What Is a Perimeter Firewall?
A perimeter firewall is a security device that filters traffic, acting as a barrier between an internal network and untrusted external networks.
It applies a set of rules to control access based on criteria like IP addresses, domain names, protocols, ports, and the content of the traffic. By permitting or denying traffic, a perimeter firewall protects the network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
How Does a Perimeter Firewall Work?
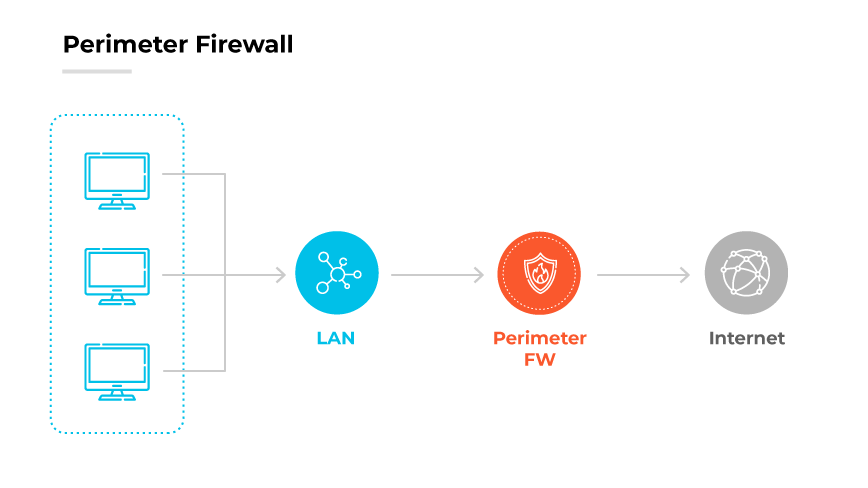
A perimeter firewall works as a filter between a company's internal network and external, untrusted networks like the internet. It scrutinizes all inbound and outbound network packets and allows or blocks them based on pre-established security rules. The perimeter firewall typically makes this decision by examining packet headers, which include source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocol types.
In an enterprise setting, a perimeter firewall often uses complex algorithms to analyze the state of active connections. It uses stateful inspection to track the state of network connections—such as whether they are new, established, or related to existing connections—and makes access decisions accordingly. This method ensures incoming packets are part of an ongoing conversation, rather than unsolicited attempts to access the network.
Modern perimeter firewalls can also perform deeper inspections, including examining the payload of packets for known threats or anomalies. Deep packet inspection (DPI) is crucial for identifying and mitigating sophisticated cyber threats that may otherwise bypass basic security checks.
Types of Perimeter Firewalls
Packet Filtering Firewall

Packet filtering firewalls function at the network layer and manage data packet movement across networks. These devices enforce a set of predefined criteria that scrutinize packet characteristics like the source and destination IP addresses, ports in use, and communication protocols. When a packet’s attributes conform to these rules, the firewall grants passage; otherwise, the firewall denies entry.
Stateful Inspection Firewall
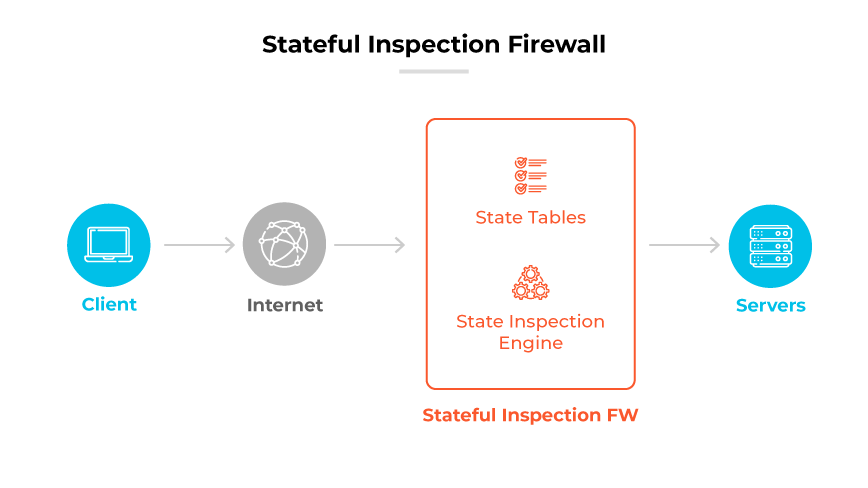
Stateful inspection firewalls play a crucial role in monitoring active network connections. They scrutinize the context of data packets flowing in and out of the network, permitting only recognized safe packets. These firewalls function at the network and transport layers (Layers 3 and 4 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model), focusing on filtering traffic by understanding its current state and the context of traffic flows. This security approach offers a more comprehensive defense than simple packet filtering by considering the wider context of network traffic.
