-
- What created the need for SD-WAN?
- How does SD-WAN work?
- What is SD-WAN architecture?
- What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
- What are the challenges associated with SD-WAN?
- What are the different types of SD-WAN deployment models?
- How secure is SD-WAN?
- What is the role of SD-WAN in SASE?
- Comparing SD-WAN with other security and technology solutions
- SD-WAN FAQs
What Is SD-WAN? Software-Defined Wide Area Network
9 min. read
Table of Contents
SD-WAN (software-defined wide area network) is a type of networking technology that uses software-defined networking (SDN) principles to manage and optimize wide area network (WAN) performance.
It gives organizations the ability to securely connect users, applications and data across multiple locations. Plus, it improves performance, reliability and scalability.
SD-WAN also simplifies WAN management by providing centralized control and visibility over the entire network.
What created the need for SD-WAN?
Businesses need SD-WAN because traditional wide area networks can't keep up with how organizations now operate, connect, and use applications.
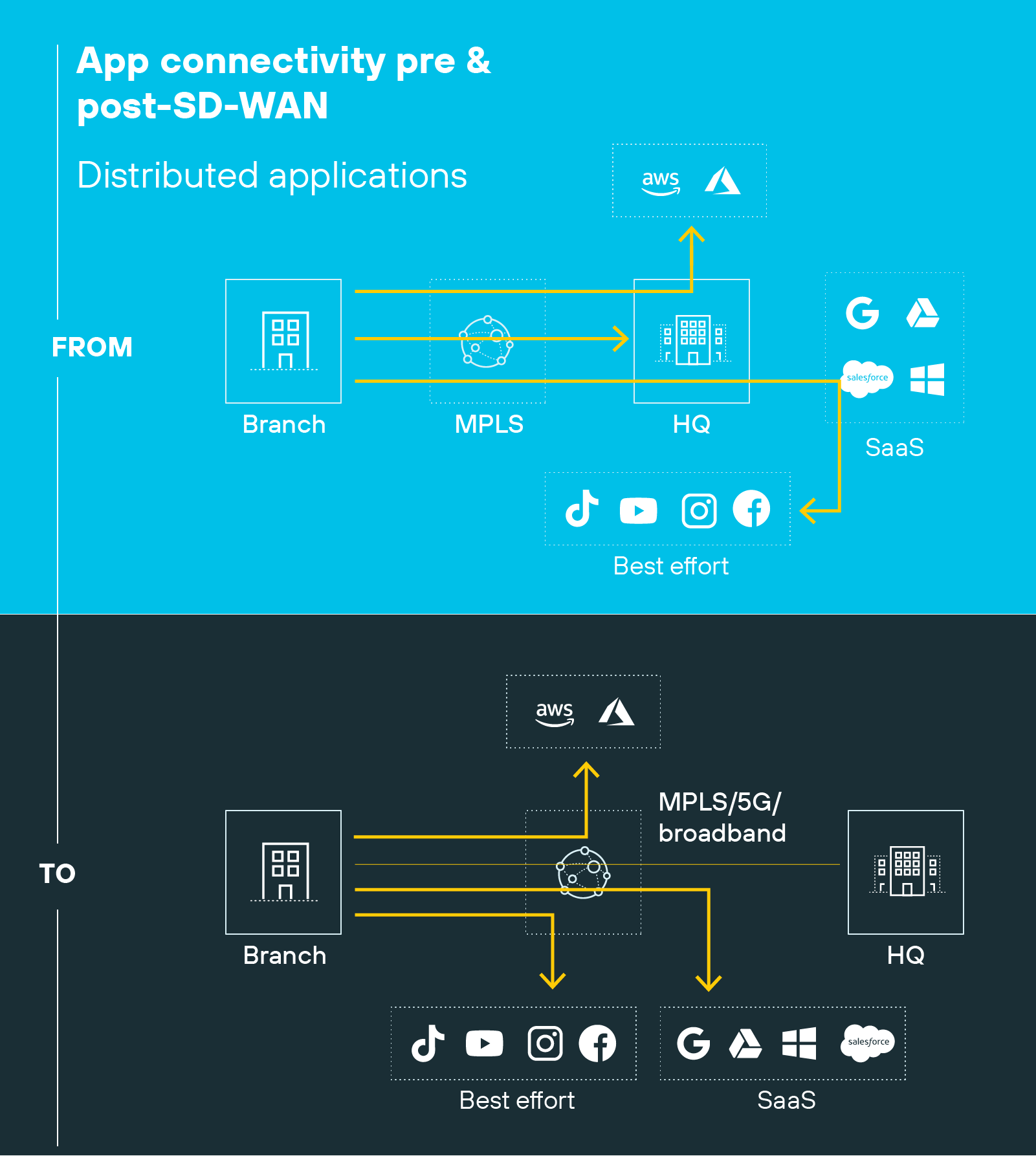
That's because organizations no longer rely solely on centralized data centers. Today, applications are spread across public clouds, SaaS platforms, and hybrid environments.
"92% of workloads are now hosted on some form of cloud platform, indicating a significant shift from traditional on-premises solutions. Only 8% of workloads remain solely on-premises, showing a substantial move towards cloud-based infrastructure across various industries."
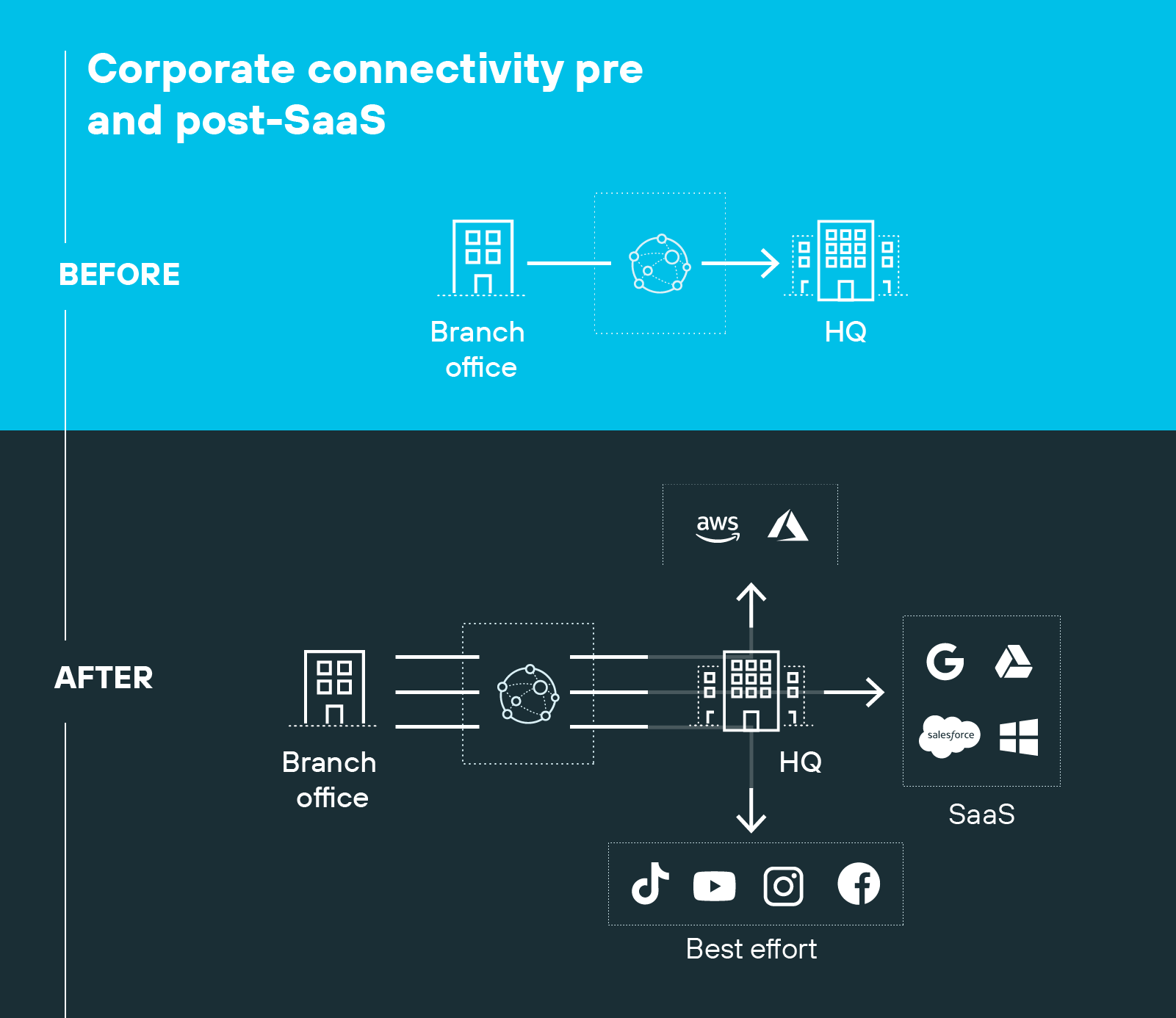
And legacy WANs weren't designed for that. They assumed traffic would flow between branch offices and a central data center. So they routed everything through a single hub—where connectivity and security were centralized.
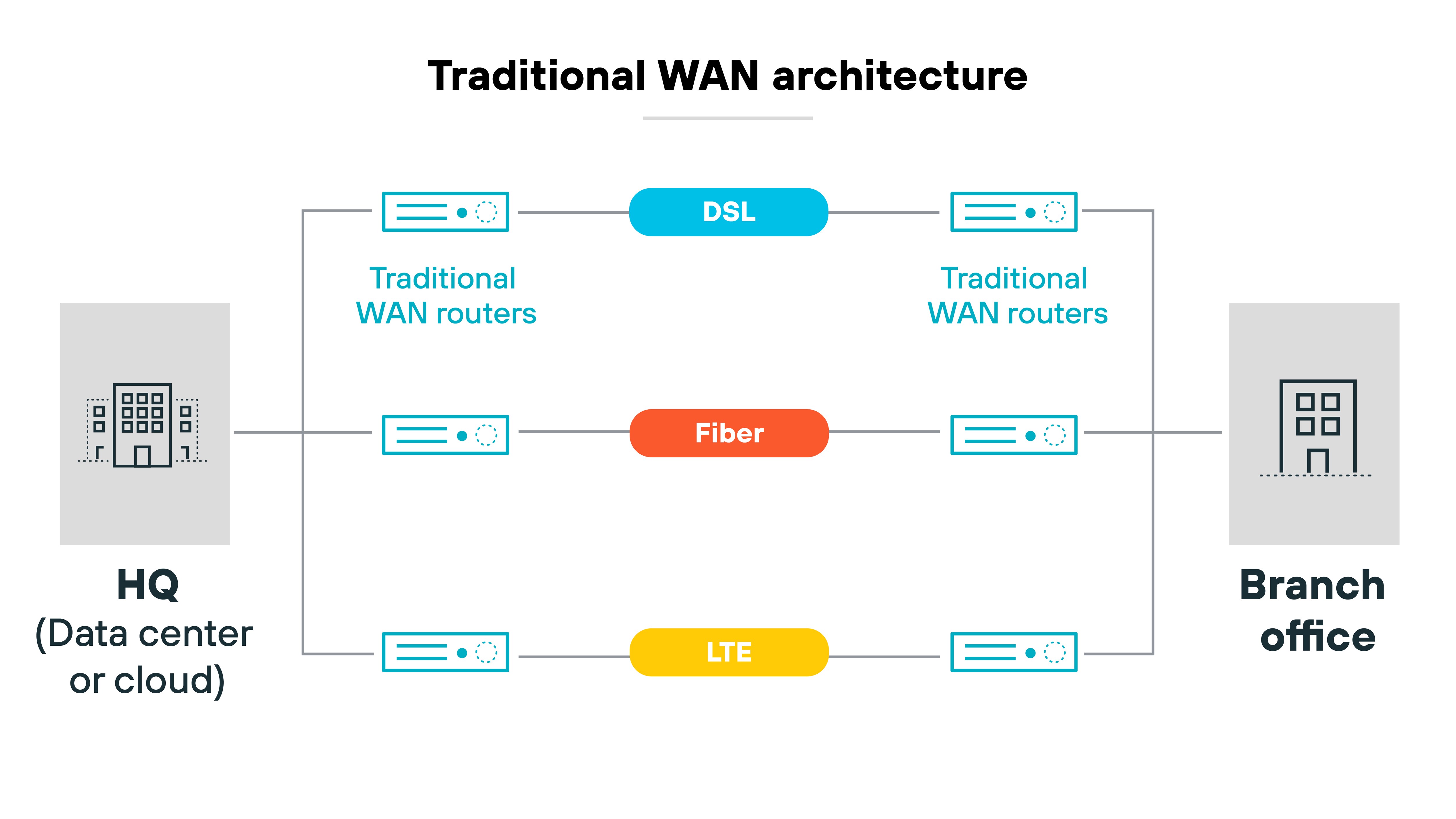
But that model breaks down when apps are in the cloud and users connect from everywhere.
