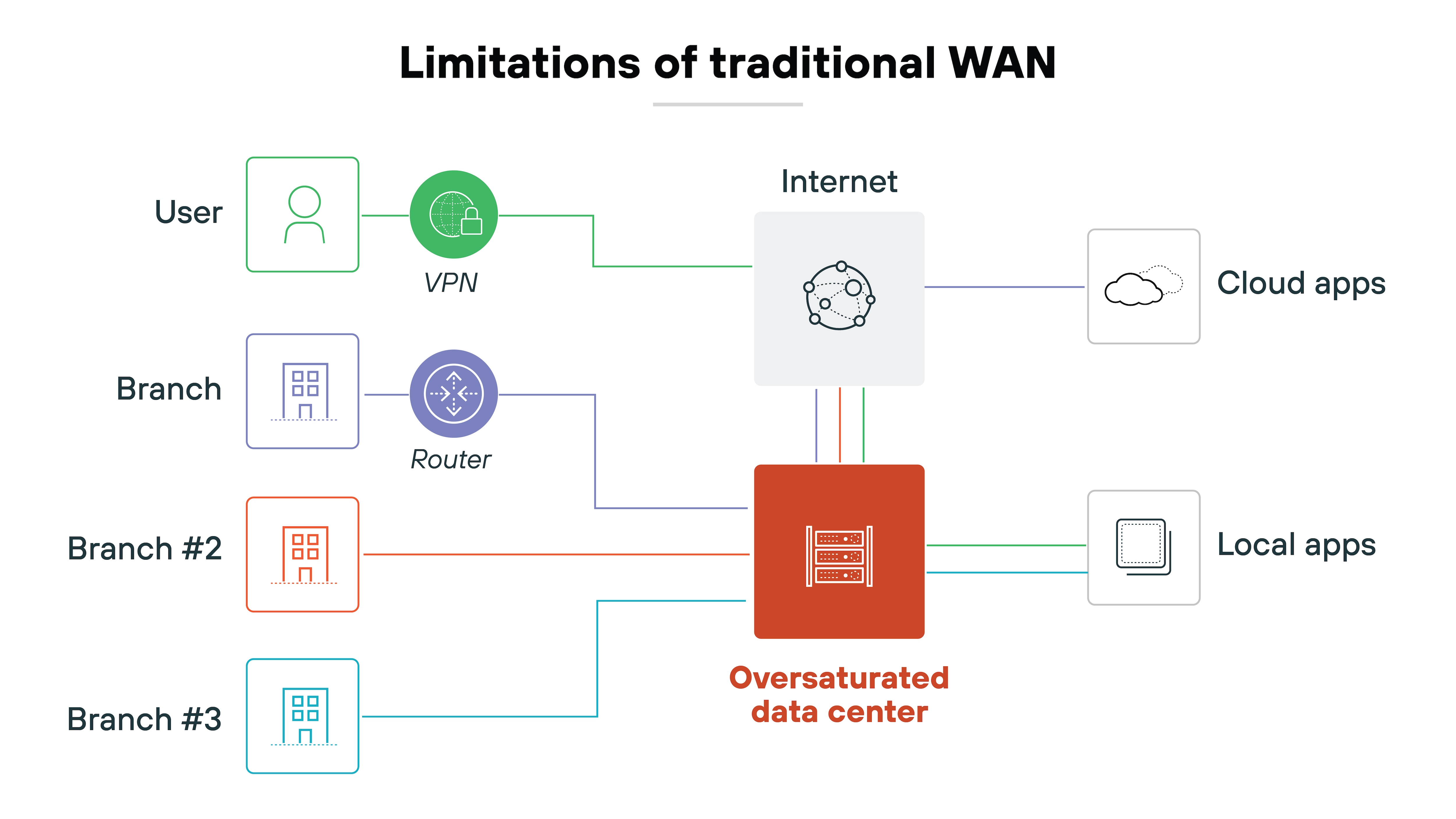
However: The role of MPLS has shifted.
Modern networks are cloud-first. Applications run in SaaS platforms or public cloud, not only in central data centers.
Backhauling all that traffic over MPLS adds latency and cost. Enterprises also expect agility. Provisioning MPLS circuits often takes months.
