- 1. What created the need for a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- 2. How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms and network firewalls compare?
- 3. How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms work?
- 4. What are the main features of an HMF platform?
- 5. What are the main hybrid mesh firewall use cases?
- 6. What are the benefits of a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- 7. Top 5 hybrid mesh firewall platform myths
- 8. Hybrid mesh firewall FAQs
- What created the need for a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms and network firewalls compare?
- How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms work?
- What are the main features of an HMF platform?
- What are the main hybrid mesh firewall use cases?
- What are the benefits of a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- Top 5 hybrid mesh firewall platform myths
- Hybrid mesh firewall FAQs
What Is a Hybrid Mesh Firewall (HMF)? [Starter Guide]
- What created the need for a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms and network firewalls compare?
- How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms work?
- What are the main features of an HMF platform?
- What are the main hybrid mesh firewall use cases?
- What are the benefits of a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
- Top 5 hybrid mesh firewall platform myths
- Hybrid mesh firewall FAQs
A hybrid mesh firewall platform (HMF) is a single-vendor solution that unifies hardware, software, and cloud firewalls under one management system.
It provides consistent security and centralized control across every environment: on-prem, cloud, remote, or hybrid. This approach allows organizations to enforce the same policies everywhere, regardless of how or where firewalls are deployed.
What created the need for a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
Business networks have changed.
Traditional firewalls weren't designed to support today's mix of on-prem data centers, cloud workloads, branch offices, remote users, and agile development pipelines.
Meanwhile, security teams need consistent visibility and control across all of it. But stitching together separate firewall products has made that harder.
The problem isn't that organizations need more firewalls. It's that they need better integration across the ones they already use.
Here's why:
Most organizations now rely on more than two types of firewall deployments. Hardware. Virtual. Cloud-native. As-a-service. All with different interfaces, update cycles, and policy management systems.
