- 1. What is the difference between 4G and 5G security?
- 2. What makes 5G networks harder to secure?
- 3. What exactly needs protecting in a 5G network?
- 4. What are the biggest 5G security risks?
- 5. What security features are built into 5G?
- 6. Who's responsible for keeping 5G secure?
- 7. Which environments demand the strongest 5G security?
- 8. What's next for 5G security?
- 9. 5G security FAQs
- What is the difference between 4G and 5G security?
- What makes 5G networks harder to secure?
- What exactly needs protecting in a 5G network?
- What are the biggest 5G security risks?
- What security features are built into 5G?
- Who's responsible for keeping 5G secure?
- Which environments demand the strongest 5G security?
- What's next for 5G security?
- 5G security FAQs
What Is 5G Security? A Primer on 5G Network Security
- What is the difference between 4G and 5G security?
- What makes 5G networks harder to secure?
- What exactly needs protecting in a 5G network?
- What are the biggest 5G security risks?
- What security features are built into 5G?
- Who's responsible for keeping 5G secure?
- Which environments demand the strongest 5G security?
- What's next for 5G security?
- 5G security FAQs
5G security is the protection of 5G network infrastructure, data traffic, and connected users from cyber and physical threats.
It addresses the expanded attack surface introduced by virtualization, cloud-native functions, and software-defined components.