SD-WAN, in contrast, can bring new sites online in days and route directly to the cloud.
Important: MPLS isn't irrelevant.
Some industries still value it for deterministic performance. Financial trading, healthcare imaging, and real-time collaboration can still benefit from reserved, private paths.
At the same time, many organizations reduce their MPLS footprint by offloading SaaS and branch traffic to SD-WAN.
In other words: MPLS is no longer the automatic answer.
SD-WAN now covers most enterprise needs with more flexibility and lower cost. But MPLS remains in use for specific workloads and locations.
The reality for many enterprises is a hybrid WAN, where MPLS and SD-WAN operate side by side until the business no longer requires carrier-grade predictability.
How does SD-WAN differ from MPLS in architecture and operation?
MPLS and SD-WAN approach wide area networking in very different ways.
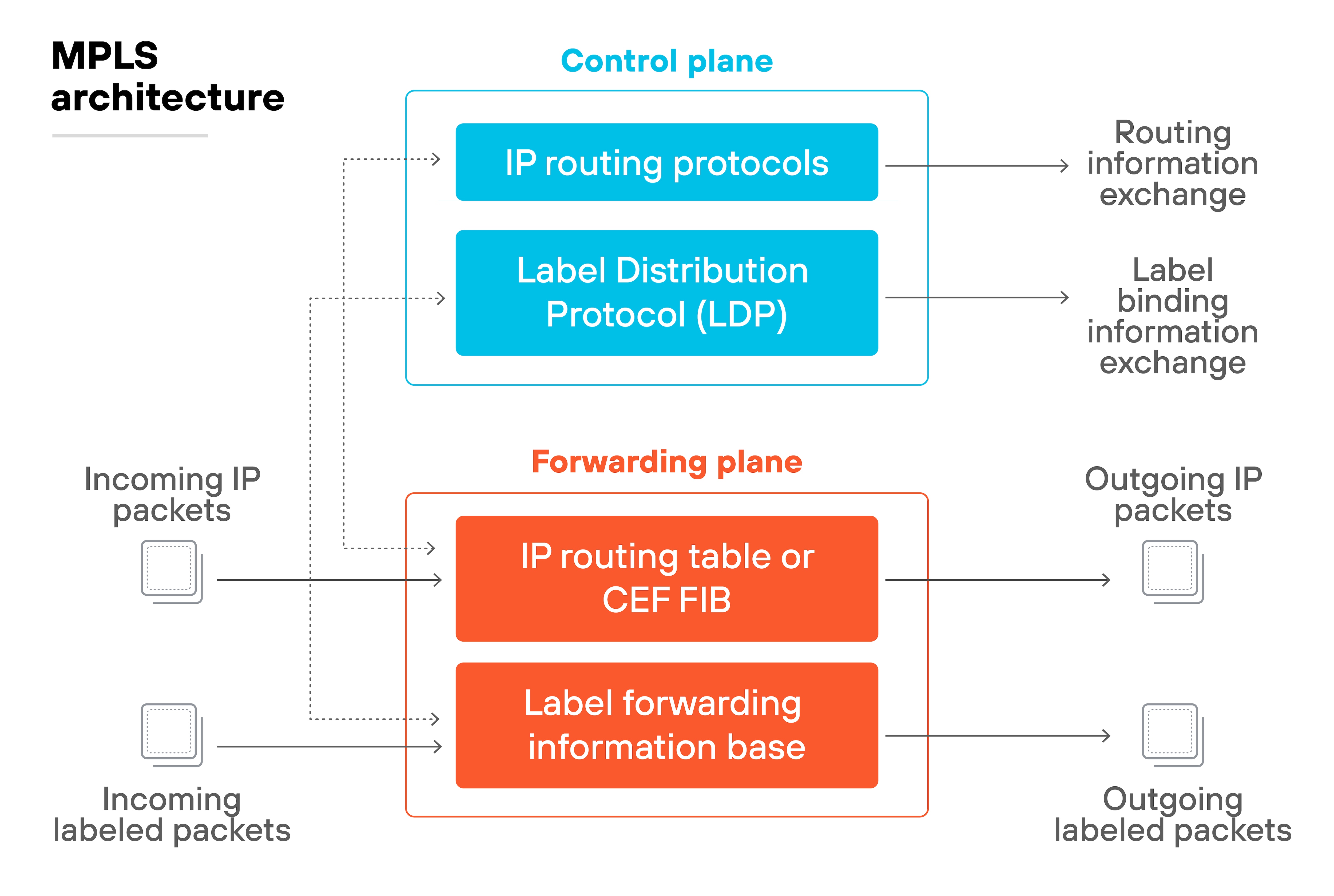
MPLS relies on private circuits and forwards traffic using label switching.
