What Is a Cloud VPN? | Cloud-Based Remote Access VPNs Explained
A cloud VPN is a network service that provides secure and encrypted connections over the internet between remote users and an organization's resources hosted in the cloud.
Cloud VPNs enable remote users to connect securely to the company network, ensuring sensitive data transmitted across public networks is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access. This type of VPN is beneficial for organizations with a mobile workforce or those utilizing cloud services extensively. Cloud VPNs are quickly deployable and can be managed by enterprise VPN solution providers, offering a cost-effective and efficient solution for modern businesses.
How Does a Cloud VPN Work?
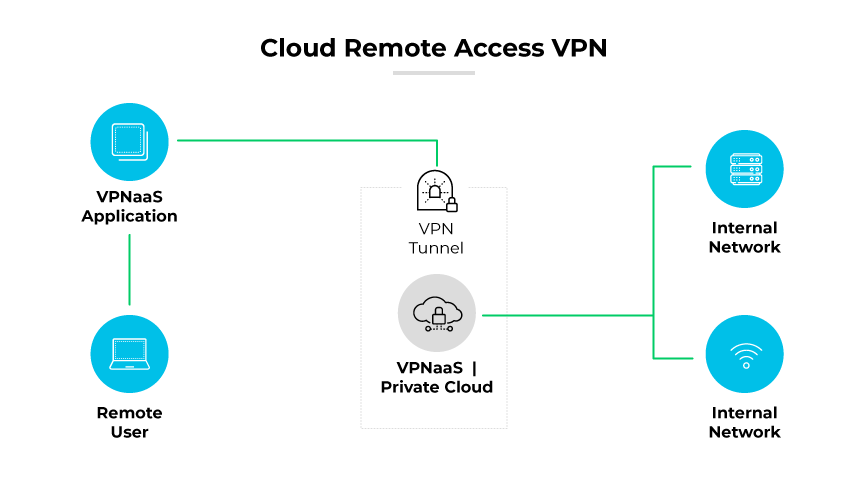
A cloud VPN is also known as VPN as a service (VPNaaS) or cloud based remote access VPN. A cloud-based VPN works by creating an encrypted VPN connection over the internet between a user and the company's network infrastructure hosted in the cloud. The encrypted connection is often facilitated by a VPN gateway that acts as an intermediary, encrypting and decrypting data sent to and from the cloud resources.
The process begins when a user connects to the cloud VPN service, usually through a client application. The service authenticates the user and their device, often incorporating multifactor authentication for enhanced security. Once authentication is successful, the cloud VPN sets up an encrypted tunnel using established VPN protocols, such as IPsec or SSL/TLS. This tunnel ensures that data transferred between the user and the cloud remains secure and unreadable to any unauthorized entities intercepting the traffic.
Within the cloud, a VPN gateway encrypts outgoing data before it travels across the internet and decrypts incoming data for the receiving device. This encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information as it traverses potentially insecure networks. The cloud VPN maintains the encryption tunnel, adapting as necessary to network changes. This is especially important for remote workers who may switch between different internet connections.
Cloud-based VPNs often include advanced security measures beyond the encrypted tunnel. These can include network segmentation to control application-level access, ensuring users only reach the specific resources they are authorized to use. Security features may also extend to threat prevention, with cloud VPN services providing protections against malware, phishing, and other cyberthreats, reinforcing the security posture of cloud-based networks.
Cloud VPN Models
Cloud VPNs offer two distinct models. These models are primarily differentiated as high availability (HA) VPNs and classic VPNs.
Both models serve the foundational purpose of securing data transmission between an enterprise's on-premises network and the cloud. However, the choice between an HA VPN and a classic VPN will depend on the specific needs of the business.
High Availability (HA) VPNs

High availability VPNs provide a resilient, redundant VPN connection to ensure continuous service uptime. When configuring an HA VPN, a unique IP address from a dedicated pool is assigned automatically/. This promotes a robust service with a typical availability of 99.99%. This model is vital for enterprises that require uninterrupted access to cloud resources. HA VPNs often employ active/active or active/passive configurations to handle failovers smoothly, ensuring network operations persist even during gateway failures.
Classic VPNs
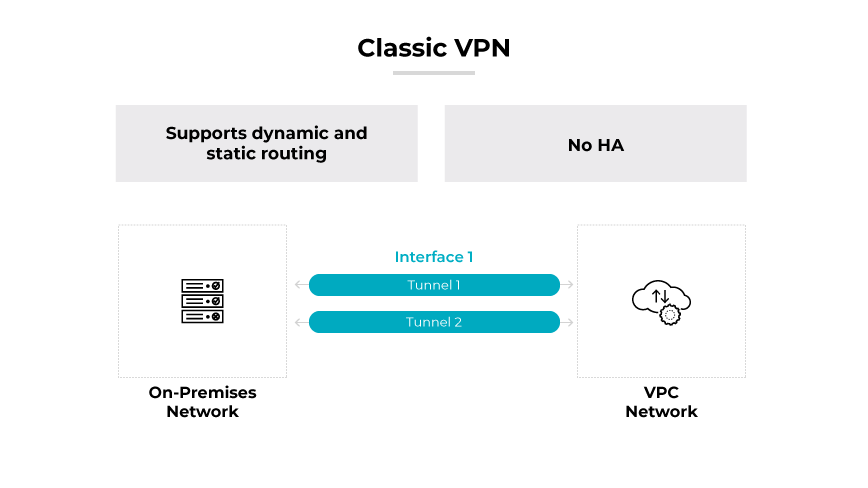
Classic VPNs are the traditional approach, where a single interface with an external IP address is used to support the VPN's functionality. While offering a more basic setup with 99.9% service availability, classic VPNs still support both dynamic and static routing options. This model might be more suitable for organizations with less stringent uptime requirements or those looking to implement a cost-effective solution. Classic VPNs are typically easier to configure and maintain, though they may not provide the same level of redundancy as HA VPNs.