Effective 5G security requires securing both the network architecture and the services built on top of it.
What is the difference between 4G and 5G security?
5G introduces major architectural changes that impact how networks must be secured. Unlike 4G, which is hardware-based and centrally managed, 5G relies on virtualization, software-defined components, and distributed infrastructure.
This shift increases flexibility but also broadens the attack surface.
In 4G networks, most functions are integrated and vendor-controlled. Components operate within a fixed system, and traffic flows through well-defined paths.
That setup makes it easier to enforce uniform security. The system is simpler. And the risks are easier to isolate.
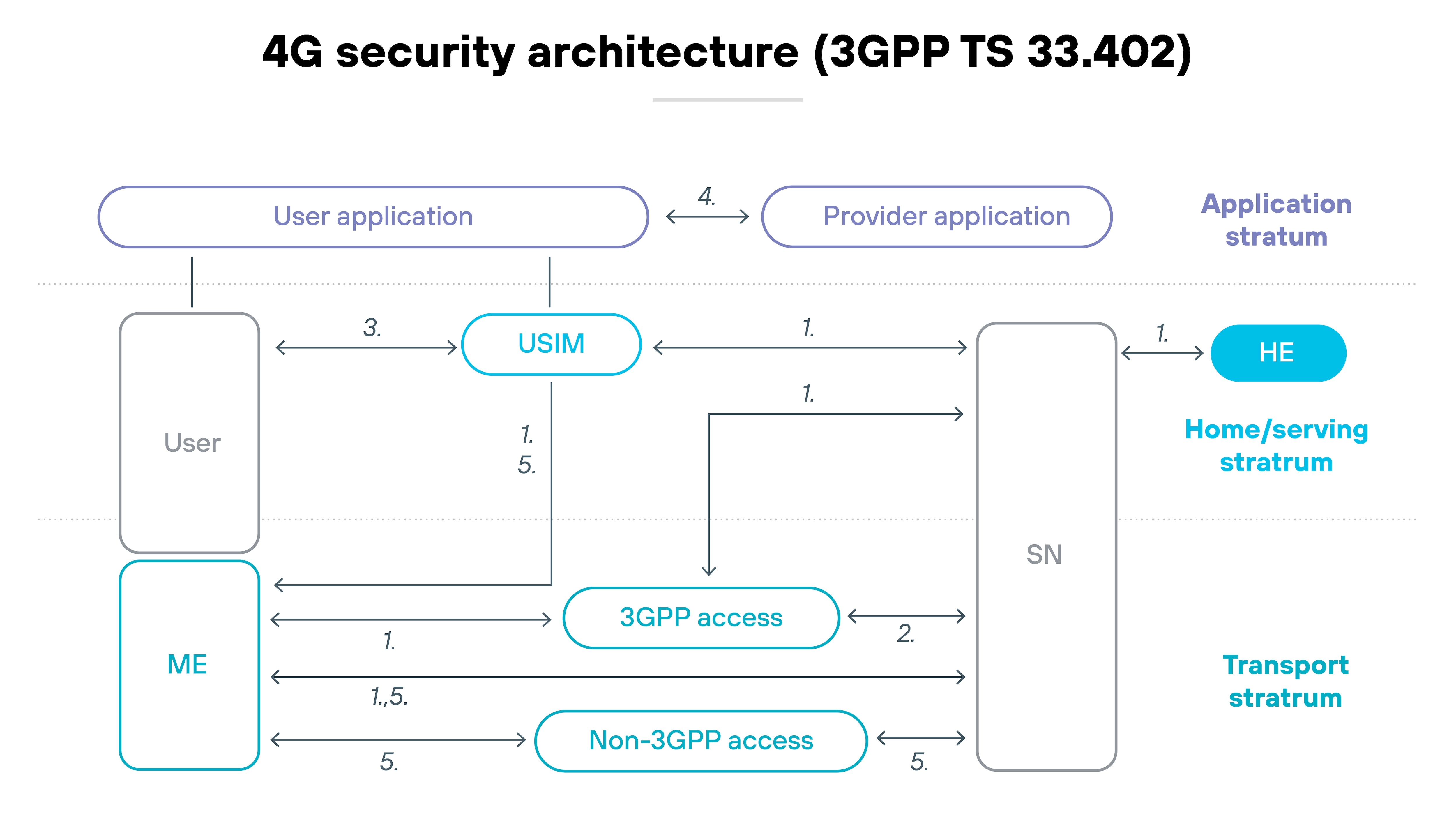
5G is different.
Its core is disaggregated. Functions run as virtual machines or containers on shared infrastructure. Interfaces are open. And deployment spans across public and private clouds.
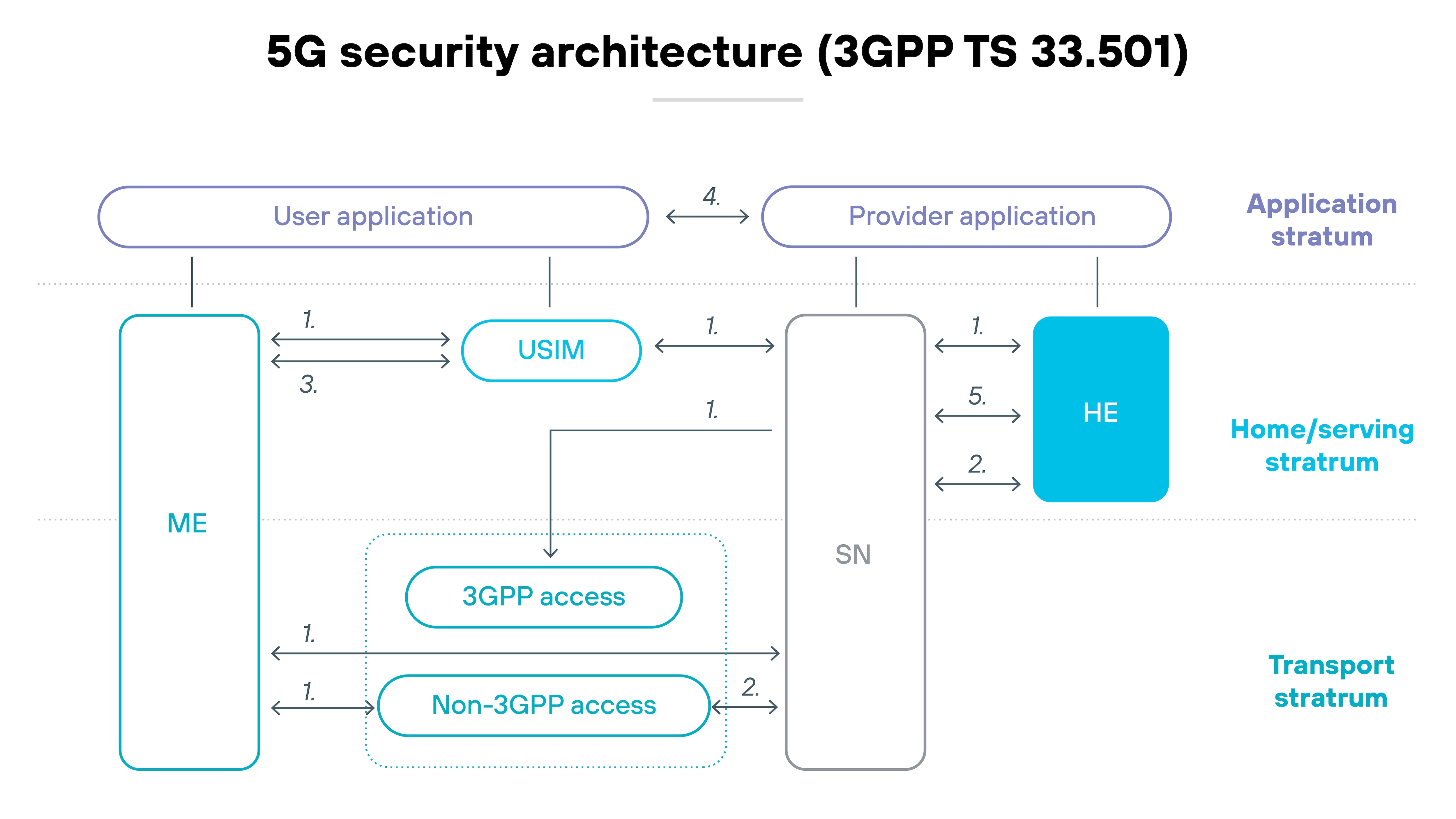
Which means: New vulnerabilities emerge at each layer. Security controls must now account for lateral movement, misconfigurations, and exposure across multiple domains.
The model that worked for 4G doesn't scale to 5G without change.
What makes 5G networks harder to secure?
5G introduces new technologies that break from the more contained and predictable architecture of previous generations.
In 4G, most core functions are centralized and run on purpose-built hardware. That makes traffic flow easier to track and control. And it gives network operators clear boundaries for implementing security.
5G is different. It's decentralized, software-defined, and often cloud-hosted. Functions are virtualized and spread across shared infrastructure. Control moves closer to the edge. Open RAN replaces proprietary hardware. And interfaces between components are no longer vendor-specific.
Here's why that matters:
The system becomes more flexible—but also more complex. The shift expands the number of exposed interfaces. It creates new dependencies between vendors and layers. And it introduces more risk of misconfiguration or lateral movement.
Network slicing adds another layer. Each slice is logically separate and tailored for a specific use case. But each slice also requires its own controls. Which means the number of policies, users, and traffic flows to secure increases significantly.
The net result:
Security has to scale across more parts of the system. And traditional perimeter-based approaches no longer apply. Instead, operators and enterprises need deeper visibility, more automation, and architecture-aware policies that account for the way 5G is built.
What exactly needs protecting in a 5G network?
Securing a 5G network requires protection at multiple layers.
These include the physical and virtual infrastructure, the data and signaling traffic it carries, and the users and devices that connect to it.