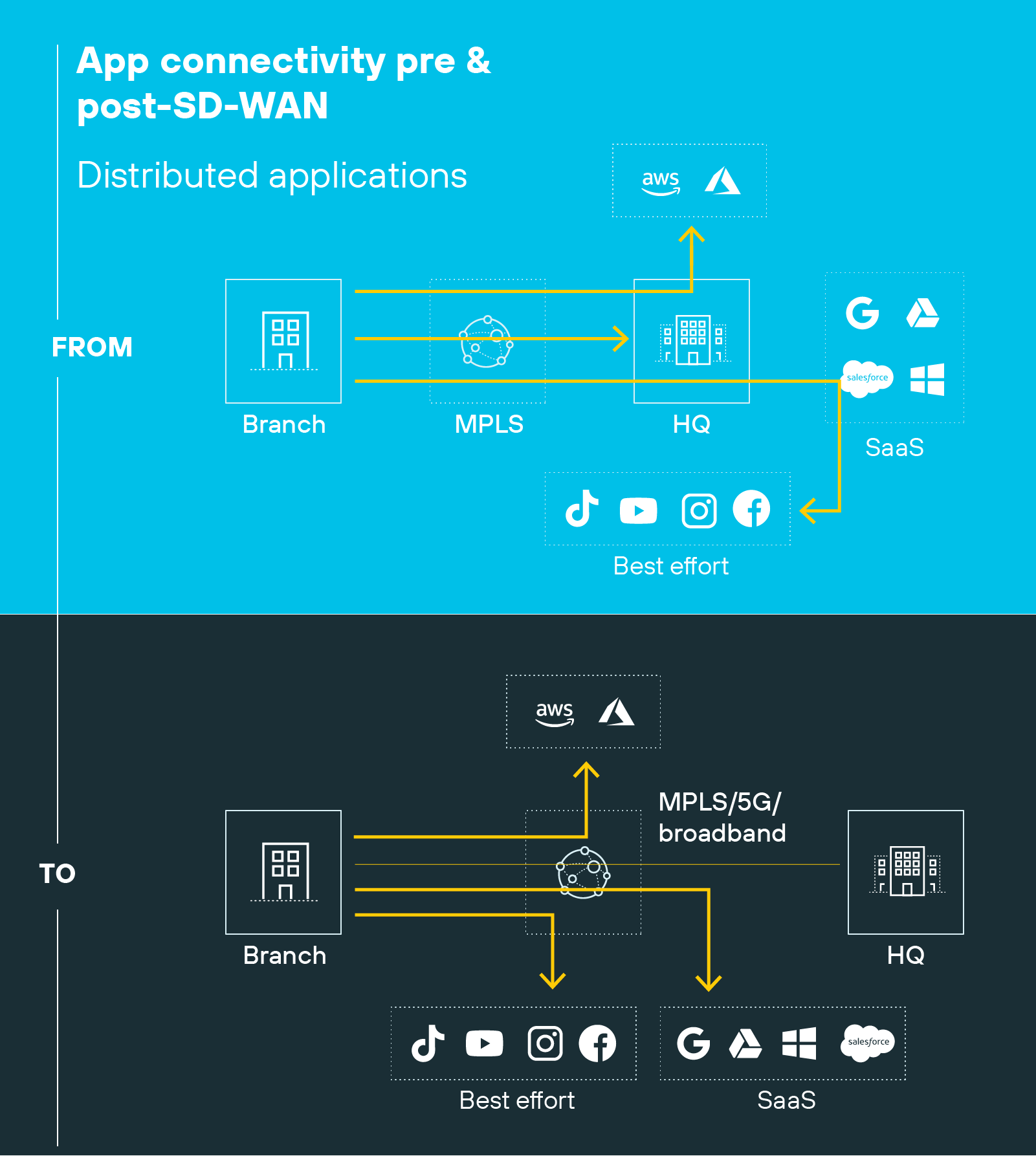
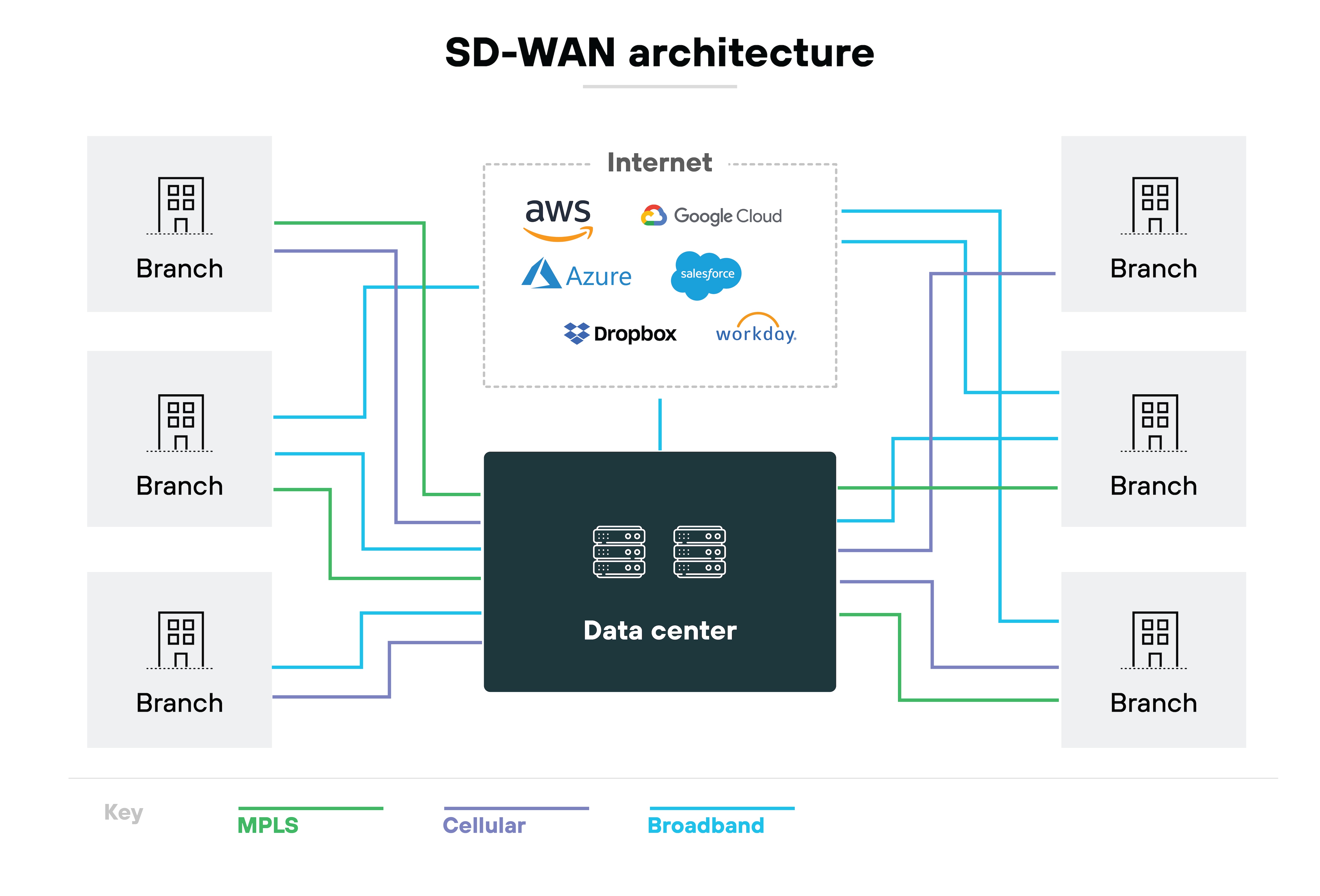
SD-WAN creates a software overlay that runs on top of any transport, including broadband, LTE, or even MPLS itself.
Here's why that matters:
MPLS architecture is hardware-centric.