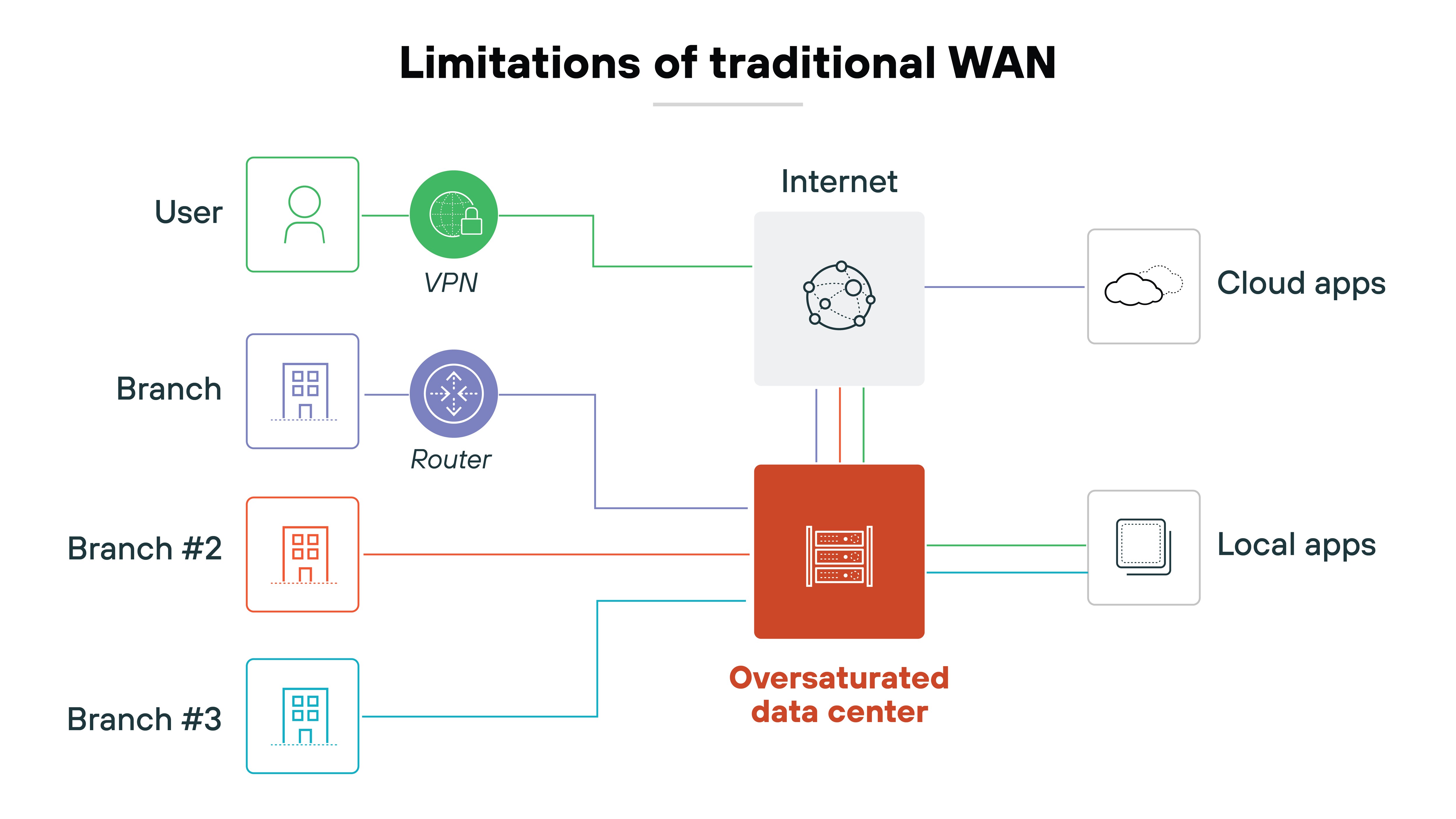
Direct-to-internet traffic has surged. Cloud-based services now power branch offices, remote work, and mobile teams. And older WANs can't efficiently support that kind of distributed traffic. Routing everything through a hub leads to delays, congestion, and higher costs.
Plus, hybrid work has changed traffic patterns, too. Employees now connect from homes, coworking spaces, and on the road. Not just branch offices.
"80% of organizations report that they allow some level of remote and hybrid model for their employee's ways of working."
Traditional WANs weren't built for this level of flexibility. And with more locations, users, and apps, managing network performance and visibility has become harder.
That's the gap SD-WAN was built to fill. It gives organizations a way to support modern workflows. Without relying on outdated assumptions about where users are or how traffic flows.