Each area introduces its own set of exposure points and operational considerations:
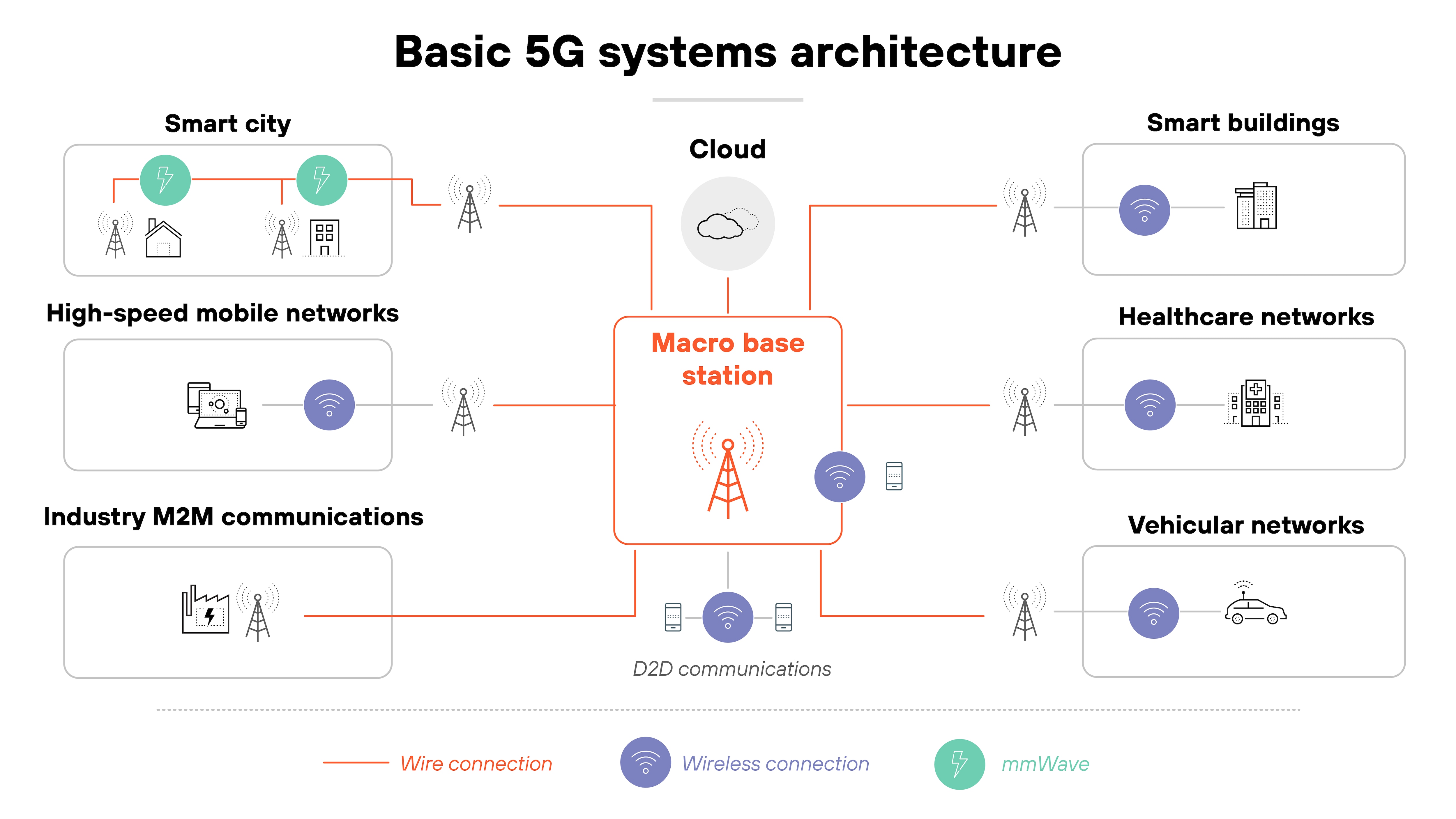
Start with the infrastructure.
In 5G, this includes base stations, radio units, edge computing nodes, and the virtualized functions that operate in cloud environments. Because many of these components are disaggregated and software-defined, they can be hosted in public, private, or hybrid environments.