The carrier provisions dedicated links and enforces routing across its backbone. Policies are tied to those circuits. In contrast, SD-WAN separates the control and data plane. It uses centralized software to steer traffic dynamically across multiple paths.
Traffic handling is another key distinction.
MPLS uses class of service settings defined by the carrier to prioritize voice, video, and other critical flows. These priorities remain static once configured. SD-WAN measures link conditions in real time. It can shift traffic based on latency, jitter, or packet loss. Which means: applications get the best available path at that moment.
Provisioning also differs sharply.
Adding or changing MPLS circuits can take weeks or months. SD-WAN overlays can be deployed in days. New sites can join simply by connecting an edge device or vCPE to the controller. That difference in speed directly impacts how fast an enterprise can adapt its WAN.
Management is equally important.
With MPLS, the service provider manages the network and applies policies. Enterprise IT teams depend on carrier processes for every change. With SD-WAN, control is returned to the enterprise. Administrators can define policies centrally and push them to all sites instantly.
- What Is an SD-WAN Appliance? | SD-WAN Hardware & Equipment
- What Is an SD-WAN Gateway? | Definition, Explanation, Use Cases
- Types of SD-WAN Deployment Models: A Complete Guide
Which is more reliable, MPLS or SD-WAN?
MPLS has long been known for reliability.
It provides deterministic performance on latency, jitter, and packet loss. That reputation comes from its design. Traffic travels on private circuits with reserved bandwidth, and carriers guarantee delivery through service level agreements (SLAs).
SD-WAN works differently.
It doesn't reserve private paths. Instead, it uses multiple links at once and constantly measures their performance. If latency spikes or a line fails, traffic can move to a healthier path automatically. It uses multipath. It monitors links in real time. It fails over automatically. That gives SD-WAN resilience in practice.
| Reliability: MPLS vs. SD-WAN |
|---|
| Aspect | MPLS reliability | SD-WAN reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Performance basis | Deterministic, with fixed latency, jitter, and packet loss | Adaptive, based on real-time monitoring of multiple links |
| Traffic handling | Reserved bandwidth over private circuits | Dynamic path selection with multipath and failover |
| Guarantees | Backed by carrier SLAs | Dependent on overlay intelligence and underlay quality |
| Best fit | Mission-critical apps where every millisecond counts (e.g., trading, imaging) | Branch SaaS, cloud apps, and general business traffic |
Here's why this matters:
MPLS reliability is contractual. The carrier is obligated to deliver the promised quality. SD-WAN reliability is adaptive. It depends on the intelligence of the overlay and the quality of available underlay connections.
So which is more reliable? It depends on the workload.
For a trading floor or medical imaging system, MPLS may still be the safer choice because every millisecond counts. For branch offices using SaaS, SD-WAN may be more effective. It provides enough consistency for cloud applications while avoiding MPLS provisioning delays and costs.
On the other hand, many enterprises find that a mix works best.
MPLS remains in place for mission-critical flows. SD-WAN carries the bulk of everyday business traffic. That balance lets organizations get deterministic reliability where it matters and adaptive reliability everywhere else.
See it in action
Book a personalized Prisma SD-WAN demo to see how it supports your network's reliability and applications.
Request demoHow secure is SD-WAN compared to MPLS?
MPLS has often been described as secure because it runs on private circuits.
But that security is limited. MPLS isolates traffic from other customers, yet it does not encrypt the data. If someone gained access inside the provider's backbone, the traffic would be visible.
SD-WAN approaches security differently.