Like this:
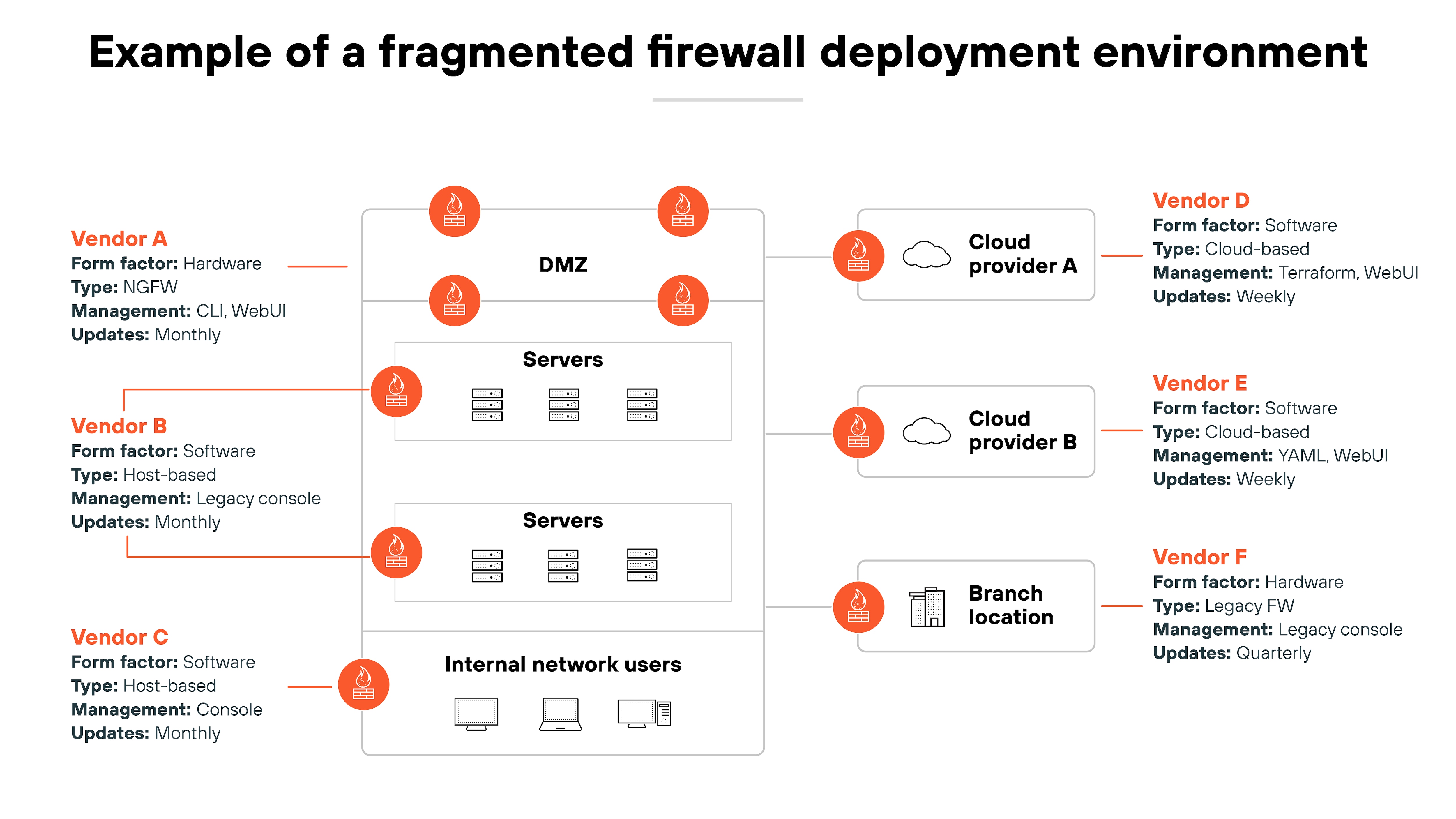
Managing them independently takes too much time and leads to policy drift. So centralized control has become critical.
That shift is what led to the rise of hybrid mesh firewalls.
Instead of treating firewall form factors as separate products, the HMF model unifies them under a single platform with shared policy, automation, and threat prevention capabilities.
The consistency makes security way easier to manage. And easier to adapt, too.
Centralized management is what makes that possible. Plus, it improves response time, provides real-time threat prevention, and simplifies scaling across multi-cloud environments.
How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms and network firewalls compare?
Traditional network firewalls were designed for perimeter defense and data center segmentation. Typically as hardware or virtual appliances managed separately.
But today's networks are hybrid, dynamic, and distributed.
HMF platforms respond to this shift by integrating multiple firewall types—physical, virtual, cloud-native, and FWaaS—under a single cloud-based management plane.
This lets teams enforce consistent policy, respond to threats faster, and support evolving use cases like microsegmentation and CI/CD.
Here's a side-by-side comparison:
| Traditional network firewall vs. hybrid mesh firewall platform | ||
|---|---|---|
| Capability | Traditional network firewall | Hybrid mesh firewall platform |
| Deployment options | Typically hardware or virtual appliances | Supports 3+ types: hardware, virtual, cloud-native, FWaaS |
| Management | Managed separately by form factor | Centralized, cloud-delivered control plane |
| Policy enforcement | Location-specific, prone to drift | Shared, context-aware policies across environments |
| Integration | Limited integration with cloud and automation tools | Built-in CI/CD, microsegmentation, and cloud-native visibility |
| Threat prevention | Deployment-dependent | Unified across platform with advanced detection |
| Use case flexibility | Suited to perimeter use cases | Extends to hybrid, cloud, DevOps, and remote work models |
How do hybrid mesh firewall platforms work?
Hybrid mesh firewall platforms unify different firewall deployment models into a single, coordinated system.
That includes hardware appliances, virtual firewalls, cloud-native firewalls, and firewall-as-a-service.
Each enforcement point still handles traffic locally. But the control, visibility, and policy management all come from a shared, centralized plane.