![Architecture diagram titled 'Basic 5G systems architecture' featuring a central red-outlined box labeled 'Macro base station' with red lines branching out as wire connections to various network types and a cloud icon above labeled 'Cloud.' On the left, three rectangular zones represent 'Smart city' with buildings, a light pole, and a factory connected by mmWave and wireless links; 'High-speed mobile networks' with a smartphone and wireless signal; and 'Industry M2M communications' with machines and control panels connected by wire. On the right, three zones labeled 'Smart buildings,' 'Healthcare networks,' and 'Vehicular networks' include icons such as offices, hospital equipment, and a car, all connected to the macro base station via wireless links. At the bottom center, several wireless nodes surrounding the macro base station are labeled 'D2D communications' and represent direct wireless links between devices. A legend at the bottom indicates red lines for 'Wire connection,' purple icons for 'Wireless connection,' and teal icons for 'mmWave.'']()
Which means infrastructure protection must account for both physical tampering and unauthorized access to virtualized assets.
Then there's the traffic.
That includes both user data and control plane signaling. These elements move across a network made up of multiple domains, operators, and services. Without proper segmentation and encryption, attackers may intercept or manipulate traffic.
It's also possible for traffic flows to reveal sensitive patterns if metadata is not sufficiently protected.
Finally, the users.
Devices on 5G networks span a wide range of types and capabilities. From smartphones and laptops to IoT sensors and industrial equipment. This variety increases the number of potential entry points.
And some use cases require extremely low latency, which limits how much delay security controls can introduce. Authentication, access management, and privacy safeguards must be adapted based on device type, use case, and trust level.
In other words:
What needs protecting in 5G is not just the core network. It's the full operational chain—from how traffic moves to who or what connects to it. And each part must be addressed in a way that reflects how modern 5G networks are actually deployed.
What are the biggest 5G security risks?

5G opens the door to new capabilities—but also new attack surfaces. The architecture introduces risks that didn't exist, or didn't matter as much, in earlier generations.
In short: 5G security risks reflect how the network is built—cloud-native, disaggregated, and programmable. Understanding the attack surface is the first step toward protecting it.
Here are the most critical ones to understand:
Rogue slices
Network slicing isolates traffic into virtual networks tailored to specific needs. But if a slice is misconfigured or hijacked, it can bypass shared controls. That creates a security gap that's hard to detect and easy to exploit.
Cloud misconfigurations
5G functions rely heavily on virtualized infrastructure and cloud services. A misconfigured API, unpatched container, or overly permissive access policy can expose critical systems. These issues often originate outside the traditional telecom perimeter.
Side-channel attacks
Attackers don't always need to breach software. In some cases, they can extract information from indirect signals like timing, power, or memory usage. In 5G, dense edge deployments and shared resources can increase exposure to these types of attacks.
Denial-of-service (DoS)
Availability is a core service goal in 5G. But that also makes it a target. Attackers may flood network slices, jam radio access channels, or overload APIs. Without safeguards, even short outages can disrupt critical applications.
Eavesdropping and traffic analysis
Encryption protects data in transit—but not always metadata. Attackers who observe traffic patterns can infer user behavior, location, or application type. In dense networks, this can lead to privacy violations even without decrypting payloads.
Meddler-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
In some cases, attackers may intercept or manipulate traffic between endpoints. This can happen through rogue base stations or weak mutual authentication. If successful, MITM attacks can compromise both confidentiality and integrity.