| Further reading:
- Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: What Are the Differences?
- How to Do an SD-WAN Migration From Any Starting Point
- How to Execute an MPLS to SD-WAN Migration Step-by-Step
- What Is the Cloud-Delivered Branch?
How does SD-WAN work?
SD-WAN is a virtualized approach to managing wide area networks.
It connects users and branch sites to enterprise applications across multiple transport types. Like MPLS, broadband, wireless links, VPNs, and public internet.
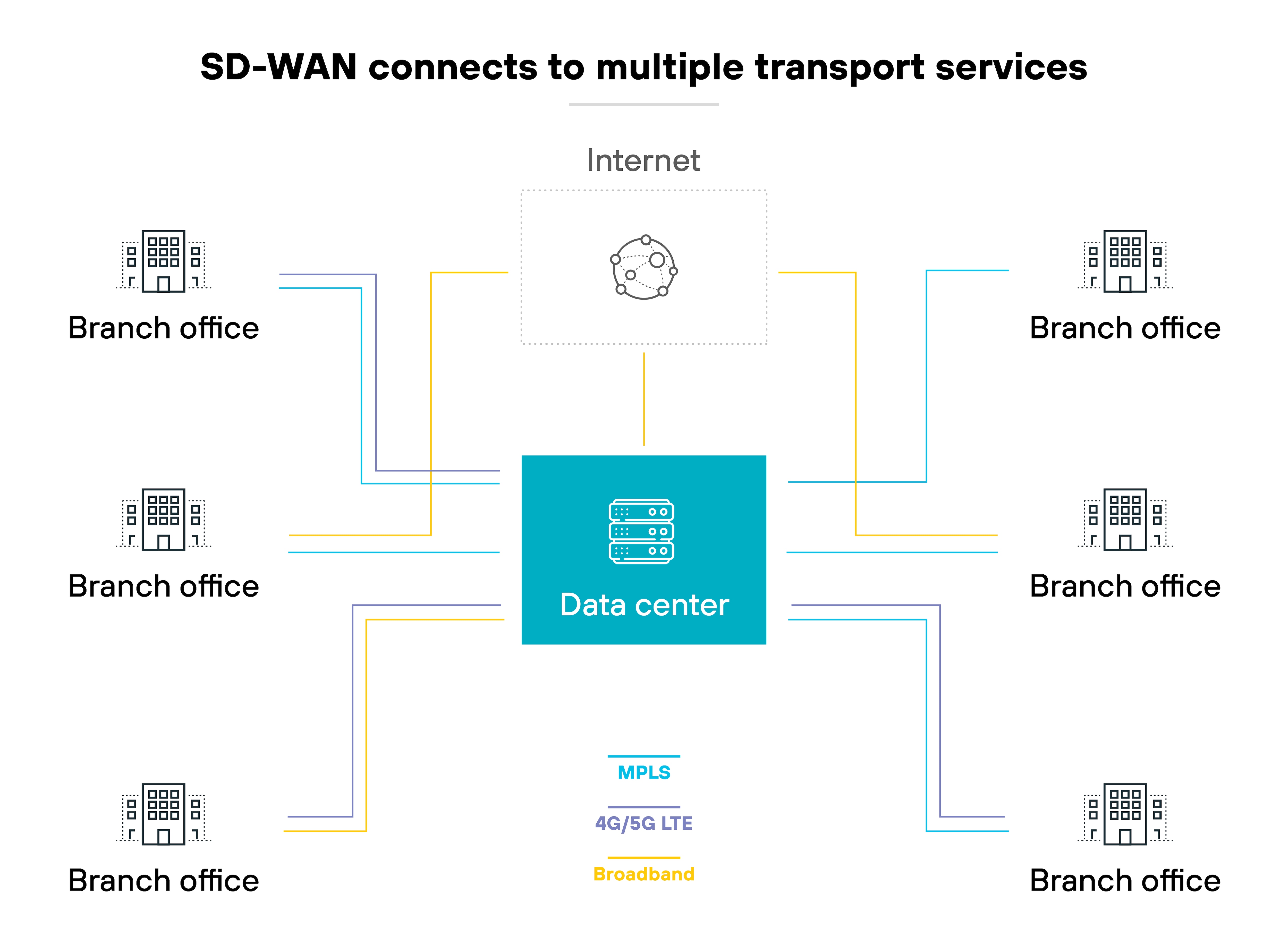
It works like this:
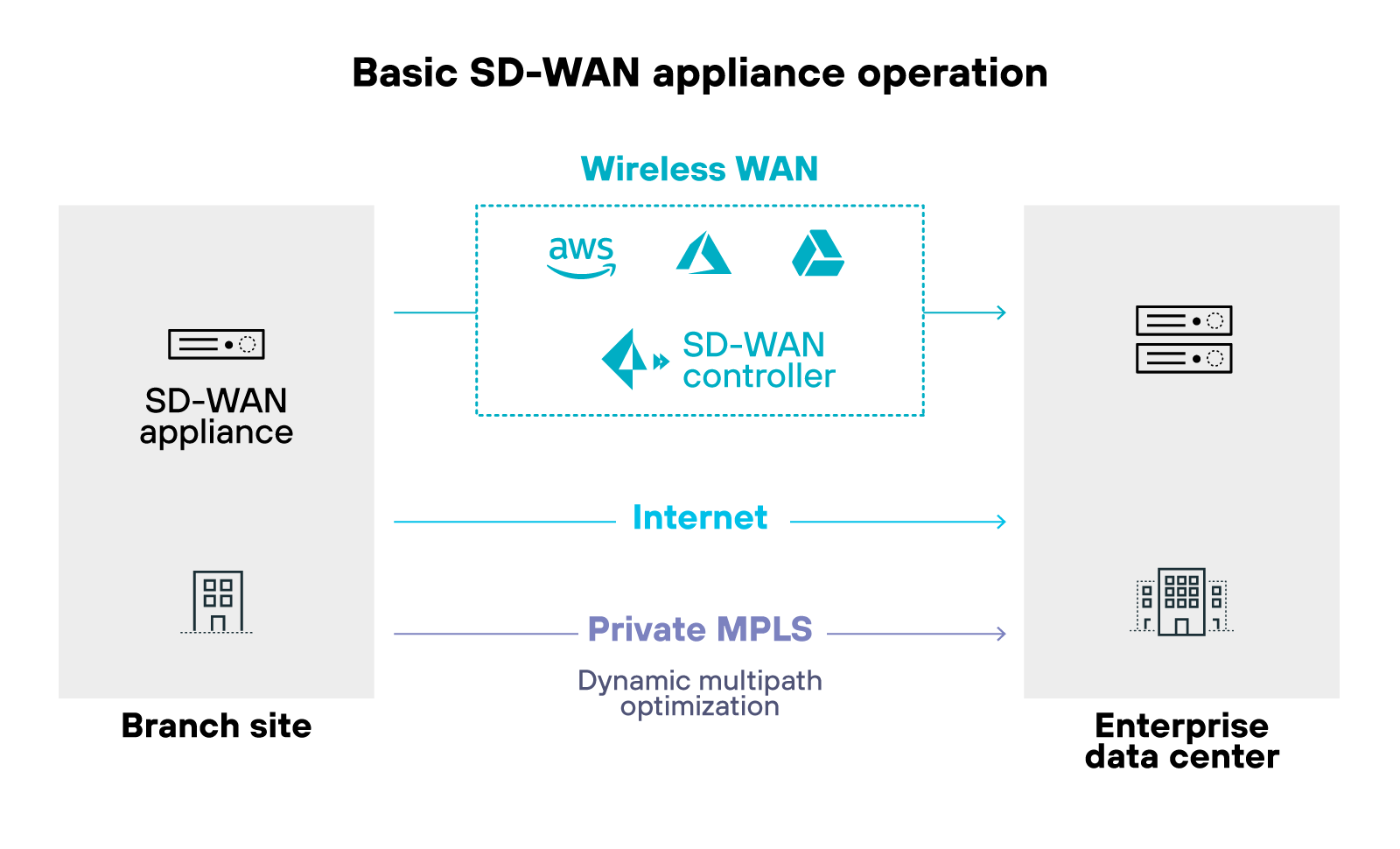
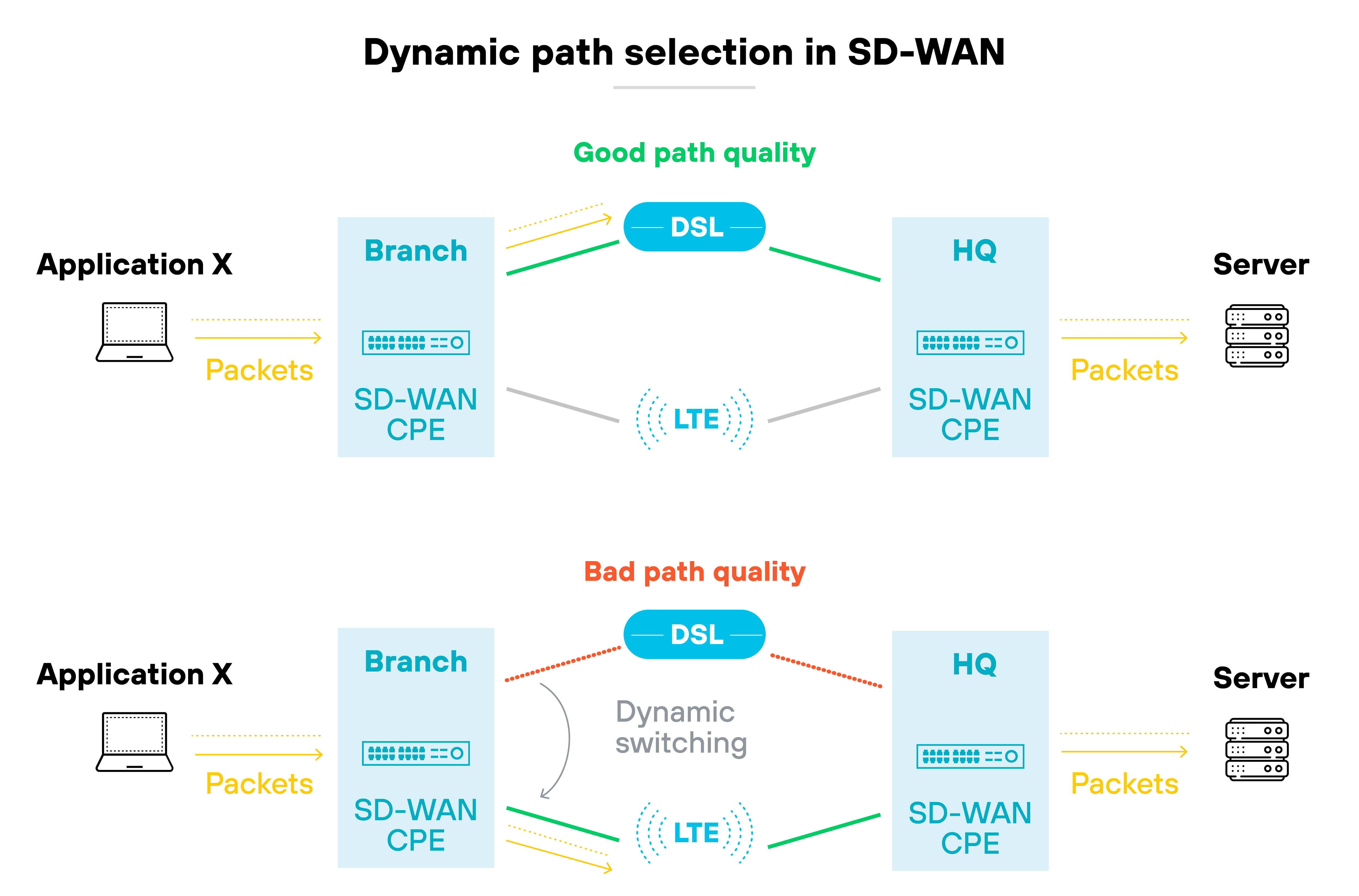
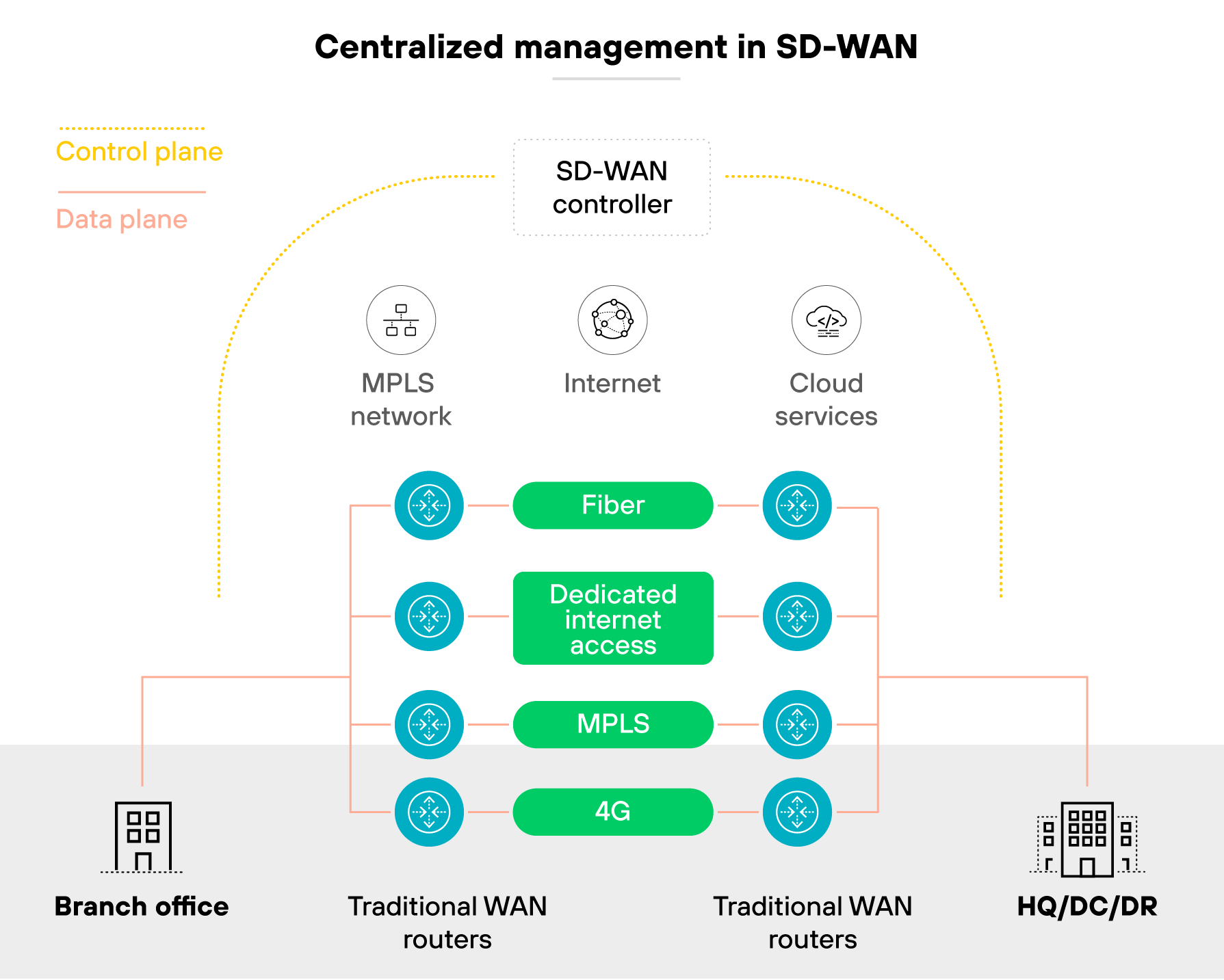
Each SD-WAN appliance connects to a centralized controller. The controller monitors network conditions—latency, jitter, packet loss—and decides how traffic should flow. If a link degrades, SD-WAN automatically reroutes traffic to a better-performing path.