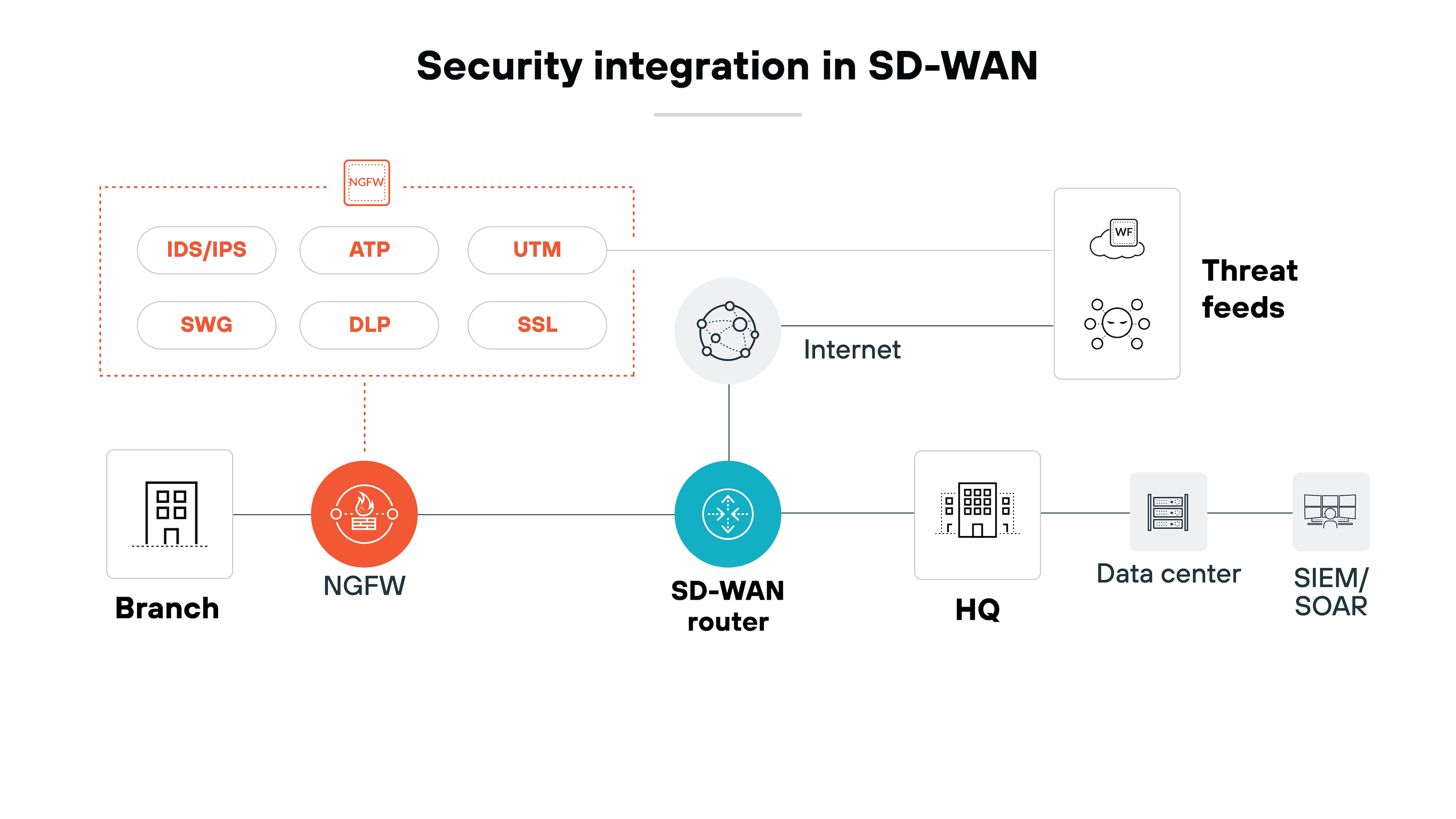
Every connection is built over encrypted tunnels. This ensures that data stays protected even when the underlying transport is the public internet.
Many SD-WAN solutions also integrate firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS) or are delivered as part of a larger secure access service edge (SASE) framework. Which means: security is embedded more directly into the architecture.
Here's why this comparison matters:
MPLS is private but not inherently secure. It depends on trust in the carrier and physical isolation. SD-WAN is not private by default but compensates with encryption and layered security controls.
Both models still require a defense-in-depth approach. Enterprises often deploy additional firewalls, intrusion detection, or monitoring alongside either option.
On the other hand, SD-WAN gives enterprises more direct visibility into security policies.
They can manage segmentation, apply application-level controls, and tie network access into identity systems. MPLS leaves these tasks outside its scope.
The takeaway: MPLS provides privacy through isolation, while SD-WAN provides confidentiality through encryption and integrated controls.
Neither is enough on its own, but SD-WAN better aligns with the security needs of cloud-first and distributed environments.
- How Are Firewalls and SD-WAN Related?