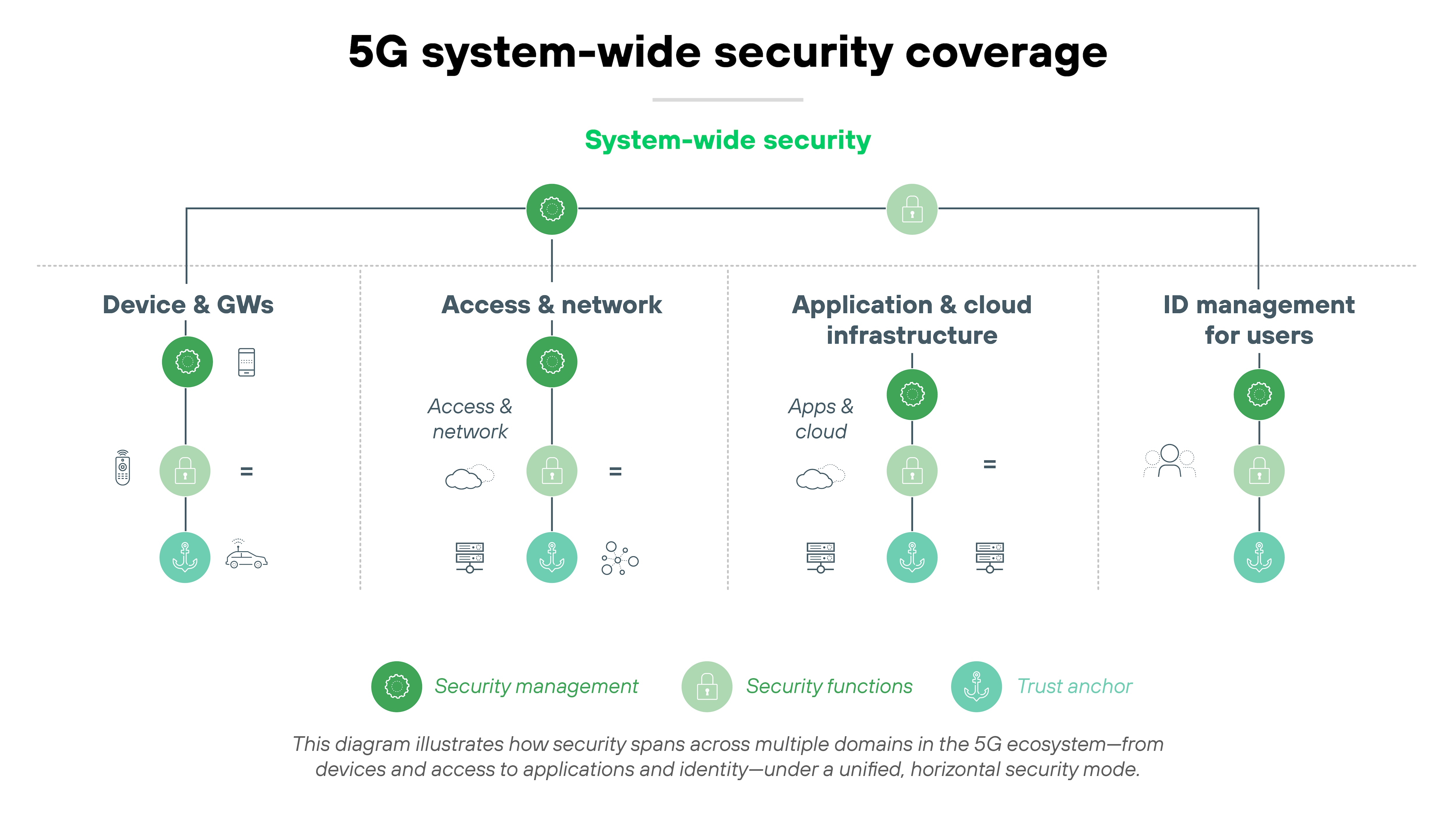
What security features are built into 5G?
5G includes foundational security features built directly into its architecture. These features span four security domains: network access, network domain, user domain, and application domain.
Each one is responsible for protecting a different part of the system. Starting at the physical connection and extending to how apps exchange data.
Network access
At the network access level, 5G introduces stronger mutual authentication between the user device and network. Control-plane signaling is now protected with integrity checks. Subscriber identity protection is also enhanced, replacing the unencrypted IMSI used in earlier generations with a concealed identifier to reduce tracking risk.
Network domain
Within the network domain, encryption, authentication, and integrity protections are applied between functions like the access network and 5G core. Because the architecture is software-defined, many of these protections also apply across virtualized functions and service-based interfaces. Network slicing introduces logical isolation between services, supported by separate policy controls (PCF) and user data management (UDM) for each slice.
User domain
On the user side, 5G supports more complex trust models. Mutual authentication can now include not just the mobile device and operator—but also service providers or other third parties. This flexibility supports different use cases but also adds complexity to identity management.