Like so:
Policies are created centrally and pushed to all sites without manual configuration. Which means changes can be rolled out quickly and consistently.
Routing decisions aren't made locally. They follow global policies set by the control plane. That's what allows for dynamic, policy-based traffic management.
Basically, SD-WAN continuously adapts based on real-time performance. It supports application-aware routing, steers traffic across the best available link, and helps maintain uptime.
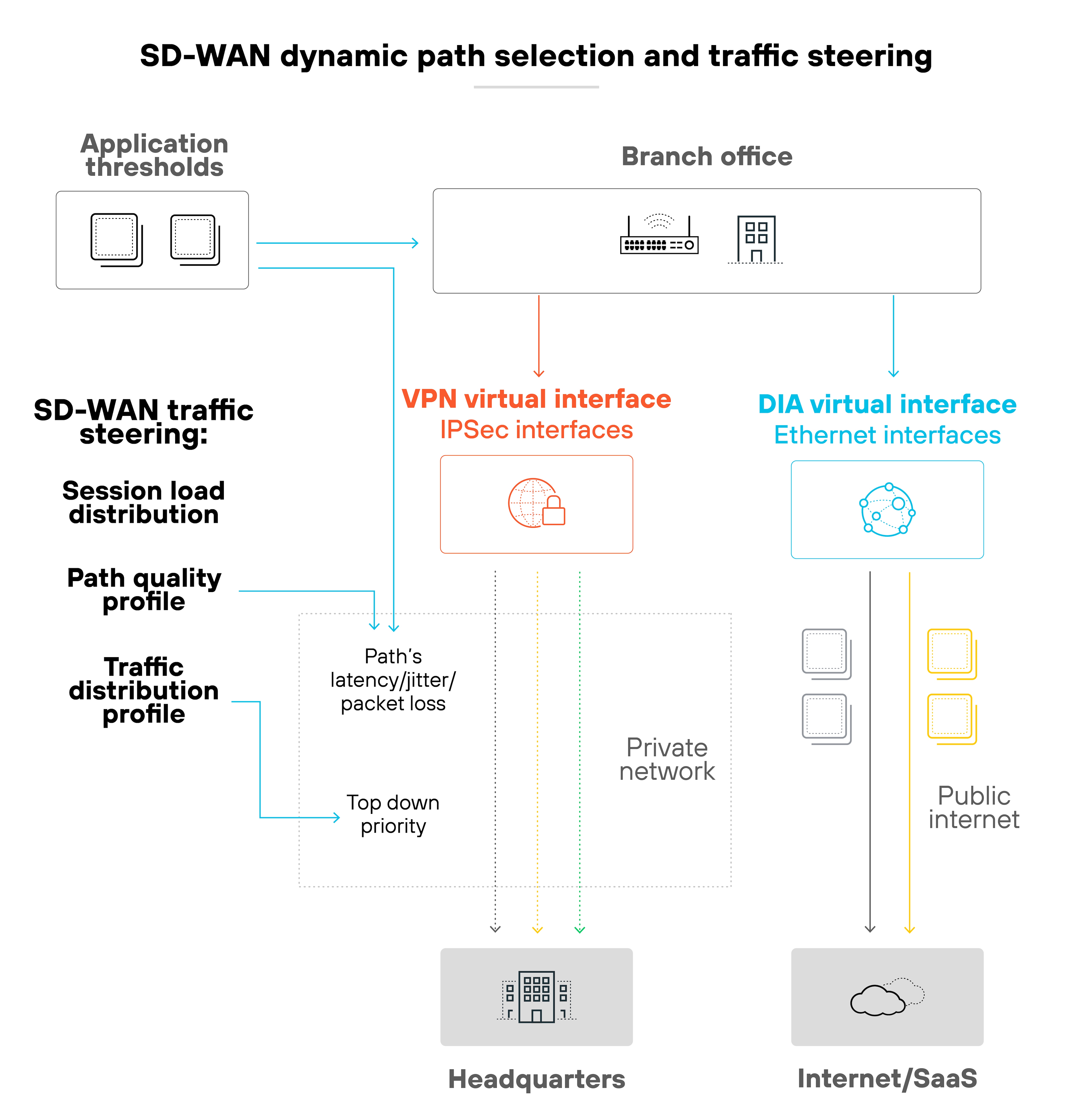
It also separates the control and data planes. That's what makes it easier to manage and scale. Especially across distributed sites.
| Further reading:
- What Is an SD-WAN Appliance? | SD-WAN Hardware & Equipment
- What Is Hybrid SD-WAN?
- How Does SD-WAN Automation Simplify Network Operations?
What is SD-WAN architecture?
SD-WAN architecture refers to the conceptual structure and logical design of a software-defined wide area network.
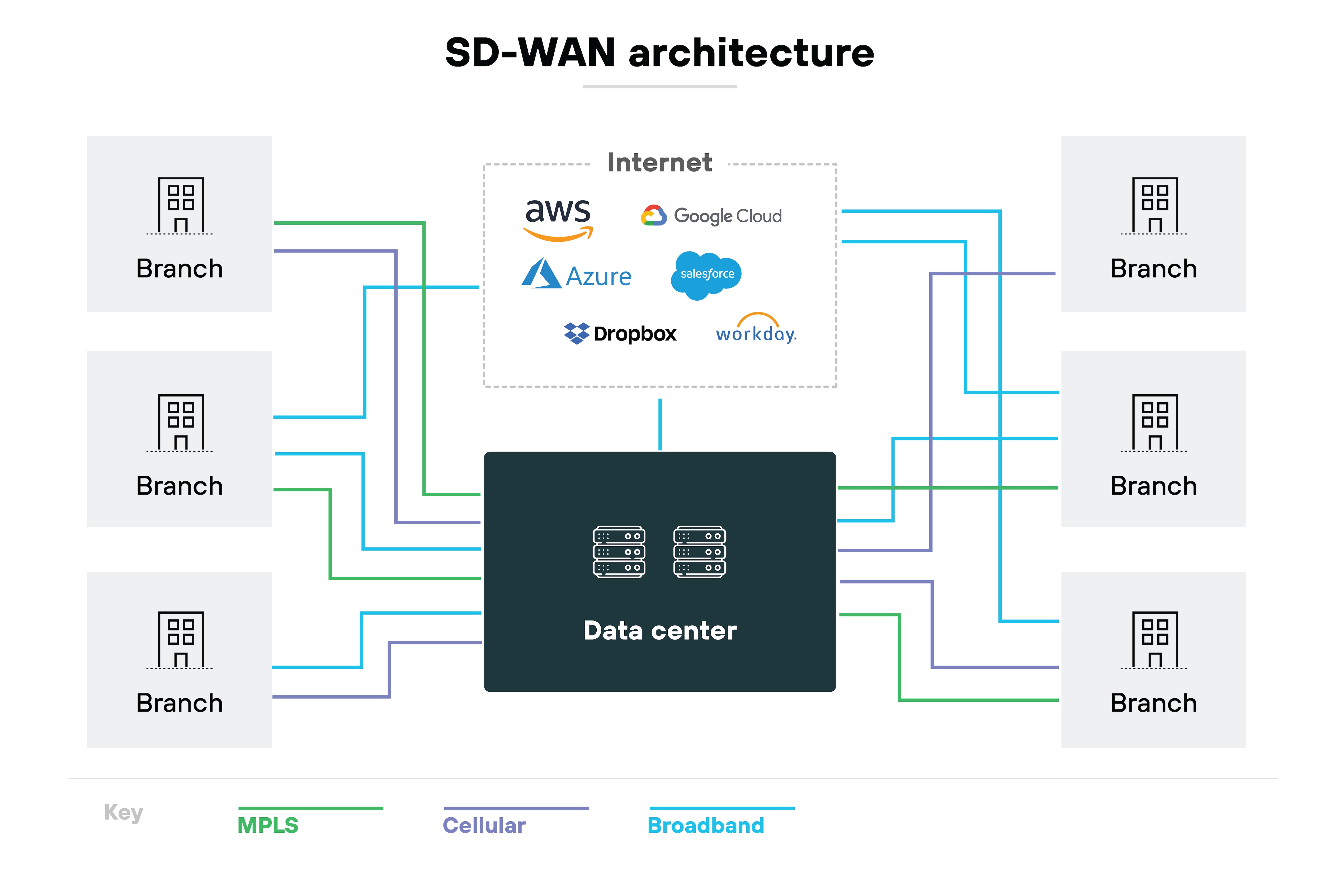
It defines how the system is built, how components interact, and how traffic is routed and managed. Understanding the architecture helps clarify what SD-WAN does. And how it works behind the scenes.
It's worth noting: SD-WAN architecture isn't just about physical setup. It's also about how the solution enables centralized control, dynamic traffic steering, and flexible deployment.
This section explains both the core components of SD-WAN and the different models used to deploy it.
Let's start with components of SD-WAN architecture.
SD-WAN is made up of several core components that work together to provide centralized control, efficient traffic routing, and flexible deployment across locations.
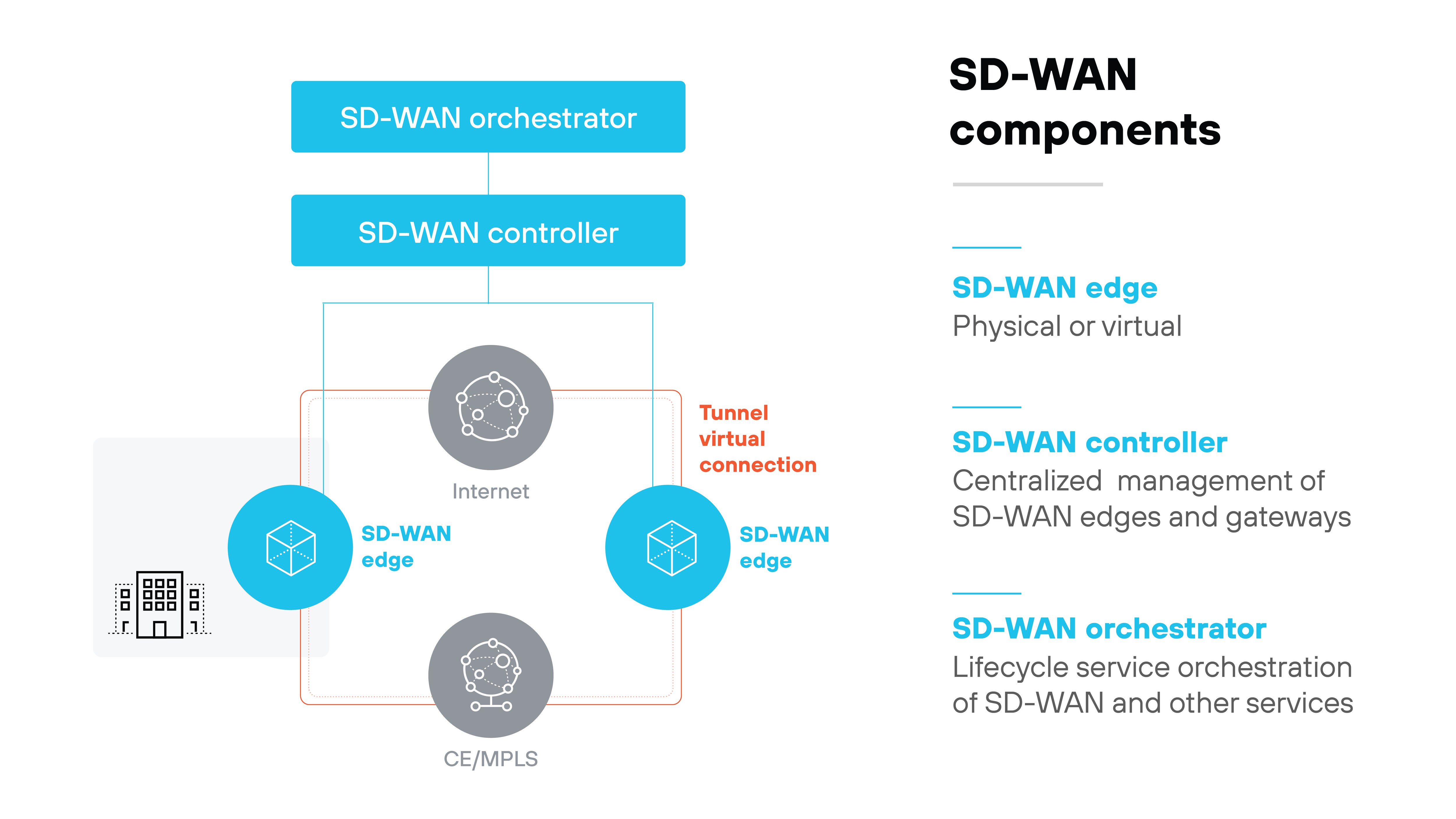
- SD-WAN edge: The edge is the enforcement point where SD-WAN connects to the physical network, typically at branches or cloud sites. It forwards traffic and applies local policies based on controller instructions.