Like so:
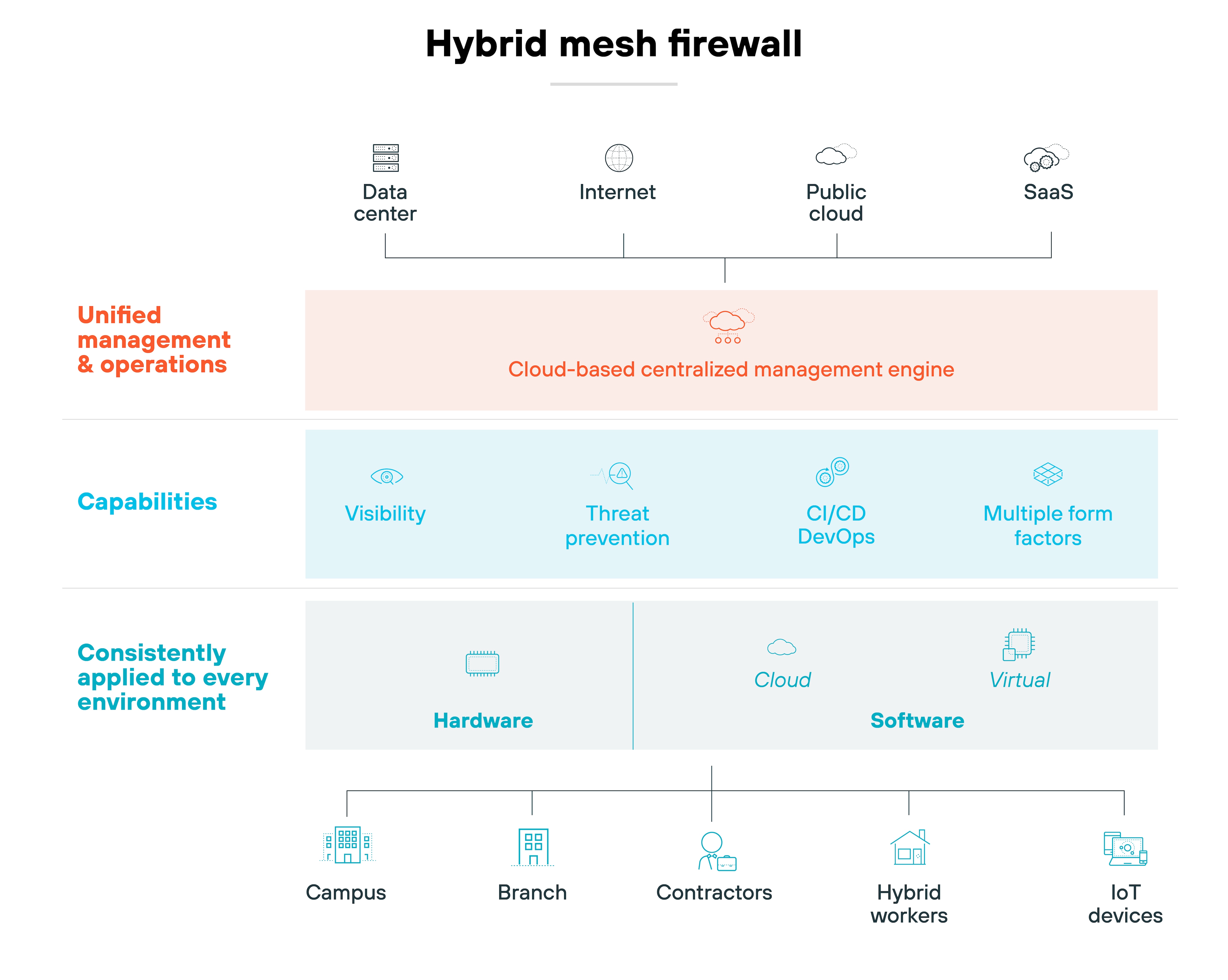
In other words: You manage in one place. And enforce everywhere.
Let's break down how it works.
An HMF platform collects telemetry across all firewall form factors.