Application domain
Finally, at the application domain level, 5G specifies secure messaging between apps, user equipment, and providers. These mechanisms support integrity and confidentiality across service layers—even in environments with shared infrastructure.
Who's responsible for keeping 5G secure?
Security in 5G isn't someone else's job. Responsibility is shared—clearly, but not equally.
Communications service providers (CSPs) lead the charge. They design, deploy, and operate the infrastructure. So they're directly accountable for hardening the radio access network (RAN), securing the 5G core, and implementing industry standards like 3GPP-defined authentication and encryption.
But that's not the full picture.
Enterprises play a different role. They use slices and services built on top of CSP infrastructure. This includes deploying their own applications, enforcing endpoint and session-level security, and securing edge workloads. If a slice is compromised or misconfigured—say, due to poor policy controls or insecure application logic—it often starts with the enterprise, not the provider.
Now zoom out.
Governments shape the environment. Agencies like DHS, CISA, NIST, and the FCC set standards, fund testbeds, and publish threat models. Their work ensures CSPs and tech vendors meet baseline expectations around supply chain, resiliency, and cross-border trust. And globally? They push for secure, interoperable standards through partnerships like 3GPP and the ITU.
In other words: Everyone has a part. But each party must understand their scope.
Without that, 5G's complexity becomes a liability. Because when responsibility is blurred, threats slip through.
Which environments demand the strongest 5G security?
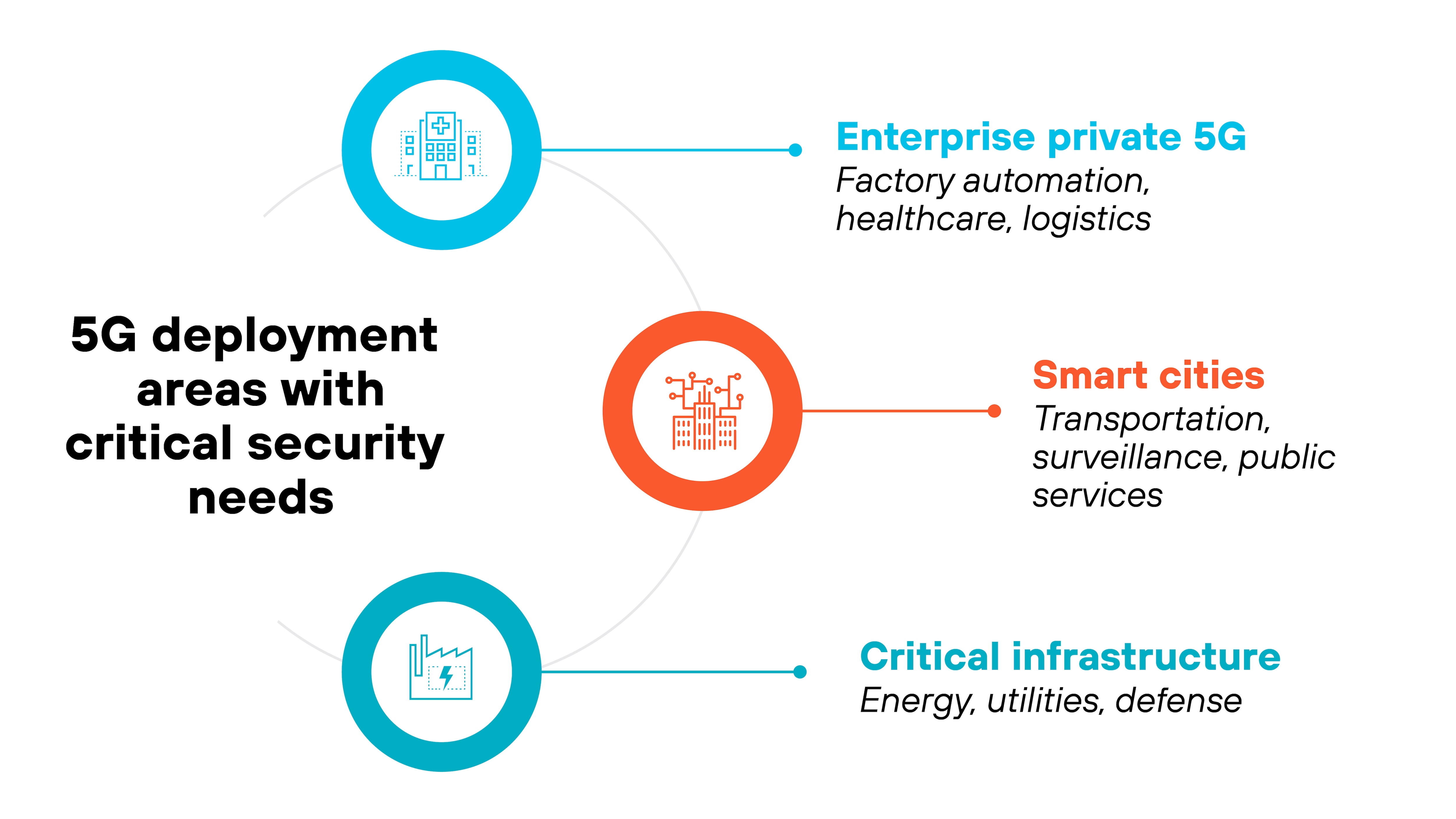
5G security matters most in environments where risk tolerance is low and operational disruption can have serious consequences. These are the pressure zones: places where 5G is either already in production or rapidly expanding into high-stakes applications.
Start with enterprise private 5G.
These are custom-built networks deployed by organizations to support factory automation, logistics, healthcare, or large-scale campuses.
Because private 5G networks often integrate tightly with production systems and IoT devices, a vulnerability doesn't just affect data—it can impact physical operations. That means compromised access control, delayed industrial automation, or unauthorized commands to devices.
Security controls need to account for both traditional IT risks and the broader cyber-physical consequences of an incident.