- SD-WAN orchestrator: The orchestrator provides centralized management, pushing configurations and updates across all sites. It reduces manual work by letting admins control the network through a single interface.
- SD-WAN controller: The controller makes centralized policy decisions and monitors network conditions. It directs how traffic should flow and communicates those decisions to edge devices.
- Virtual or physical nodes: These optional nodes help expand SD-WAN coverage or capacity at key points in the network. They can improve traffic routing and scalability across distributed environments.
Now for types of SD-WAN architecture.
SD-WAN can be deployed in different ways depending on network design and operational needs.
Each type takes a different approach to routing, control, and cloud integration.

- On-premises SD-WAN: This model deploys SD-WAN appliances directly at each site for local control and enforcement. It's often used when data sensitivity or hands-on traffic management is a priority.
- Cloud-enabled SD-WAN: This setup connects branch locations to cloud services through virtual gateways over the public internet. It improves access to distributed applications and simplifies cloud integration.
- Cloud-enabled SD-WAN with backbone: This architecture uses regional PoPs to route traffic over a private backbone. It helps reduce latency, improve reliability, and maintain performance during internet disruptions.
| Further reading:
What are the benefits of SD-WAN?
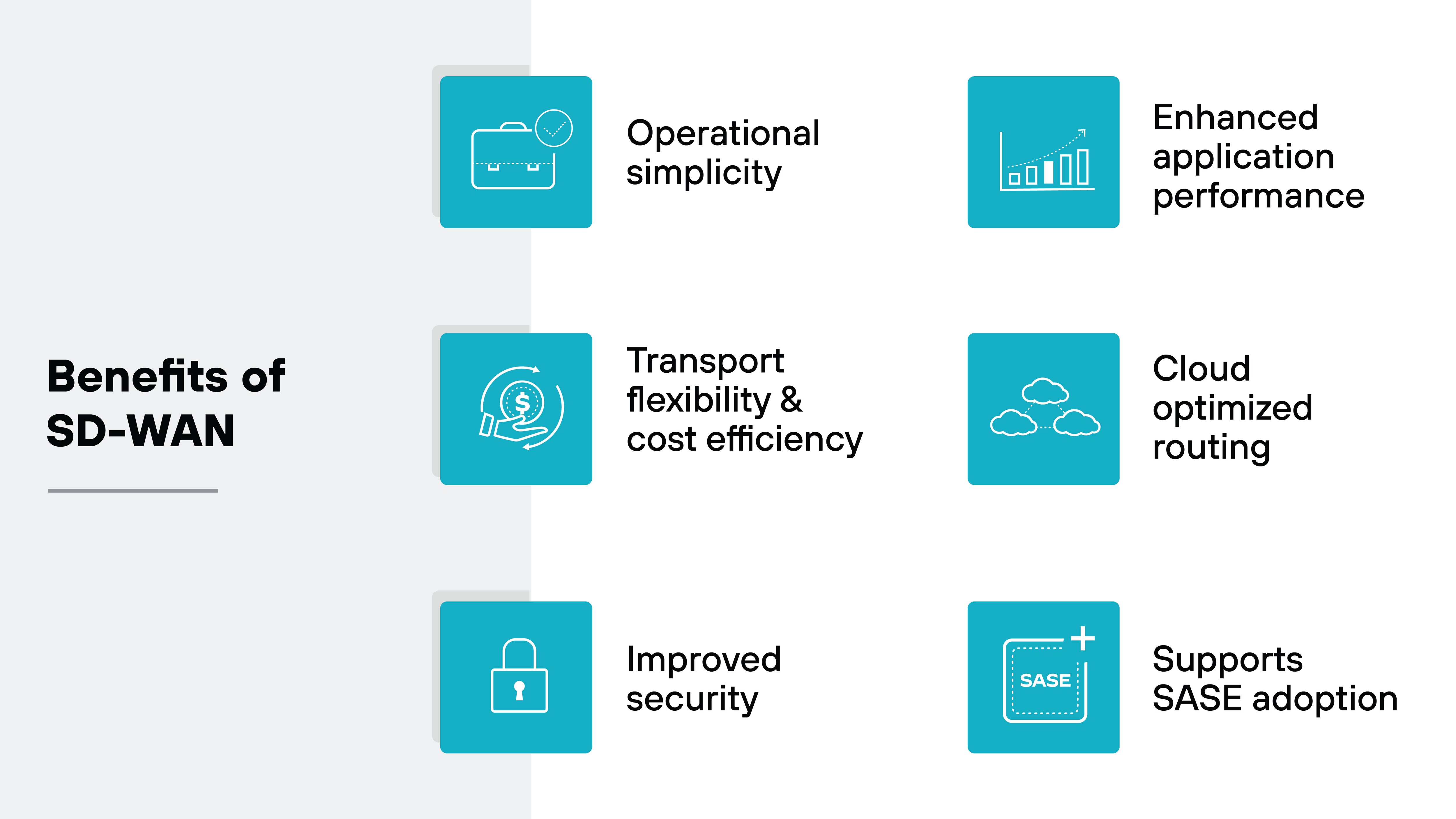
- Operational simplicity: Centralized management, zero-touch provisioning, and automated policy enforcement reduce manual work and make it easier to scale distributed networks.
- Transport flexibility and cost efficiency: Supports broadband, MPLS, 5G, and more. Organizations have the freedom to choose the most cost-effective links and avoid vendor lock-in.
- Improved security: Encrypted site-to-site connections and centralized policy controls help secure remote locations, with integration options for SWG, CASB, and other advanced tools.
- Enhanced application performance: Monitors traffic in real time and prioritizes critical apps like voice and video to maintain reliable performance under changing conditions.
- Cloud optimized routing: Allows branch sites to reach cloud apps directly, avoiding the latency of backhaul and selecting the best available path for each session.
- SASE readiness: Lays the foundation for SASE by combining policy-based traffic control with seamless cloud integration, supporting long-term network and security convergence.
| Further reading: What Are the Benefits of SD-WAN?
What are the challenges associated with SD-WAN?
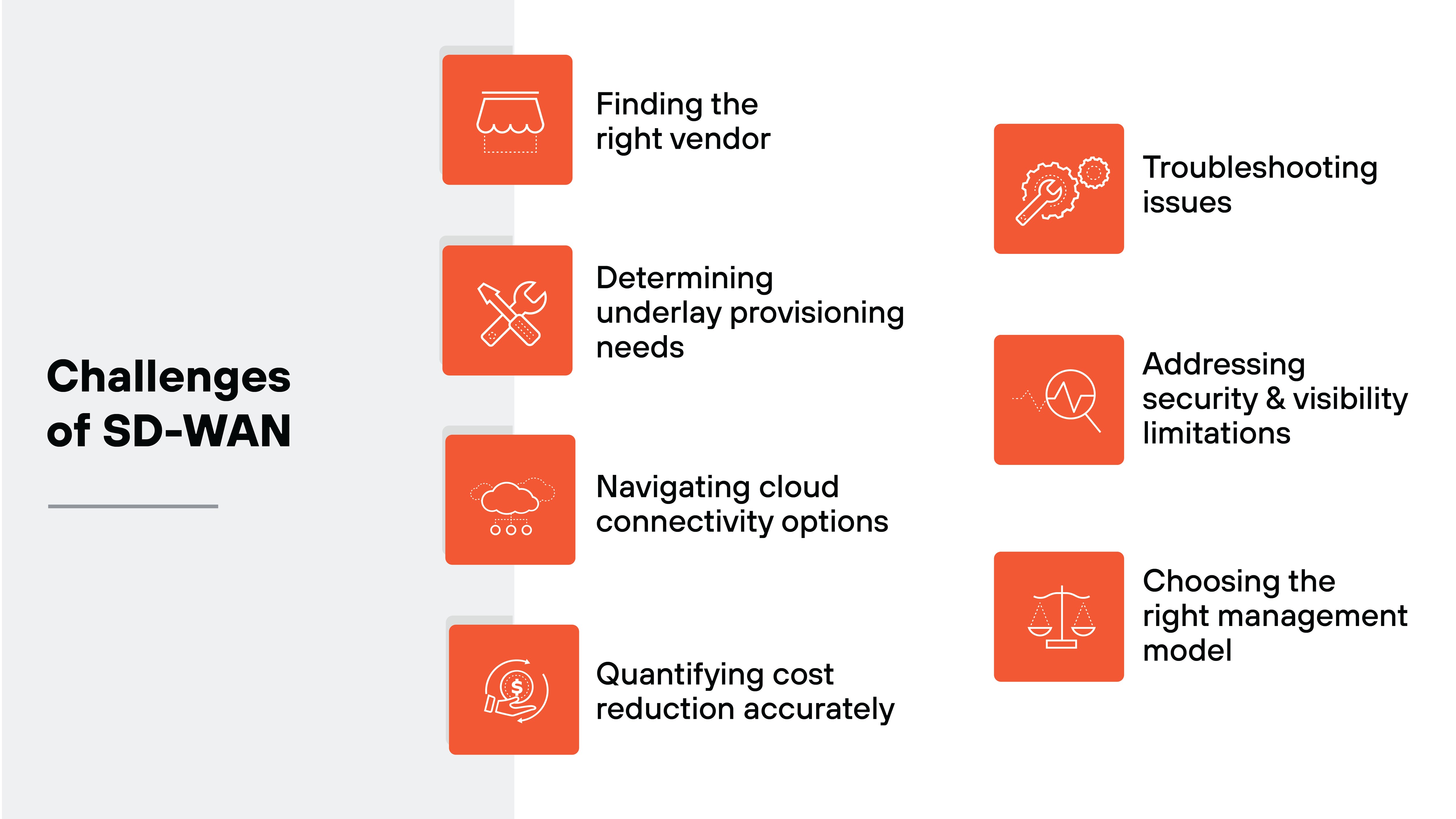
- Vendor selection: With so many similar-looking offerings, it can be hard to align the right provider with your specific goals, infrastructure, and support needs.