That data feeds into a unified management layer—typically cloud-delivered—which provides a single interface for configuring policies, monitoring activity, and resolving issues.
The central console applies shared security rules across every deployment. Whether that means a branch firewall, cloud container, or IoT gateway, the platform ensures consistent policy.
It also integrates security services like threat detection, DNS filtering, and decryption across the entire estate.
Some platforms offer built-in tools for automation, anomaly detection, or policy optimization. This helps reduce human error and catch configuration drift early.
Others provide AI-powered recommendations to fine-tune rule sets or flag unused policies.
The result is less fragmentation, better visibility, and fewer gaps between firewall types. Without changing how each form factor is deployed.
- What Is Firewall Management?
- What Is Network Security Management?
- What Is Cybersecurity Platformization?
- What is Cybersecurity Consolidation?
See firsthand how unified firewall management and AI-driven insights simplify network security operations. Watch the Strata Cloud Manager demo.
Watch demoWhat are the main features of an HMF platform?
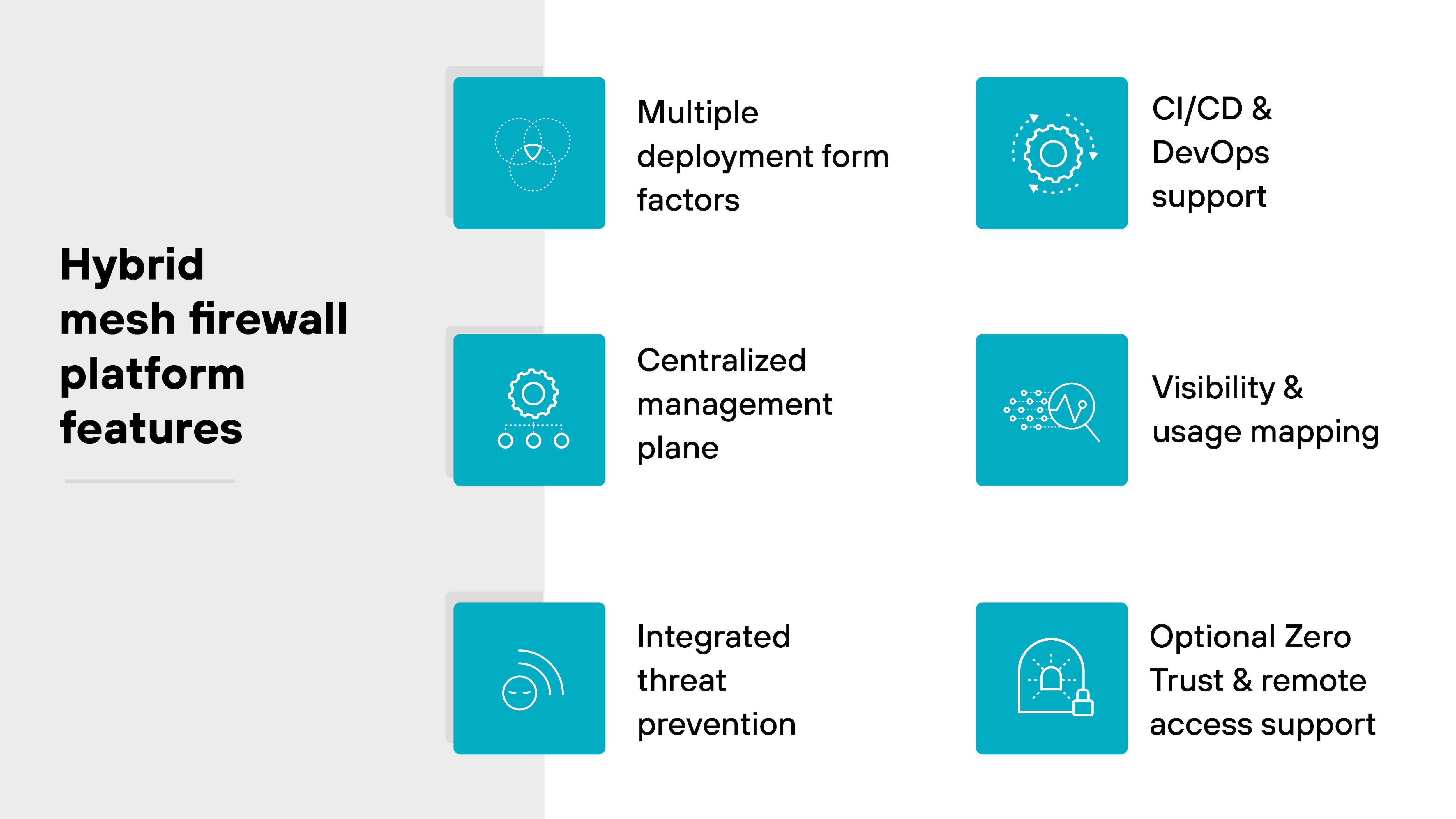
Hybrid mesh firewall platforms share a few essential characteristics:
- Multiple deployment form factors
- Centralized management plane
- Integrated threat prevention
- CI/CD and DevOps support
- Visibility and usage mapping
- Optional Zero Trust and remote access support
Each of these capabilities supports consistent policy enforcement and makes it easier to manage security at scale.
Let's break down each feature one by one:
Multiple deployment form factors
HMF platforms support more than one type of firewall deployment—often three or more.