The core capability of a stateful inspection firewall is the packet examination process. It meticulously checks each packet's details to see if they align with established patterns of safe connections. If a packet corresponds to a known safe connection, it can pass; if not, it is subject to additional checks to determine legitimacy.
Proxy Firewall
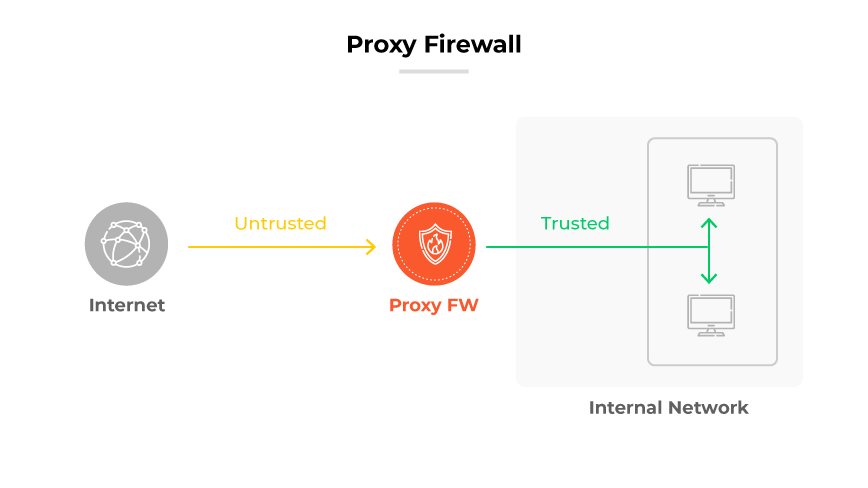
A proxy firewall serves as an essential line of defense at the application layer for network security. Its key role is to act as an intermediary, scrutinizing messages that pass between internal systems and external servers. This process helps shield network resources from potential cyber threats.
Proxy firewalls go beyond the capabilities of standard firewalls, which typically do not decrypt or perform in depth inspections of application protocol traffic. Instead, proxy firewalls conduct thorough examinations of incoming and outgoing traffic, looking for indicators of cyberattacks or malware infiltration. A critical aspect of their design is their IP addresses, which prevents any direct contact between external networks and the secure internal network.
Computers on the internal network use the proxy as their portal to the internet. When a user seeks access to an external resource, the proxy firewall captures the request and assesses it according to established security guidelines. If the request meets the safety criteria, the firewall connects to the resource on the user's behalf, ensuring only secure and permitted connections.
Next Generation Firewall (NGFW)
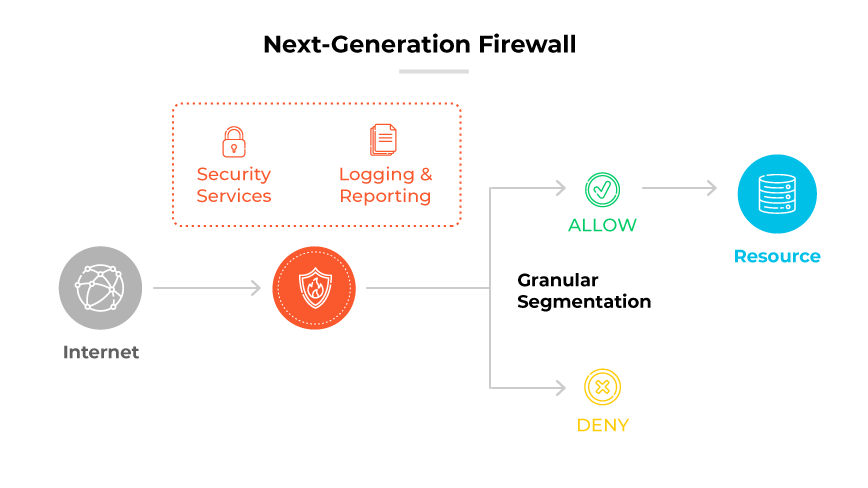
An NGFW, or next generation firewall, represents an advancement in network security technology. It extends the capabilities of a conventional stateful firewall by incorporating additional features. These features typically include application awareness, which allows the NGFW to detect and control traffic at the application level, and integrated intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) that work to identify and block complex threats.
An NGFW operates by enforcing security policies not just at the traditional levels of port and protocol but also the application traffic level. This allows more granular control over a network's ingress and egress points. Using application level insight, an NGFW can prevent potentially dangerous activities that could bypass a standard firewall's protections.