- Underlay provisioning: Performance depends heavily on the transport layer. Choosing between internet, MPLS, or hybrid underlays requires evaluating application and geographic demands.
- Cloud connectivity: Integration with cloud providers varies by solution. Selecting the right approach means balancing performance, complexity, and cost.
- Cost analysis: Savings aren't always obvious. ROI depends on more than just circuit costs. It includes reduced downtime, operational efficiency, and feature consolidation.
- Troubleshooting: Dynamic routing and policy complexity can make root cause analysis difficult without strong visibility and diagnostic tools.
- Security and visibility gaps: Local breakouts and decentralized traffic increase the attack surface. Maintaining consistent enforcement requires thoughtful integration with security frameworks like SASE.
- Management model decisions: Whether fully managed, co-managed, or DIY, each option has trade-offs in control, effort, and support. So internal readiness matters.
| Further reading:
What are the different types of SD-WAN deployment models?
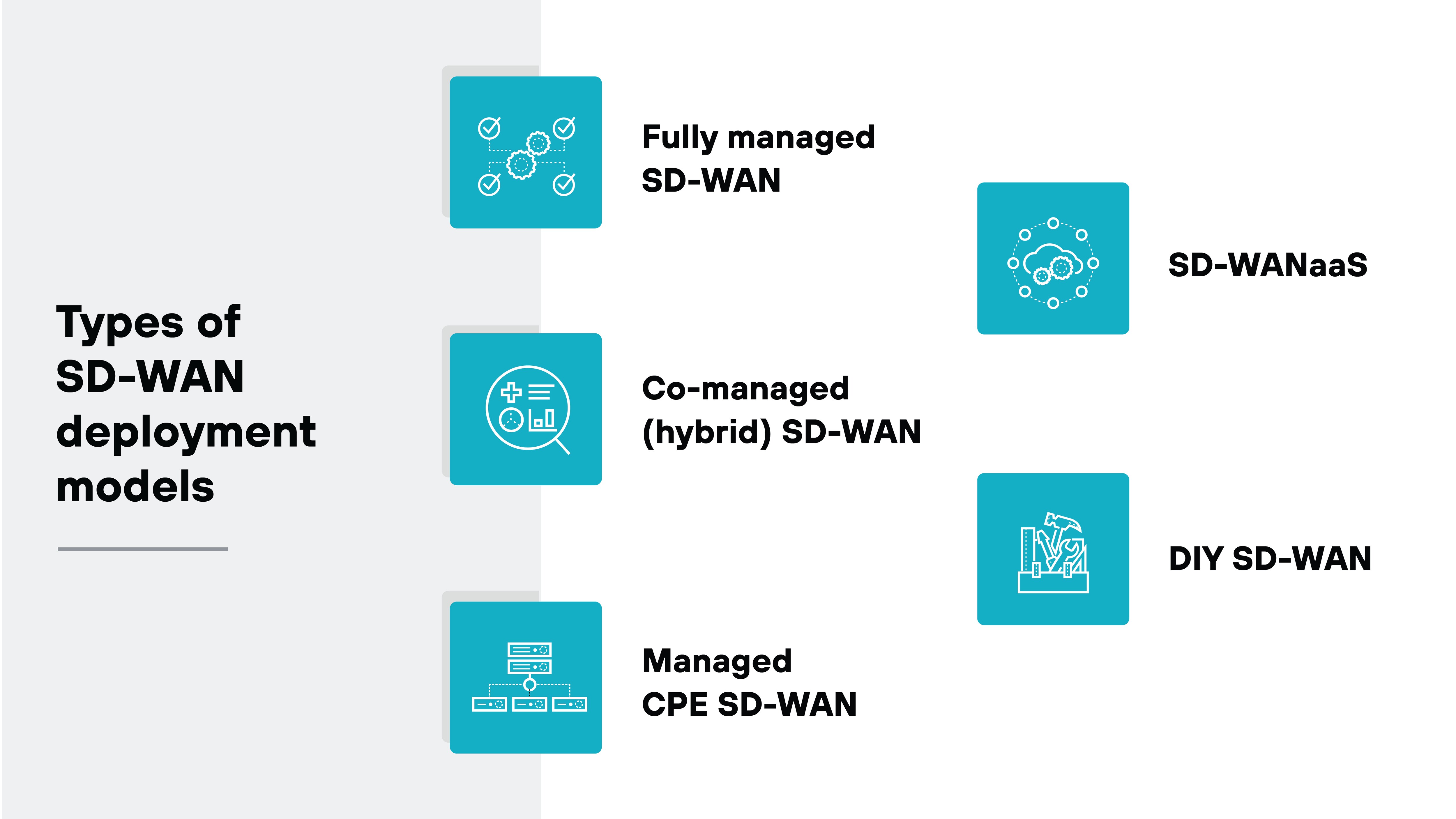
Different SD-WAN deployment models offer varying levels of control, flexibility, and operational responsibility.
Choosing the right one depends on your internal capabilities, available resources, and business goals.
DIY SD-WAN
In a DIY model, you manage the entire deployment yourself. That includes design, provisioning, policy creation, and ongoing maintenance. This approach gives you full control but requires deep technical expertise, staffing, and time to manage the environment effectively.
Fully managed SD-WAN
A fully managed model puts everything in the provider's hands, from deployment to policy enforcement and performance monitoring. It's a good option for organizations with limited IT resources or those looking to offload operational complexity.
Co-managed SD-WAN
This shared model lets your team retain visibility and control while the provider handles select operational tasks. It's ideal for organizations that want expert support but still need to influence policies and monitor performance.
Managed CPE SD-WAN