- What Is SD-WAN Security? | SD-WAN Security Considerations
- What Is SASE (Secure Access Service Edge)? | A Starter Guide
Is SD-WAN really cheaper than MPLS?
MPLS has always carried a high price tag.
The main reason is recurring circuit costs. Carriers lease private lines, and enterprises pay a premium for guaranteed performance. Provisioning is also inflexible. Adding or changing circuits often takes months, which adds to both direct and indirect costs.
SD-WAN is often presented as the cheaper option.
It can aggregate lower-cost internet and broadband links to replace or supplement MPLS. That shift usually reduces the recurring expenses tied to private circuits. On the surface, it looks like clear savings.
However: SD-WAN is not free of costs.
Licenses for the software overlay must be purchased. Edge devices or virtual CPEs are required at each site. If a managed service is chosen, ongoing fees are added. Which means: the savings are not absolute. They depend on how the solution is deployed and consumed.
Here's why this matters:
Total cost cannot be measured by circuits alone.
Management overhead, agility, and opportunity costs all factor in. MPLS is slower to provision, which can delay branch rollouts or cloud migrations. SD-WAN enables faster deployment and direct-to-cloud access, which reduces operational costs over time.
In practice, many enterprises find that the agility and flexibility of SD-WAN offset its licensing and hardware costs.
The takeaway: SD-WAN is often less expensive in the long run. But the actual cost advantage depends on the mix of transport, licensing model, and management approach an enterprise selects.
Can SD-WAN replace MPLS, or do they coexist?
SD-WAN often enters the picture as a replacement for MPLS. But in practice, most networks operate the two in parallel.
Here's why:
MPLS has long been valued for its reliability. Enterprises rely on it for mission-critical applications that demand predictable performance.
At the same time, SD-WAN provides flexibility. It can route SaaS and cloud traffic directly over the internet, reduce dependence on carrier circuits, and connect branch sites faster.
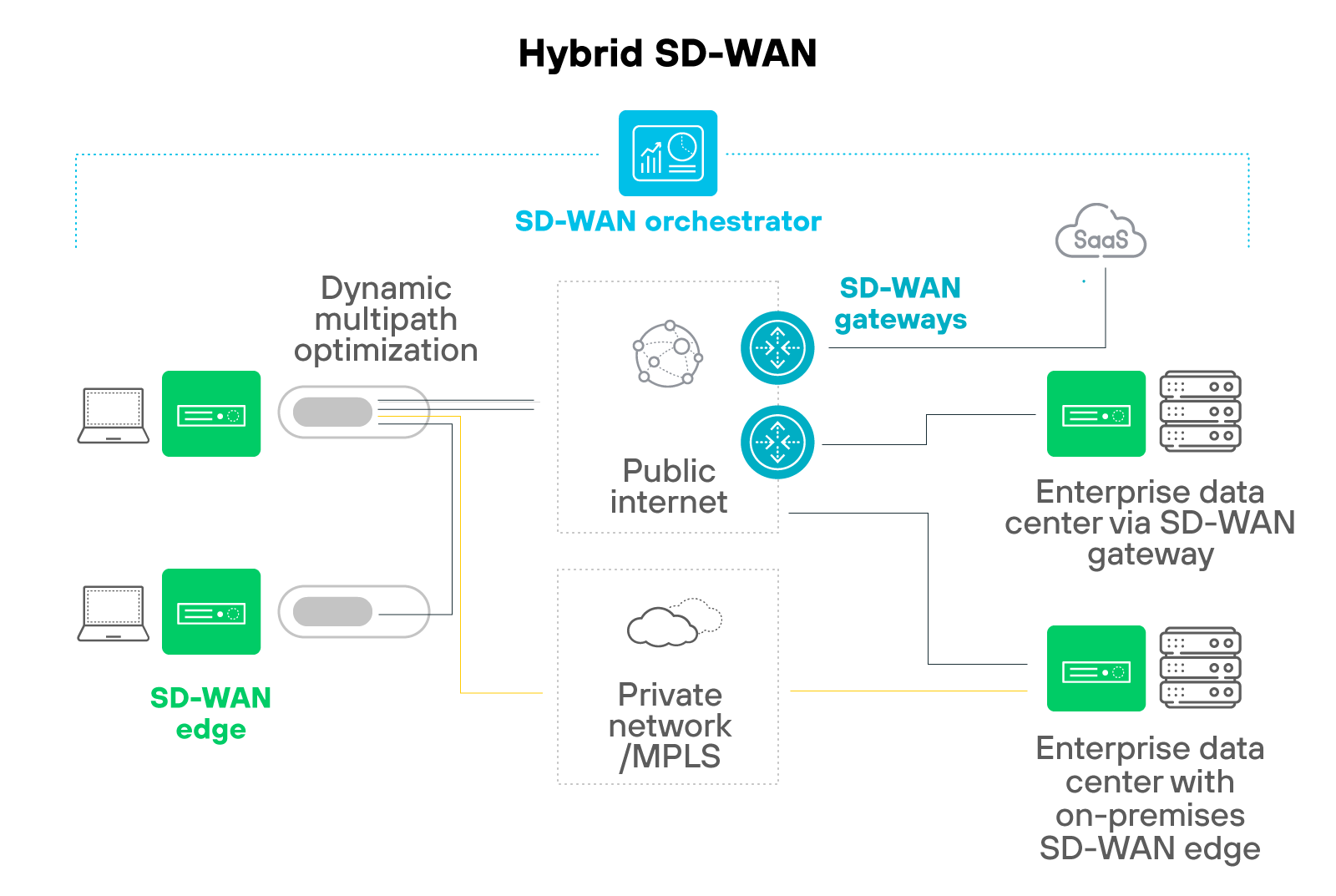
The result is a hybrid WAN.
MPLS stays in place for workloads that need strict guarantees. SD-WAN handles traffic that benefits from agility and cost efficiency. This coexistence gives IT teams a balance of performance and adaptability.
Migration strategies reflect this reality.
Few organizations make a clean cut from MPLS to SD-WAN. Instead, they phase in SD-WAN across sites, monitor performance, and keep rollback options available. Over time, MPLS contracts may be reduced as more traffic shifts to SD-WAN overlays.