That includes hardware appliances, virtual machines, cloud-native firewalls, containerized firewalls, and firewall-as-a-service.
Each one acts as an enforcement point. But the platform brings them together for unified control.
Centralized management plane
Policy creation, rule enforcement, and visibility are handled in one place. Typically, this is a cloud-based console.
From here, teams can push updates, monitor traffic, investigate threats, and audit activity. Without logging into each firewall individually.
Which reduces drift and simplifies change control.
Integrated threat prevention
Most platforms include advanced threat protection services.
These may block DNS-based attacks, identify malicious IoT activity, or detect known and unknown threats using deep packet inspection and threat intelligence.
Controls are applied consistently across environments.
CI/CD and DevOps support
To support cloud-native use cases, HMF platforms offer CI/CD integration. This allows teams to apply security policies in step with code deployments or infrastructure changes.
Some platforms allow tag-based controls or integration with common automation tools.
Visibility and usage mapping
HMFs often include tools for application discovery and connectivity mapping. These help teams visualize traffic flows, detect misconfigurations, and spot anomalies in real time.
Visibility and usage mapping also helps enforce segmentation and policy alignment in hybrid environments.
Optional Zero Trust and remote access support
Some platforms offer optional features like agent-based microsegmentation, unified endpoint clients, and secure remote access.
These aren't core to every deployment, but they help extend coverage to roaming users, home offices, or sensitive workloads.
What are the main hybrid mesh firewall use cases?