In this model, the provider manages the physical customer premises equipment (CPE) at each site. You may still define high-level policies, but hardware provisioning, updates, and site-level troubleshooting are handled externally.
SD-WAN as a service (SD-WANaaS)
This cloud-delivered model provides SD-WAN as a subscription service, often with minimal on-site hardware. It's designed for scalability, cloud-first strategies, and organizations that prefer a simplified, pay-as-you-go approach.
| Further reading: Types of SD-WAN Deployment Models: A Complete Guide
How secure is SD-WAN?
Traditional SD-WAN isn't inherently secure. It improves performance and routing efficiency–and does include some basic security features–but doesn't offer the advanced protections needed to guard against today's cyber threats.
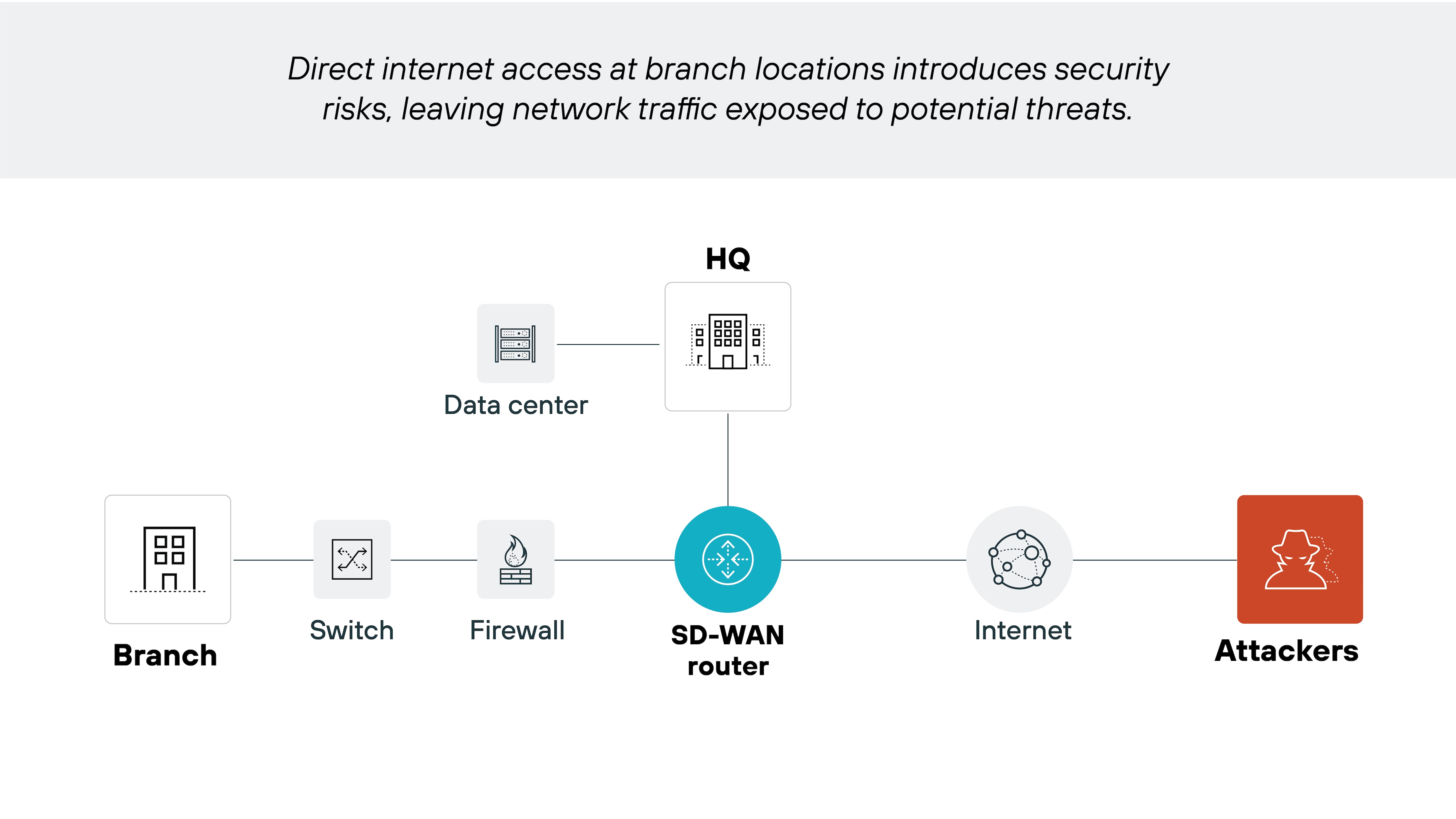
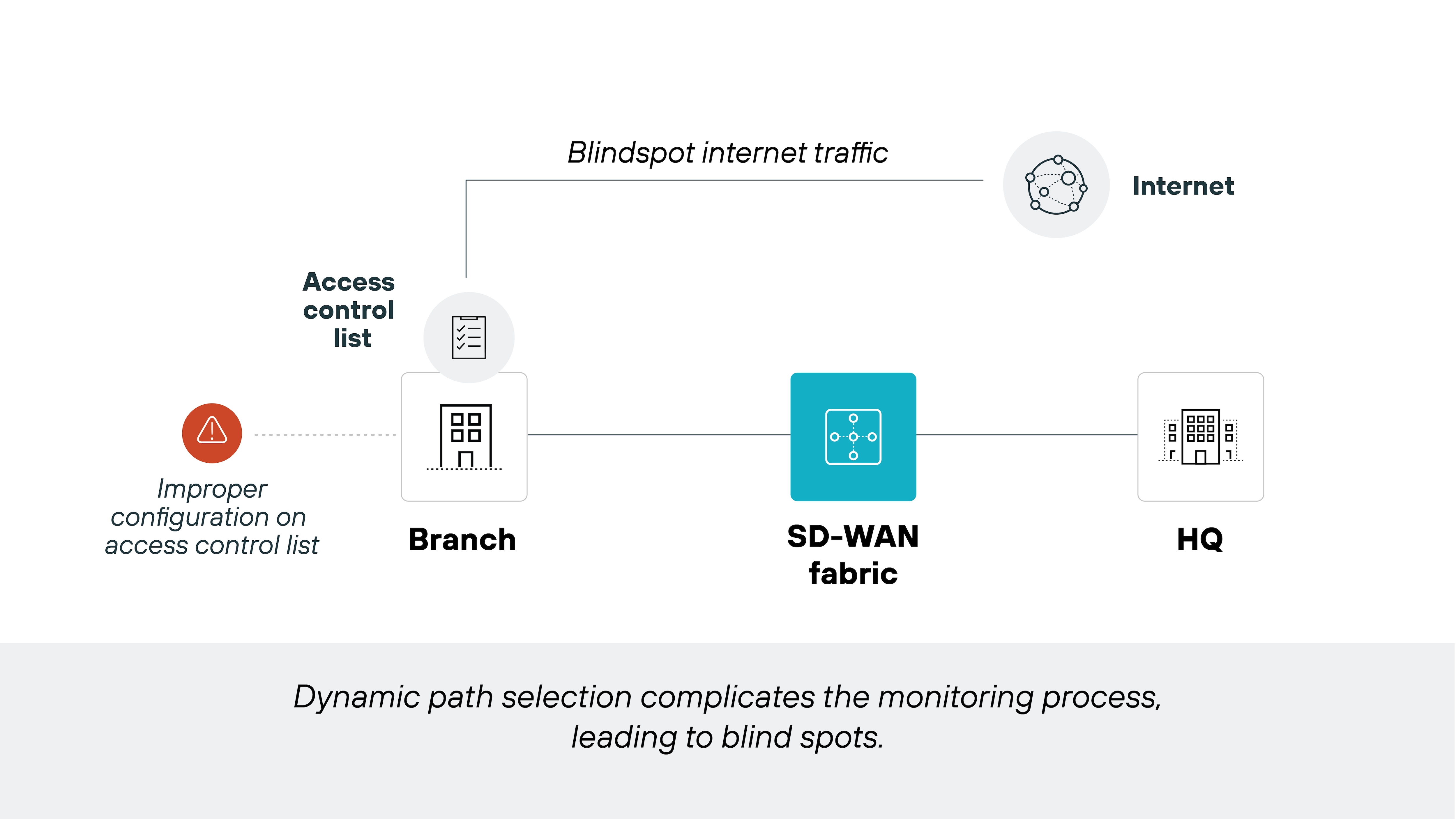
With that said, the security level of an SD-WAN solution depends on how it's designed and deployed. That's why many organizations either layer in security tools separately or adopt secure SD-WAN solutions that integrate them by default.
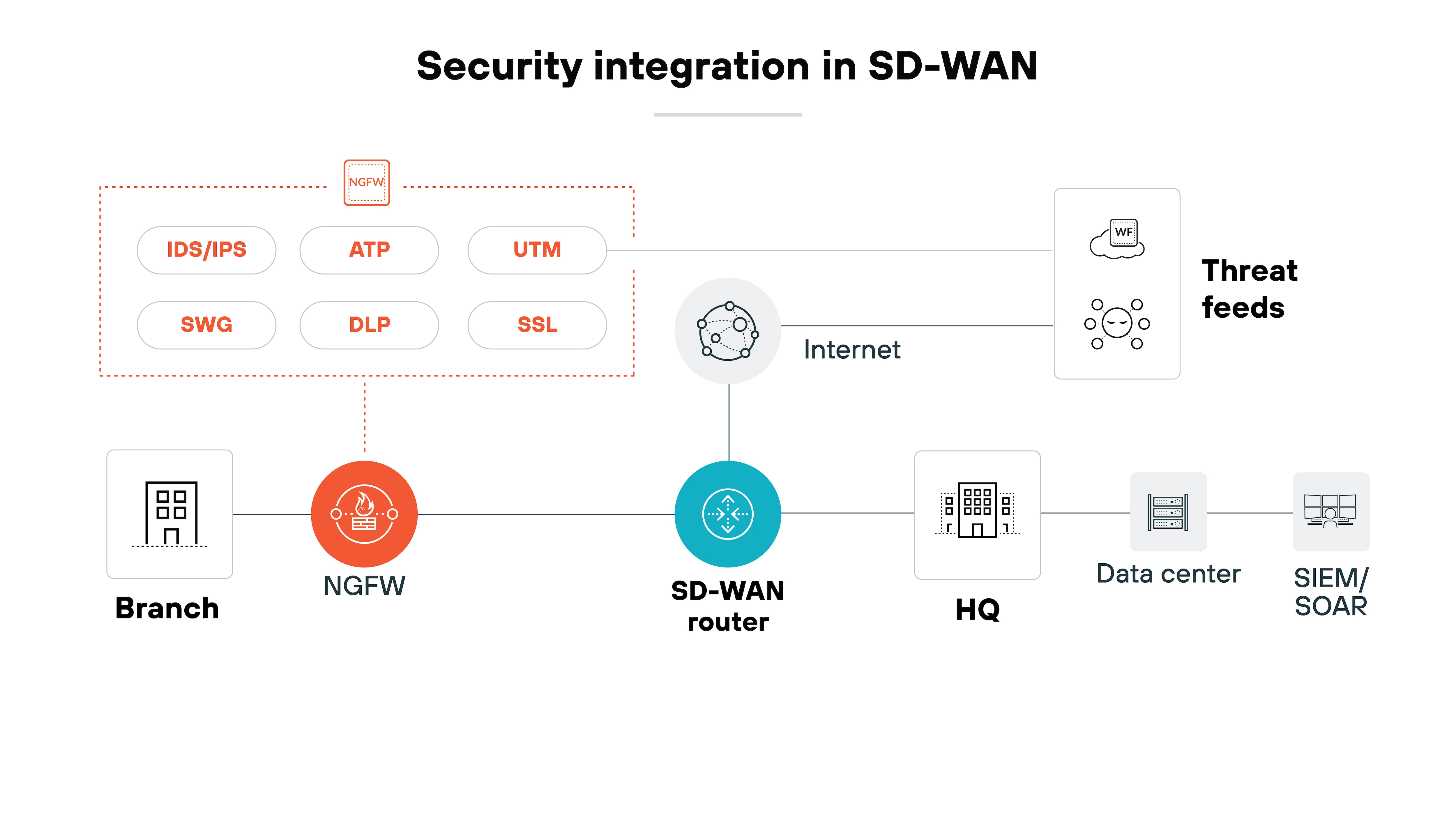
Secure SD-WAN includes features like next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention, and SSL inspection built directly into the SD-WAN infrastructure. It also enables centralized policy management, which reduces the risk of configuration errors across distributed locations.
Ultimately, with the right security measures in place, SD-WAN can support strong, consistent protection across the WAN. It just doesn't qualify as a security solution on its own.
| Further reading:
- What Is SD-WAN Security? | SD-WAN Security Considerations
- What Is Secure SD-WAN? | What It Is and How It Works
- How Are Firewalls and SD-WAN Related?
What is the role of SD-WAN in SASE?
"By 2027, 65% of new SD-WAN purchases will be part of a single-vendor secure access service edge (SASE) offering, an increase from 20% in 2024."
SD-WAN is a core component of secure access service edge (SASE). It provides the networking layer that connects users, devices, and locations across multiple WAN links.
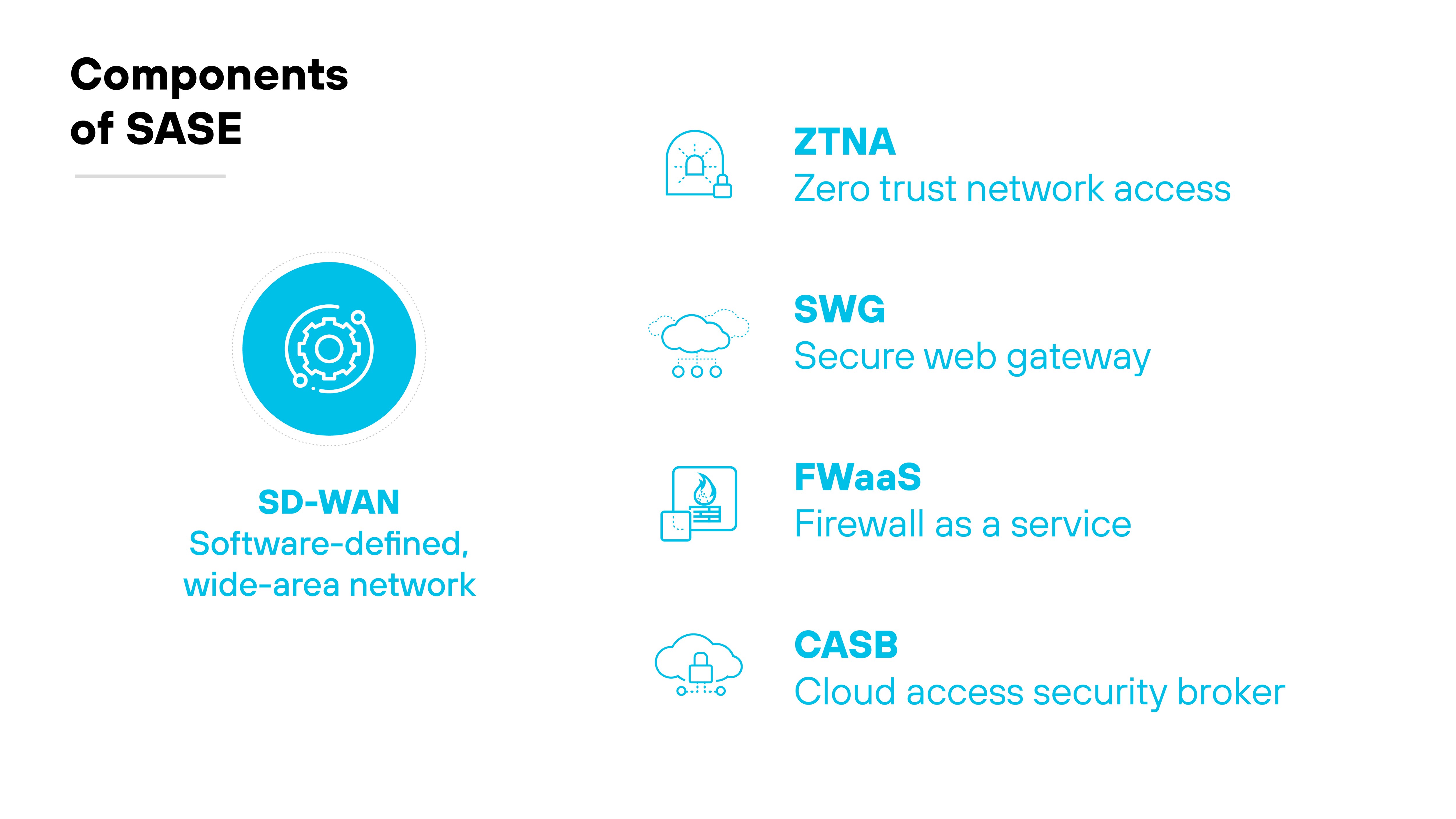
In a SASE architecture, SD-WAN manages how traffic flows between endpoints and cloud applications, ensuring efficient and policy-based routing.