On the other hand: MPLS is not disappearing.
Many enterprises will maintain a blend, using SD-WAN for scale and cloud reach while retaining MPLS where deterministic delivery is non-negotiable.
In other words: SD-WAN can replace MPLS in some cases. But for most, they coexist during transition—and sometimes for the long term.
What's the future of SD-WAN vs. MPLS?
MPLS is shrinking. But it's not disappearing.
Many enterprises are reducing MPLS to a smaller role—often just for mission-critical traffic. At the same time, they are bringing in SD-WAN as the primary transport layer or running both in hybrid mode. This coexistence helps avoid disruption and provides a smooth transition.
On the other hand, SD-WAN is quickly becoming the base for secure edge architectures. It ties into cloud adoption, zero trust, and SASE. Which means: most future-facing strategies are being built with SD-WAN at the core.
The path forward is likely gradual. First hybrid—where MPLS and SD-WAN run together during transition.. Then internet-first, where broadband, fiber, and wireless links replace MPLS as the dominant transport. And eventually, a secure edge model where SD-WAN integrates with broader SASE frameworks for policy enforcement and security at every point of access.
Important: MPLS still offers guaranteed performance through SLAs, and in some regions, it remains the most reliable option. That's why MPLS won't vanish overnight.
To sum it up: enterprises are moving toward SD-WAN because it's flexible, cost-efficient, and cloud-ready. But MPLS will continue to play a supporting role for years to come, especially where performance guarantees are critical.
Try it in your network
Start a Prisma SD-WAN free trial to test reliability and application performance in your environment.
Start free trialSD-WAN vs. MPLS FAQs
SD-WAN is not replacing MPLS entirely, but it is becoming a popular alternative for certain use cases.
SD-WAN offers cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and improved performance for cloud-based applications, making it an attractive choice for organizations seeking to optimize their WAN connectivity.
However, MPLS still has its advantages in terms of reliability, security, and dedicated connections, making it suitable for specific applications and organizations with specific requirements.
- Operational simplicity
- Carrier-Independent WAN connectivity
- Improved performance
- Cost savings
- Improved connectivity
- Increased security
- Improved reliability
- Higher cost
- Limited flexibility
- Longer deployment times
- Centralized architecture limitations
- Limited visibility and control