Then there are smart cities.
These urban environments rely on dense 5G infrastructure to power transportation systems, traffic sensors, surveillance, public Wi-Fi, and emergency services. The attack surface is massive.
And because systems are interconnected, compromise in one part of the network—like a traffic management system—can lead to downstream effects.
Maintaining availability, enforcing integrity, and verifying device trust become critical.
Finally, critical infrastructure.
5G is increasingly being explored as a communications backbone for sectors like energy, utilities, and defense. These networks operate with strict reliability requirements and minimal tolerance for disruption.
For example: Slicing may be used to isolate grid operations from public services. But if isolation or authentication breaks down, the results could be serious.
Security must ensure continuous service, enforce robust identity management, and maintain visibility into network and device behavior at all times.
What's next for 5G security?
5G security is evolving. The ecosystem is growing more complex, and legacy defenses can't keep pace.
New operational models, such as 5G-specific security operations centers (SOCs), are starting to take shape.
These SOCs focus on the unique characteristics of 5G infrastructure. That includes slice visibility, identity authentication, and latency-sensitive threats.
Another shift involves policy enforcement.
As slicing becomes more dynamic and granular, organizations need slice-aware policies that reflect how traffic flows and who owns what. Traditional network segmentation doesn't map cleanly to this architecture. Which means: Policies must be smarter and more contextual.
AI is also entering the picture. Not just for analytics—but for decision-making.
AI-in-the-loop defense can support real-time response in highly distributed environments. Especially where patterns aren't obvious to human analysts. It's early, but this kind of automation could reduce manual overhead and improve detection at the edge.
Looking ahead, 6G previews are already hinting at what's to come.
Tighter integration with AI, more precise device positioning, and expanded use of terahertz spectrum will likely introduce new security challenges. But also opportunities to rethink how networks are secured at the protocol level.
Important: These developments won't necessarily make security easier. But they will change how it needs to be done. That means teams will need to adapt their approaches, tools, and assumptions.