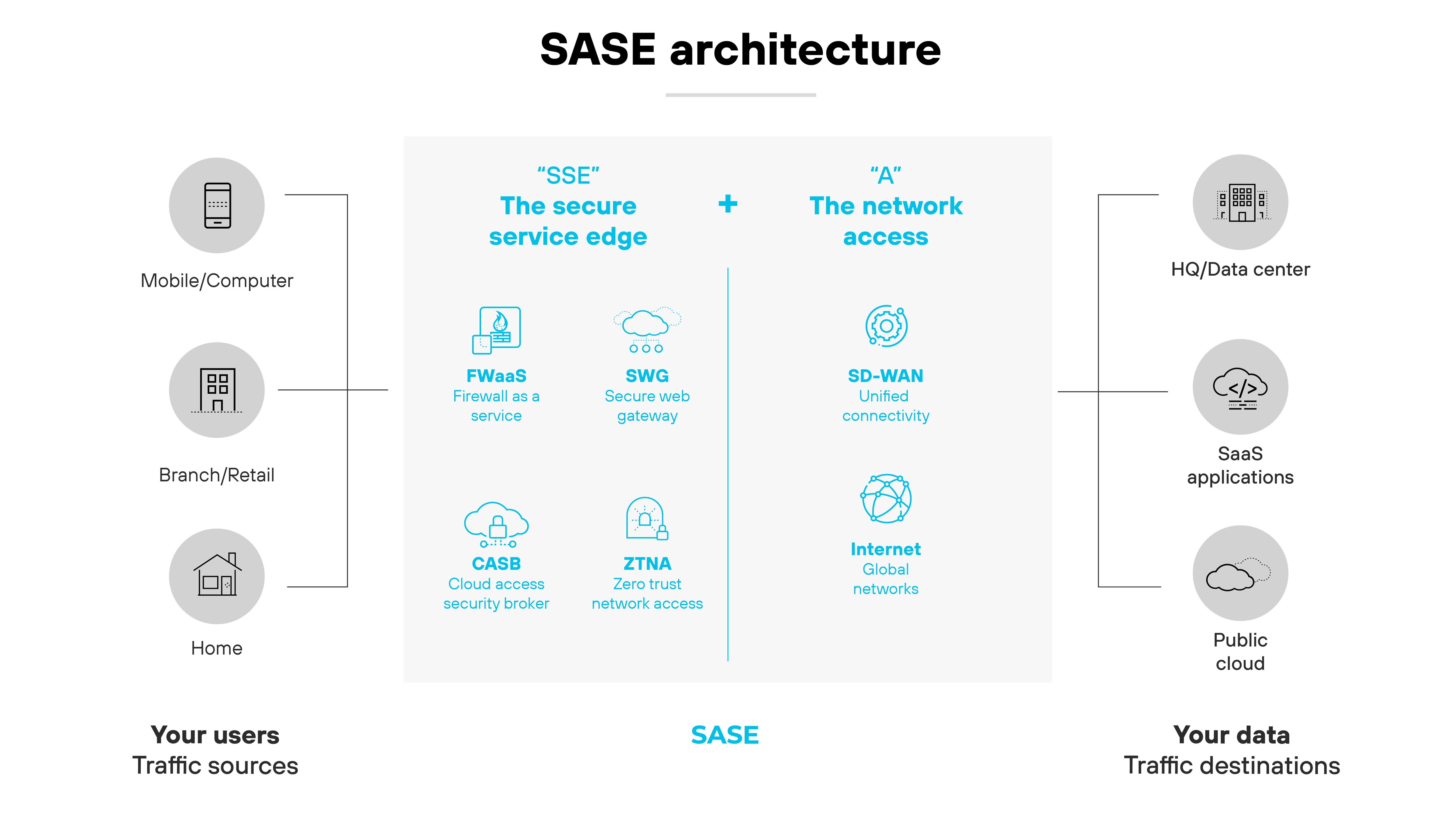
Functionally, SASE depends on SD-WAN to deliver application-aware connectivity across distributed environments.
While SASE unifies networking and security in the cloud, SD-WAN handles the transport. And that makes it a foundational part of SASE infrastructure. Without SD-WAN, SASE lacks the transport layer needed for dynamic, application-optimized routing.
The combination allows organizations to shift away from data center–centric designs. It supports direct-to-cloud access, enhances scalability, and helps enforce consistent security policies at every edge.
| Further reading:
Comparing SD-WAN with other security and technology solutions
SD-WAN doesn't operate in isolation. It overlaps with—and is often compared to—a range of networking and security technologies.
Understanding how SD-WAN stacks up across key categories like performance, scalability, and security can help clarify its role in modern infrastructure.
Below is a side-by-side breakdown to help distinguish where SD-WAN fits and how it differs from other solutions.
| Comparison: SD-WAN vs. security & technology solutions |
|---|
| Parameter | SD-WAN | MPLS | VPN | SSE | SDN | NaaS | Traditional WAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network architecture | Software-defined overlay across multiple WAN links (MPLS, broadband, LTE) | Private circuit-based WAN using label switching | Encrypted tunnels over public internet | Cloud-delivered security without network transport | Control plane separated from data plane for LAN/DC networks | Network delivered as a service via cloud provider | Point-to-point circuits, hardware-based routing |
| Traffic management | Dynamic path selection and application-aware routing | Static routing with QoS for guaranteed paths | Single-path static routing | Secures user-to-app traffic via PoPs | Central controller programs switches | Managed service provider handles traffic policies | Static routes; traffic flows to central data center |
| Performance | Low latency and optimized for cloud apps | High performance, but limited | Performance varies by internet conditions | Improves app access without backhauling | Optimized within data centers or telco networks | Performance varies by provider SLAs | Latency-prone for cloud apps |
| Security | Integrated security (NGFW, encryption, SASE-ready) | Private but lacks built-in threat prevention | Encrypts data but limited inspection or segmentation | Zero Trust, SWG, CASB, DLP, FWaaS | Requires integration with external security | Provider-managed security policies | Separate firewalls and security layers needed |
| Cost structure | Reduces costs by leveraging cheaper connections | Expensive circuits with higher operational costs | Low-cost, suitable for simple remote access | Subscription pricing; no network components | CapEx-driven; savings in operational agility | Subscription-based with flexible pricing | Costly MPLS; complex to maintain |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with centralized policy deployment | Scaling requires provisioning new circuits | Basic scalability; adds complexity at scale | Scales by adding users/apps; no physical constraints | Highly programmable, abstracted infrastructure | On-demand scale via service catalog | Difficult to expand and scale quickly |
| Management and visibility | Centralized control with visibility into app and network performance | Limited visibility; managed by service providers | Minimal monitoring; limited visibility | Centralized cloud-based security visibility | Deep visibility into network flows | Visibility limited to provider dashboard | Low visibility; fragmented management |
| Deployment flexibility | Physical, virtual, and cloud-based deployment | Physical links managed by telcos | Client-based or site-to-site configurations | Requires integration with existing network | Software-based control of physical/virtual devices | No hardware required; fully cloud-delivered | Physical site installs, centralized topology |
| Primary use cases | Cloud access, branch connectivity, app performance, security | Private WAN connectivity, real-time app SLAs | Remote access and secure point-to-point connections | Secure web access, cloud security, ZTNA | Data center automation, service provider core | Outsourced network ops, remote work enablement | Hub-and-spoke networks, site-to-site connectivity |
| Further reading:
- What Is the Difference Between SD-WAN and MPLS?
- SD-WAN vs. VPN: How Do They Compare?
- What are the Differences Between SD-WAN and SDN?
- SD-WAN vs. NaaS: What Are the Differences?
- Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: What Are the Differences?
- SD-WAN vs. MPLS vs Internet: What's the Difference? Which is Right for Your Organization?
Learn more about SD-WAN in action
Get Zero Trust Branch for SD-WAN For Dummies and see how SD-WAN architecture extends into branch security and SASE integration.
Download eBookSD-WAN FAQs
SD-WAN manages and optimizes traffic across multiple WAN links using software-defined controls. It improves performance, simplifies management, and provides secure, centralized connectivity across distributed sites.
Traditional WANs use fixed paths and centralized routing, often relying on MPLS. SD-WAN uses software-defined control to dynamically route traffic across multiple connections, improving agility, performance, and cloud access.
An enterprise uses SD-WAN to connect its branch offices to cloud applications via broadband and 5G while prioritizing video traffic and enforcing security policies—all managed centrally.
Yes. SD-WAN remains essential for hybrid work, multicloud access, and SASE adoption. It provides modern connectivity with centralized control and performance optimization.
SD-WAN optimizes application performance, simplifies network management, enables secure remote access, and provides transport flexibility across broadband, MPLS, and wireless links.
SD-WAN isn’t inherently secure and can be complex to troubleshoot without visibility tools. Its effectiveness also depends on the underlying network (underlay).
No. While both encrypt traffic, SD-WAN adds centralized management, dynamic path selection, and application-aware routing across multiple links—capabilities a basic VPN lacks.
Use SD-WAN when you need secure, reliable, and centrally managed connectivity across branches, cloud apps, and remote workers with diverse transport options.
Branch sites with direct internet access can expand the attack surface. Without integrated security, SD-WAN alone may not provide sufficient protection.
Yes, in many cases. SD-WAN appliances handle routing and more, such as application policies and encryption. But core routing functions may still be needed in complex networks.
Challenges include underlay dependence, vendor complexity, limited visibility without proper tools, and security gaps if not integrated with advanced protections.
Its main advantage is dynamic, application-aware traffic routing that improves performance and simplifies management across diverse connections and locations.
To modernize WAN connectivity for cloud access, hybrid work, and application performance—while gaining centralized visibility, control, and operational efficiency.
SD-WAN can be safe when integrated with security features like encryption, firewalls, and policy enforcement. Traditional SD-WAN alone lacks full protection.
MPLS is private but lacks threat protection. SD-WAN with integrated security (like secure web gateways or NGFWs) offers more comprehensive, adaptable protection.
It lacks built-in advanced security and requires strong visibility tools for troubleshooting dynamic traffic paths effectively.
SD-WAN replaced traditional WAN architectures built around MPLS and static routing, which struggled with cloud apps, hybrid work, and modern traffic patterns.