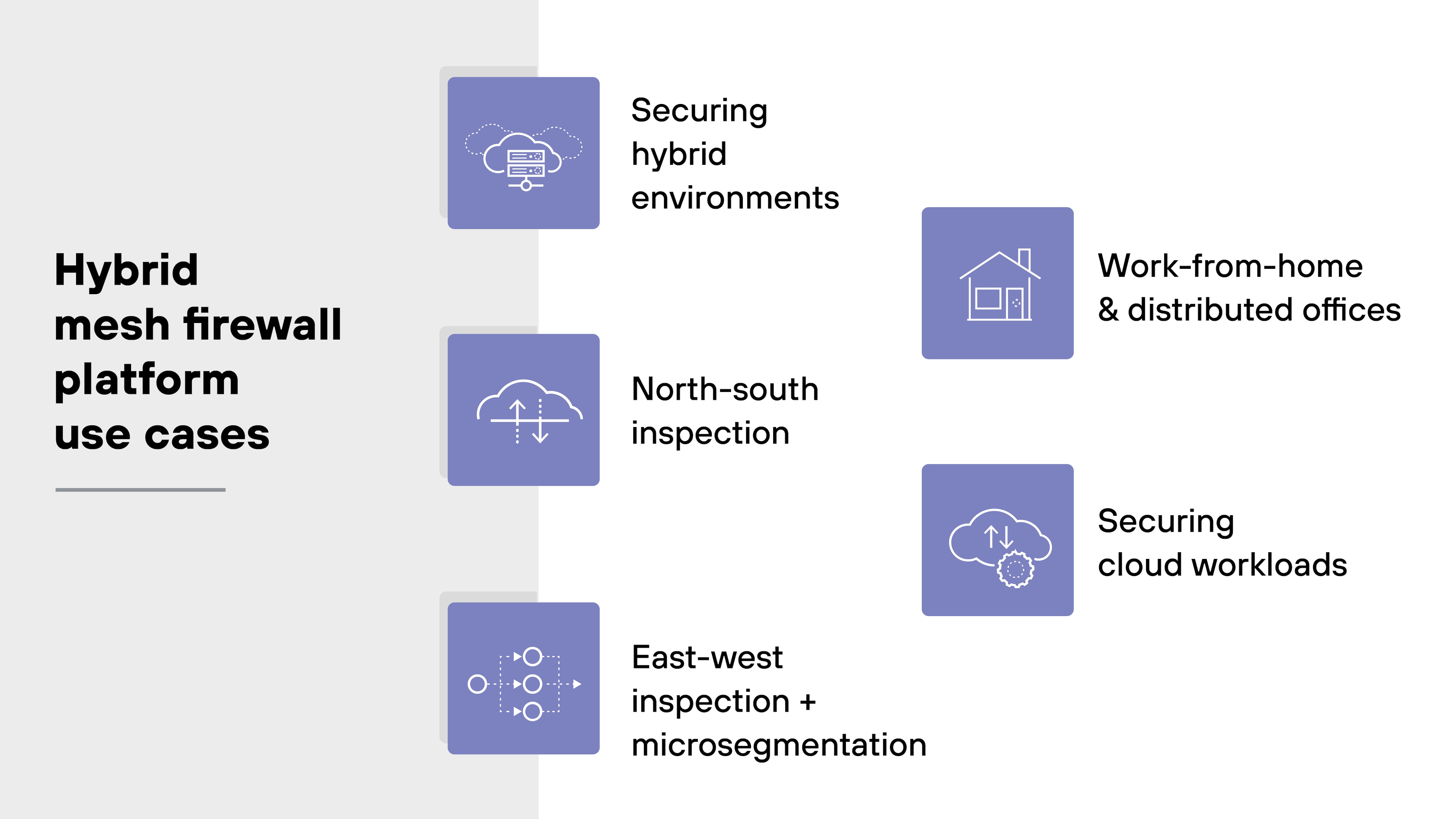
There are five major use cases for hybrid mesh firewall platforms:
- Securing hybrid environments
- North-south inspection
- East-west inspection + microsegmentation
- Work-from-home and distributed offices
- Securing cloud workloads
These platforms aren't built for a single environment. They're designed to span all of them. That's why their use cases go beyond traditional firewall deployments.
Here's how each one plays out in practice:
Securing hybrid environments
This is the foundational use case for HMFs.
Most enterprises today operate in a mix of physical and cloud environments. Some use hardware firewalls for data centers. Others rely on virtual firewalls, cloud-native security, or firewall-as-a-service.
An HMF lets teams use all of them. While also enforcing shared policies and centralizing control.
North-south inspection
North-south traffic refers to data moving between internal networks and external sources. This remains one of the primary firewall functions. But now, that traffic spans data centers, SaaS apps, cloud workloads, and more.
HMFs apply perimeter inspection across multiple form factors—from hardware appliances to containerized firewalls—without managing each separately.
East-west inspection and microsegmentation
East-west traffic refers to data moving within a network; such as between applications, workloads, or user devices.