Cloud VPN Deployment Methods
Cloud-based VPNs can be deployed using two different methods: client cloud VPNs, also known as cloud-based remote access VPNs, and network cloud VPNs, commonly referred to as site-to-site VPNs. Each type serves distinct purposes and fits different operational scenarios.
Both types of cloud VPNs leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud resources while providing different levels of access based on user needs and company policies. They are instrumental in enforcing security protocols and ensuring data transmission remains encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized entities.
Cloud-Based Remote Access VPN/Client Cloud VPN
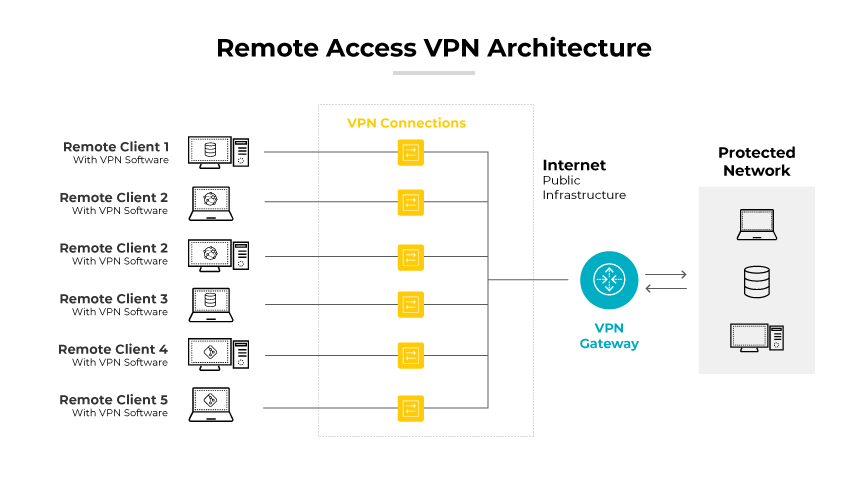
Client cloud VPNs are designed to provide remote access. They allow users, such as remote employees or mobile workers, to securely connect to the enterprise's virtual private cloud from any location. A cloud remote access VPN is vital for businesses with a distributed workforce, ensuring remote users have secure and consistent access to company resources hosted in the cloud.
Network Cloud VPN/Site-to-Site VPN
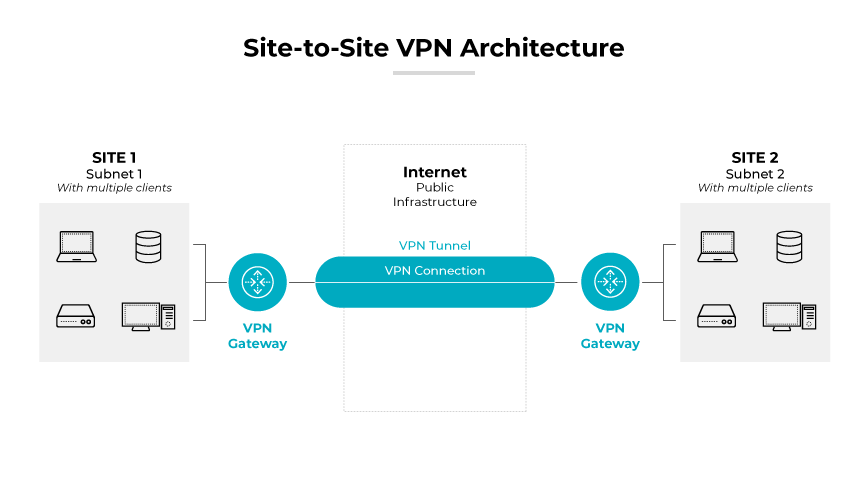
Network cloud VPNs are intended for site-to-site connectivity. This setup is utilized to securely encrypt traffic between a company’s on-premises network and its cloud infrastructure. It establishes a persistent, encrypted link that allows these separate environments to interact as though they were within the same network, offering secure communication channels for sensitive corporate data.
Cloud VPN Use Cases
Secure Remote Access for Distributed Workforces
A cloud VPN offers secure access to corporate networks for employees working remotely or on the go. They ensure connections to the company’s resources remain encrypted and protected, regardless of the employee’s location. This is especially important in hybrid work models where staff may access sensitive data from various networks.