NGFW functionality includes incorporating intelligence from outside the network to inform its defenses. This intelligence can help in identifying emerging threats and enhancing the firewall’s response to them. Unlike traditional firewalls, NGFWs improve the depth and breadth of network security while simplifying administration.
Types of Firewalls Defined and Explained
What Is the Network Perimeter?
| Network Perimeter Components | |
|---|---|
| Border Router | Defines the edge of the private network, marking the transition to the public Internet. It is the final router within the purview of an organization and links internal to external networks. |
| Perimeter Firewall | Positioned just after the border router, it serves as the primary defense mechanism against incoming hazards. This component screens out harmful traffic attempting to infiltrate the private network. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention System | The IDS monitors the network for malicious activity and alerts the system, while the IPS proactively blocks detected threats to prevent potential attacks. |
| Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) | Acts as a secured buffer zone between the private network and the external world, typically housing services accessible to the public like web and email servers, while maintaining the internal network's security. |
The network perimeter defines the edge of an organization's internal network. It represents the delineation between the internal network and external networks like the internet. The network perimeter is where security measures apply to protect the network’s integrity. Within the context of perimeter firewalls, the network perimeter is crucial as it is where firewalls filter out unauthorized access and cyber threats.
As network environments evolve with cloud computing and remote access, the concept of the network perimeter also adapts. Despite these changes, the fundamental role of the network perimeter in providing a secure boundary remains integral to network security strategies. It is the frontline defense against external threats, where various security components work in concert to safeguard the digital assets of an organization.
Perimeter Firewall Benefits
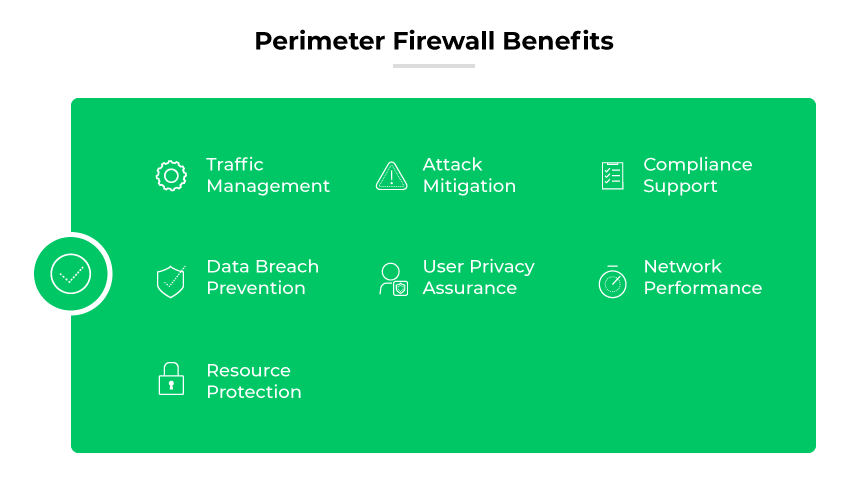
Traffic Management
Perimeter firewalls regulate network traffic flow, granting access only to authorized data packets. This enhances network security posture and prevents unauthorized access.
Attack Mitigation
These firewalls serve as a deterrent to various cyber threats, including viruses and intrusions. By blocking suspicious activities, perimeter firewalls mitigate potential attacks before they compromise network integrity.
Compliance Support
Implementing perimeter firewalls helps organizations comply with data protection regulations by enforcing security policies and documenting network traffic.
Data Breach Prevention
Perimeter firewalls are instrumental in preventing data breaches. They act as the first line of defense against external threats trying to access sensitive information.
User Privacy Assurance
By acting as intermediaries, perimeter firewalls enhance user privacy by hiding internal network details from external entities.
Network Performance
Perimeter firewalls contribute to maintaining network performance by preventing the network from becoming congested with harmful or unnecessary traffic.
Resource Protection
These firewalls protect network resources by ensuring only verified users and services can access them, which safeguards against exploitation and downtime.
Perimeter Firewall Risks
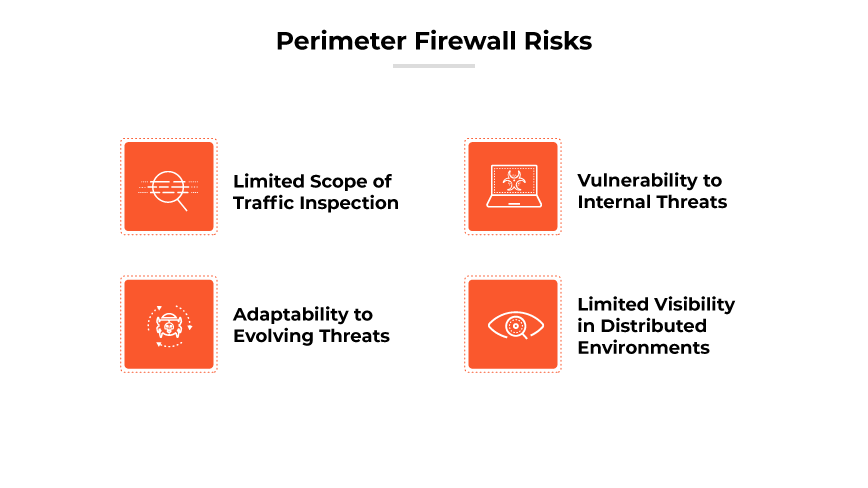
Limited Scope of Traffic Inspection
Perimeter firewalls primarily inspect inbound and outbound traffic, known as north-south traffic. Traffic moving laterally within the network, or east-west traffic, may not be monitored, potentially allowing internal threats to go undetected.