HMFs support both macrosegmentation (zone-based controls) and microsegmentation (Layer 7 enforcement). This includes virtual, cloud-native, and agent-based firewalls, all managed from a centralized console.
Work-from-home and distributed offices
This use case isn't just about remote users. It's about how modern organizations extend firewall coverage to anywhere work happens.
HMFs let you mix branch office hardware, home office firewall boxes, and firewall-as-a-service for remote users. All under a common security framework.
Securing cloud workloads
Cloud adoption has made workload protection more dynamic. Applications might run in containers, virtual machines, or serverless compute. Each one needs a different enforcement point.
HMFs support virtual firewalls, cloud-native policies, and microsegmentation—while still managing everything through one platform.
What are the benefits of a hybrid mesh firewall platform?
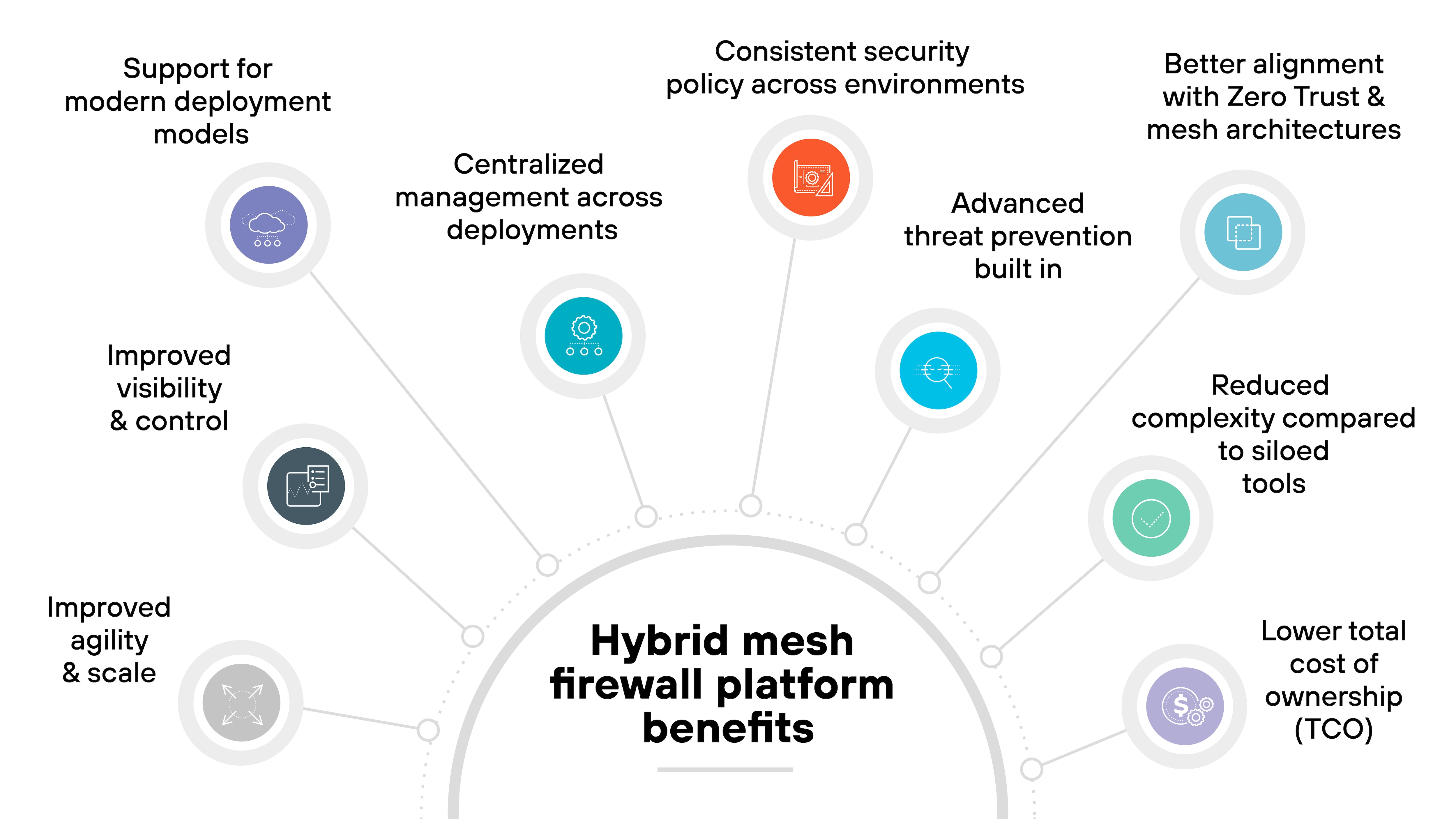
A hybrid mesh firewall platform brings security, management, and visibility into one coordinated system. The result is faster operations, consistent enforcement, and fewer gaps between firewall types.