Simplified Access for BYOD Environments
In environments where employees use their own devices (BYOD), cloud VPNs provide essential security. They offer a solution to manage access and ensure data transmitted from personal devices to the company’s network is secure. This approach maintains the integrity of corporate data and mitigates the risks associated with device heterogeneity.
Interconnecting Cloud and On-Premises Resources
Cloud VPNs are key in creating seamless connectivity between cloud-based assets and on-premises infrastructures. They provide encrypted tunnels that securely bridge the gap between different environments, allowing businesses to use the scalability of cloud solutions while keeping existing systems integrated and secure.
Streamlining Contractor and External Partner Access
For businesses that frequently collaborate with contractors and external partners, cloud VPNs offer a way to provide time-limited, secure access to specific network resources. This use case supports dynamic access control, enabling companies to maintain security while offering the necessary flexibility for project-based work.
Cloud VPN Benefits
Streamlined Secure Access
Cloud VPNs offer direct, secure access to cloud resources. Direct secure access reduces latency compared to traditional VPNs that route traffic through on-premises networks. The immediate access facilitates efficient workflows and enhances productivity for remote users.
Global Accessibility
Unlike hardware-dependent VPNs, cloud VPNs provide global reach, allowing teams in remote locations to connect from anywhere. This is necessary for organizations with a geographically dispersed workforce, and for supporting a scalable remote work model.
Enhanced Security and User Authentication
Cloud VPNs secure communications and data sharing with robust encryption and authentication. They help maintain data integrity and confidentiality across the virtual private cloud (VPC).
Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud VPNs are flexible and easily scalable, adapting quickly to changing network architectures and business requirements. Managed by VPN service providers, they offer dynamic adjustments to suit varying organizational needs without the constraints of physical infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness
By outsourcing VPN management to service providers, organizations can reduce the costs associated with maintenance, updates, and scaling. Cloud VPNs enable businesses to apply cloud economics, offering a more cost-effective solution compared to traditional VPN setups.
Cloud VPNs vs. Traditional VPNs
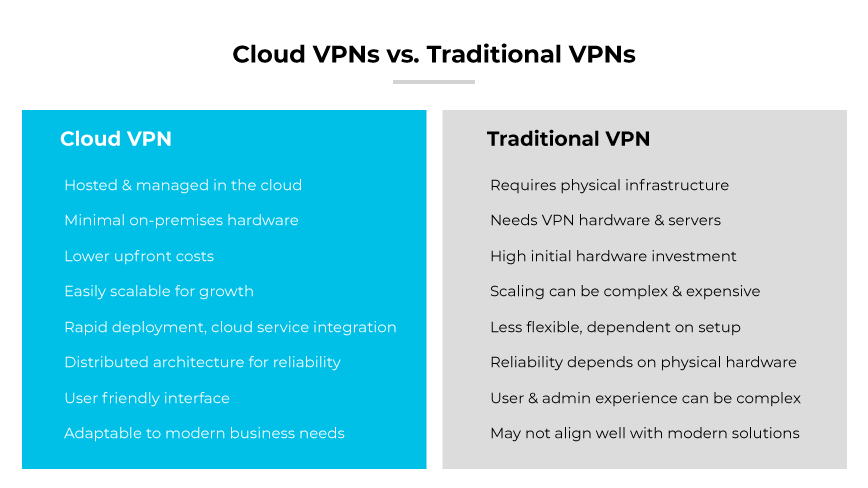
Cloud-based remote access VPNs and traditional VPNs serve the same basic purpose of secure remote access. They differ significantly in deployment and management. Traditional VPNs rely on physical infrastructure, necessitating on premises hardware such as VPN concentrators and dedicated VPN servers for authentication. They often require significant upfront investment in hardware and expertise to manage the network.
Cloud VPNs are service based, eliminating the need for extensive on-premises hardware. They offer a plug-and-play approach, where the VPN service is hosted in the cloud and managed by the VPN service provider. This translates to lower initial costs and reduces the complexity of scaling as a business grows. The flexibility of cloud VPNs allows for rapid deployment and seamless integration with cloud platform services, making them more adaptable to modern business needs.
Cloud VPNs can provide better reliability through distributed architecture, which is designed to handle the dynamic nature of internet-based networking. They also typically offer a more user-friendly interface for both administrators and end users, simplifying the management and user experience of VPN services.
Cloud VPN Best Practices
Enforce Robust Authentication Measures
Implementing strong authentication protocols is crucial. Use multifactor authentication and ensure all passwords and keys are complex and securely stored. This practice bolsters security for data in transit through the cloud VPN tunnel.
Establish Comprehensive Firewall Rules
Set stringent firewall rules at each VPN gateway to regulate traffic and fortify the endpoints. This controls access and protects against data breaches.
Optimize with Dynamic Routing
Use dynamic routing with protocols like BGP to enhance security and network efficiency. This enables more flexible and reliable communication between networks, safeguarding the integrity of data transmission.
Prioritize High Availability (HA) Configurations
For uninterrupted service and resilience, choose HA VPN solutions. They provide higher service availability, ensuring the cloud VPN remains operational even during partial network failures.