Vulnerability to Internal Threats
While perimeter firewalls are effective against external threats, they do not inherently protect against risks from within the organization, such as insider threats or compromised internal systems.
Adaptability to Evolving Threats
As cyber threats evolve, perimeter firewalls may struggle to adapt. New varieties of attacks and strategies, especially those targeting cloud services and complex infrastructures, can sometimes bypass traditional firewall defenses.
Limited Visibility in Distributed Environments
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services and decentralized architectures, the traditional network perimeter expands and becomes less defined. This makes it more difficult for perimeter firewalls to provide comprehensive protection. This shift requires organizations to adopt security controls that can operate effectively in a dispersed network environment.
Perimeter Firewall vs. Client Firewall
| Perimeter Firewall vs. Client Firewall | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Perimeter Firewall | Client Firewall |
| Placement | Integrated within the network's boundary or internal segments | Installed individually on separate hosts |
| Form factor | Physical hardware device | Software-based solution |
| Performance | Optimized for high throughput and low latency | Dependent on host system resources, may be less robust |
| Use cases | Predominantly utilized within organizational network structures | Suitable for personal computing devices and within smaller business networks |
| Network Segmentation | Facilitates segmentation at the perimeter, controlling inter-VLAN traffic | Provides micro-segmentation, managing traffic on a per-host basis |
| Management | Managed centrally, often through dedicated firewall management servers | Management can be more complex with numerous distributed hosts |
| Security | Difficult for external entities to circumvent network-based defenses | If host integrity is compromised, malicious software can disable the local firewall |
Perimeter firewalls work at the edge of a network, serving as a gatekeeper for all incoming and outgoing traffic. Their role is to protect the network infrastructure and prevent unauthorized access. Perimeter firewalls safeguard multiple systems within the network by managing and monitoring access points that connect to external networks, like the internet.
Client firewalls, on the other hand, are installed on individual devices or hosts and control the data exchange to and from these specific machines. Unlike perimeter firewalls that protect the entire network, client firewalls provide localized protection for individual systems. This means that even when a device moves outside the protected network perimeter, the client firewall remains active, continuously shielding the system from threats.
The distinction between these two types of firewalls is significant in terms of deployment and scope of protection. A perimeter firewall acts as the first line of defense against external threats for the network. Client firewalls offer a second layer of security, protecting individual systems from potential internal and external vulnerabilities. Each plays a crucial role in a comprehensive network security strategy.
Perimeter Firewall vs. Data Center Firewall
| Perimeter Firewall vs. Data Center Firewall | ||
|---|---|---|
| Perimeter Firewall | Data Center Firewall | |
| Architecture | Network layer protection for the outer edge of a network | Stateful, multitenant, network layer firewall utilizing 5-tuple SDN |
| Traffic Direction | Primarily secures North-South traffic, entering and leaving the network | Secures East-West traffic within virtual networks, as well as North-South |
| Purpose | Guarding against external attacks | Protecting virtual machines and providing agility for dynamic data center environments |
| Use Cases | General network security at the perimeter | Securing virtualized data centers with flexible resource allocation |
Perimeter firewalls deploy at the boundary of the network, where they control access to resources by monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. These firewalls block unauthorized access from external sources, protecting the network from a wide range of attacks originating from outside the network.
Data center firewalls, in contrast, secure the data center environment specifically, which often includes a multitude of virtual machines (VMs). They handle internal traffic, also known as east-west traffic, and can dynamically adapt to changes within the data center, such as VM migration. This agility is crucial given the dynamic nature of modern virtualized data centers, which can frequently reconfigure virtual resources.
The main difference between the two lies in their specialized functions and the types of traffic they manage. While perimeter firewalls are mainly concerned with north-south traffic—data entering and leaving the network—data center firewalls provide granular control over the traffic within the data center itself, ensuring security even as the virtual landscape changes.