Here's how that translates into real benefits:
- Centralized management across deployments: An HMF platform lets you manage hardware, virtual, and cloud firewalls from a single control plane. That simplifies policy enforcement and reduces operational overhead.
- Consistent security policy across environments: Policies follow the traffic—not the location. Whether data moves through on-prem, cloud, or remote locations, enforcement stays consistent.
- Improved visibility and control: Unified telemetry gives teams a complete view of traffic, threats, and configurations across the network. Which makes it easier to spot misconfigurations or gaps before they become exposures.
- Support for modern deployment models: An HMF supports dynamic environments like containers, microservices, and CI/CD pipelines. It integrates with tools used in cloud and DevOps workflows.
- Advanced threat prevention built in: Many platforms come with AI-powered detection, sandboxing, and signature-based defenses. This provides near real-time protection without relying on bolt-on tools.
- Better alignment with Zero Trust and mesh architectures: Because enforcement is distributed but managed centrally, HMFs support modern architectures that require identity-aware, context-driven security controls across domains.
- Reduced complexity compared to siloed tools: Replacing point solutions with a single integrated platform cuts down on management effort, reduces friction between teams, and simplifies troubleshooting.
- Improved agility and scale: Security teams can deploy and adapt firewall enforcement as business needs evolve, without rebuilding security models for every location.
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO): Fewer tools to license, configure, and maintain. Combined with centralized visibility and automation, that helps organizations reduce both capex and opex over time.
Top 5 hybrid mesh firewall platform myths

Hybrid mesh firewall platforms are still relatively new. That's why a few common misunderstandings still show up.
Especially when they're compared to older firewall approaches.
Here's a breakdown of the most frequent misconceptions and how they hold up:
Myth: Hybrid mesh firewalls are just a patchwork of firewall types.
Reality: A true HMF platform is built as a single, unified system. Not a collection of point products.
The management plane, policy framework, and enforcement mechanisms all work together by design. That's what enables consistent security across hardware, software, cloud, and as-a-service deployments.Myth: HMFs are too complex for most organizations.
Reality: Most of the complexity in network security comes from managing multiple firewall products separately.
HMF platforms reduce that complexity. They let teams manage policy, updates, and configurations from one place. And with automation and best practice checks to reduce overhead.Myth: You only need an HMF if you have a large, global network.
Reality: HMFs are designed for hybrid environments. Not just large ones.
Even midsize organizations often use two or more firewall types to cover cloud, data center, and branch environments. That mix is what drives the need for a centralized platform, regardless of scale.Myth: Centralized control means giving up flexibility.
Reality: Centralized control doesn't mean one-size-fits-all. It means having one place to define policies. And the flexibility to apply them based on context.
HMF platforms support granular segmentation, CI/CD integrations, and location-specific enforcement without losing visibility or coordination.Myth: It's easier to stick with traditional firewalls and layer on extra tools.
Reality: Point solutions create overlap, blind spots, and policy drift.
HMF platforms solve this by integrating capabilities like DNS protection, microsegmentation, and threat prevention into the firewall platform itself. It reduces tool sprawl and improves overall security posture.